(hairpinning - also referred to as NAT loopback or NAT reflection).
- Updated to Redesign of the webinterface
Preliminary remarks
Initial situation
- All computers are in a private network and hide behind a public IP address of the router.
- A port forwarding is set up and is used to forward requests directed to specific ports of the public IP address of the router to the internal server so that it can be reached from the Internet.
This could be remedied by setting up a Forward-zone in the UTM's name server, provided the UTM is set up as a name server for the internal clients.
In this case, the external URL that is called from Internal points directly to the Internal target server.
Instructions on how to set up the Forward-zone can be found at Forward-Zone in the Nameserver Wiki.
In this case, as described above, the UTM must be used as DNS and a Forward-Zone must be set up.
Aim of this article:
An internal server should be reachable from the internal network via the public IP of the firewall (with corresponding port specification).
This is accomplished with the help of hairpinning (also called NAT loopback or NAT reflection).
For this purpose, a DestNAT and a HideNAT rule are created.
Here the firewall only has to resolve the name to an internal address.
The actual communication doesn't take the detour over the firewall but takes place directly between client and server!
A corresponding How-To can be found in the Wiki article on the name server in the section Forward-Zone.
Packet flow
- A PC sends a SYN packet with the external IP address of the internal server (here www) to the UTM ①.
- The DestNAT rule masks the receiver IP address and thus ensures that the packet can be forwarded to the internal server.②.
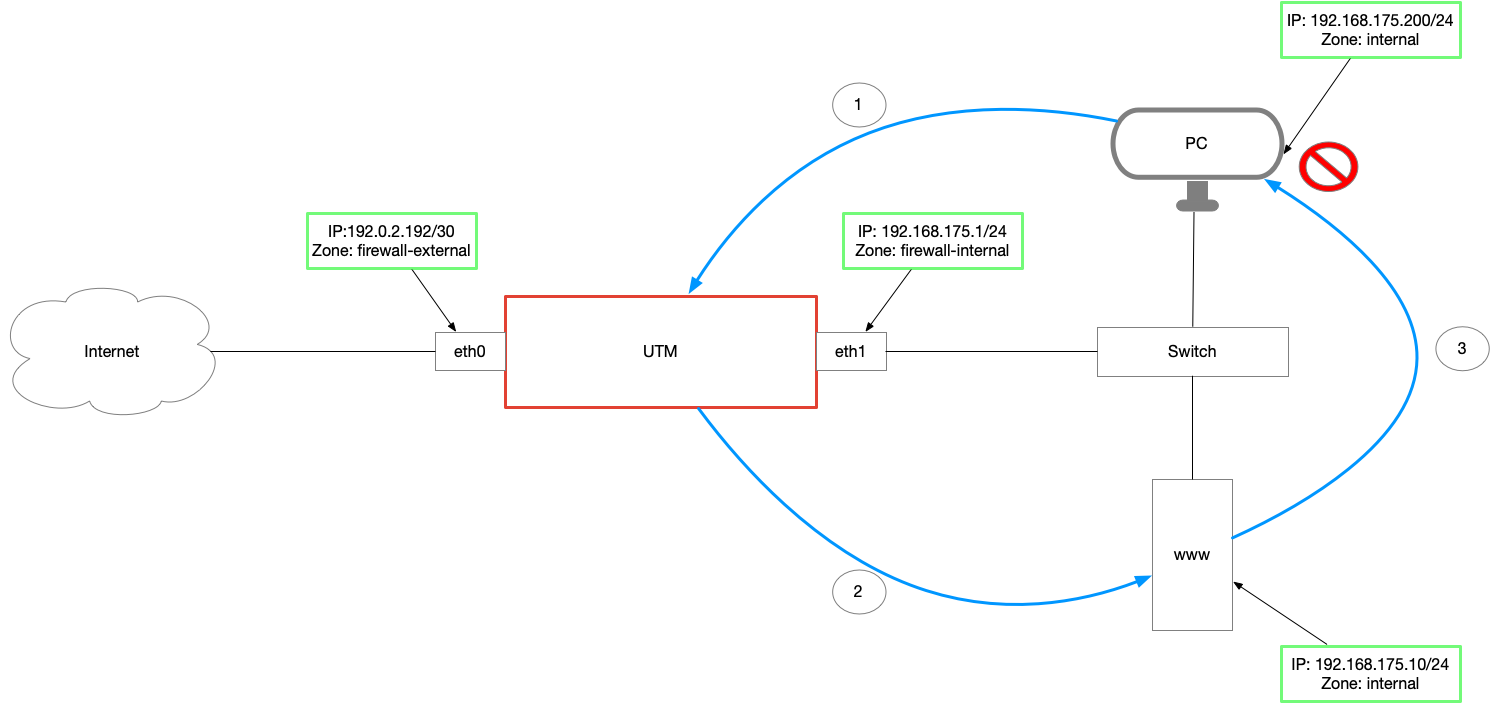
- The server sends the response SYN-ACK to the sender IP of the packet: the IP of the PC from the internal network ③.
- The PC's firewall drops the packet because it did not send a SYN packet to the sender address of the SYN-ACK packet (the server's IP from the internal network).
or - The PC has no firewall and sends its ACK packet to the public IP of the server and thus to the UTM
→ The UTM drops the packet because it has not seen a SYN-ACK packet for it.
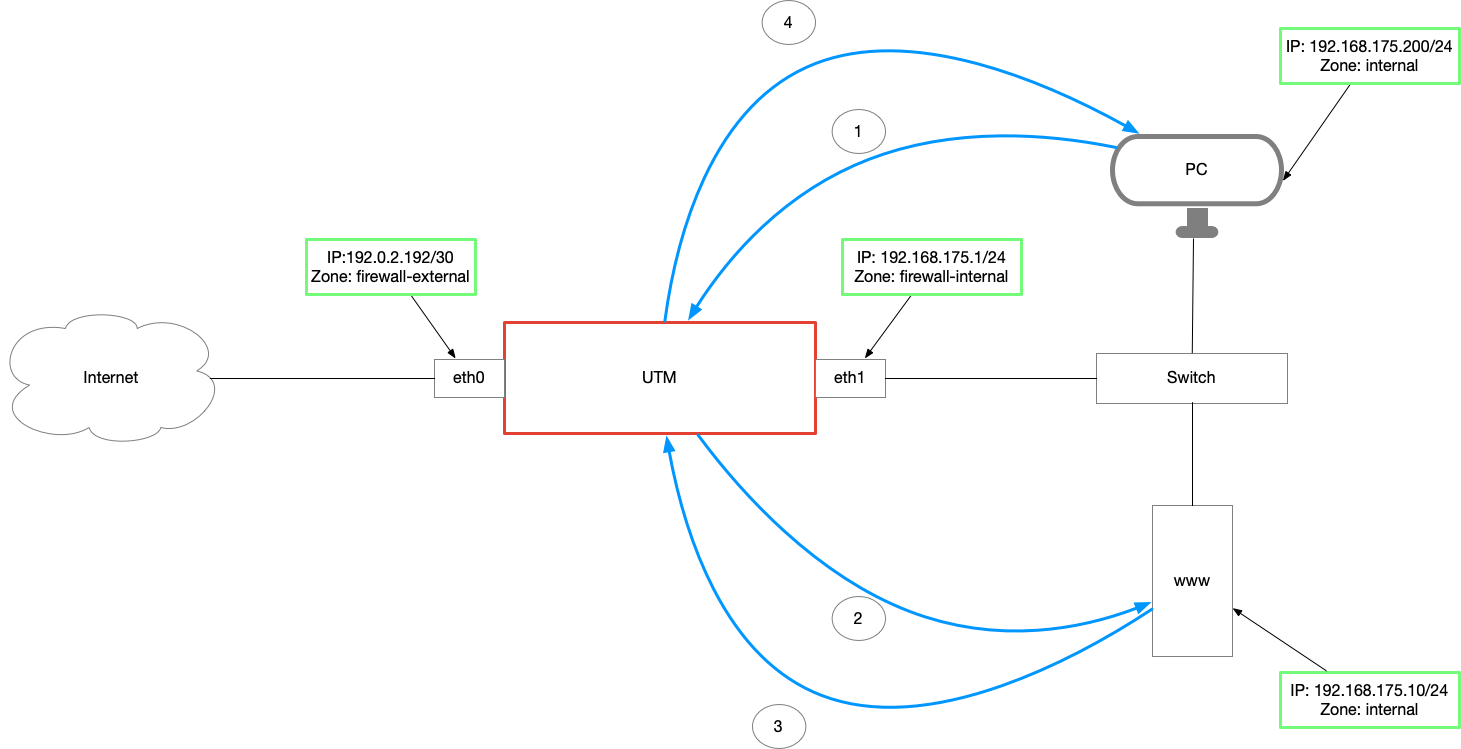
- The HideNAT rule has also changed the sender address.
The server sends the SYN-ACK packet back to the UTM ③. - The UTM NATs the packet and sends it to the original sender ④.
- The PC can now successfully send its ACK packet to the server's public IP.
The first is situated in the prerouting chain (DestNAT), the second in the postrouting chain (HideNAT) and thus in independent test sections. Only within a section, no second rule can take effect.
Configuration of the appliance
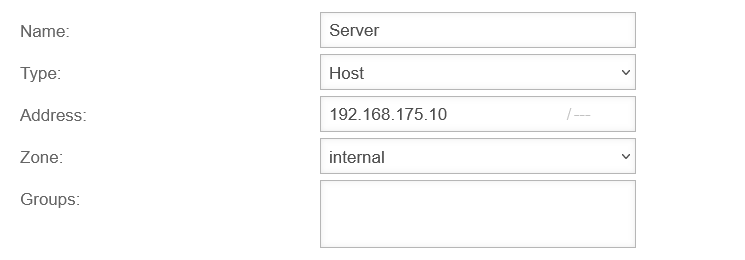
Create server as network object
There must be a network object for the server for port forwarding.
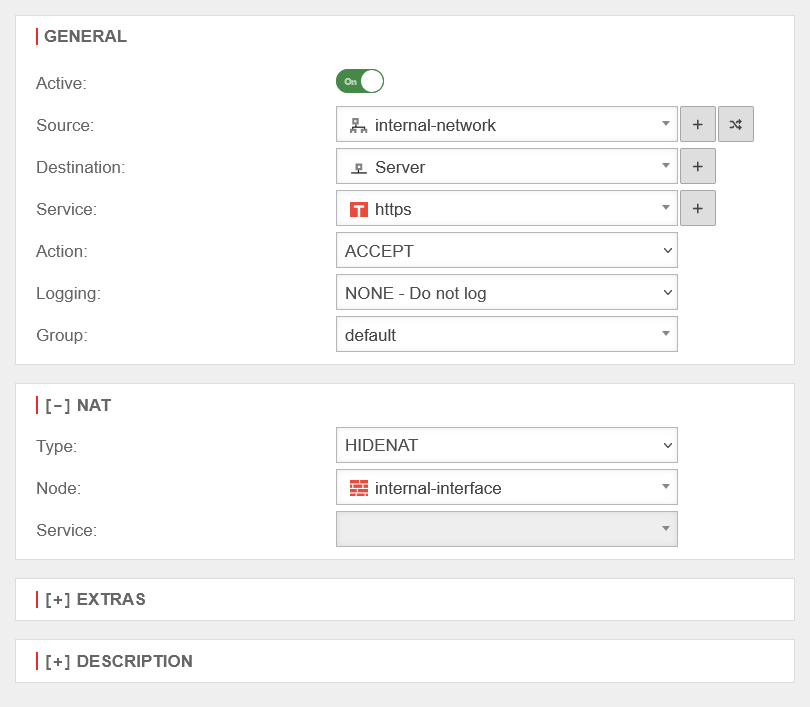
Create firewall rules for forwarding
In order for the corresponding port to be forwarded to the server, a port forwarding rule must be created. Configuration in menu Button
| Caption | Value | Description | UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewallPacketilter 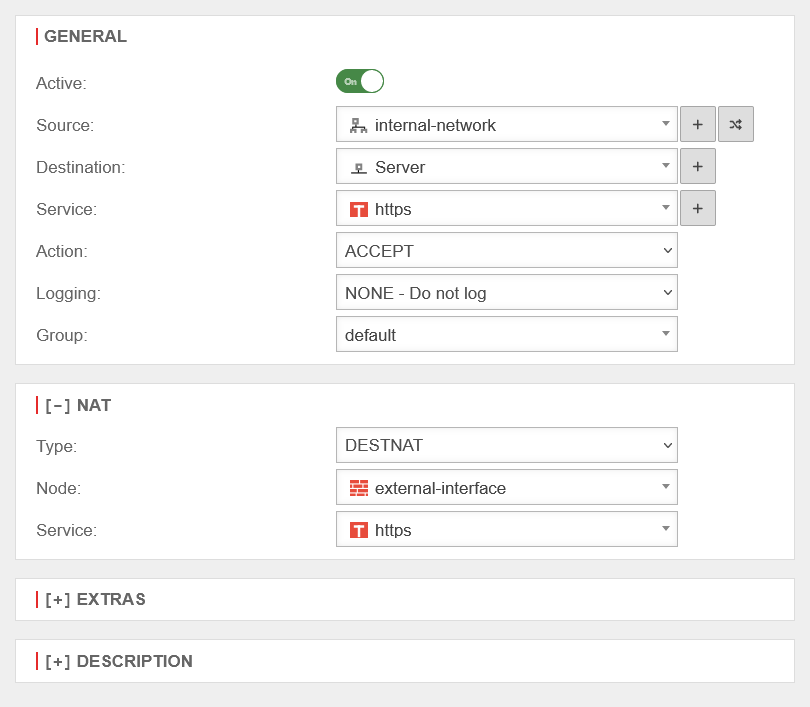 Port forwarding Port forwarding
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Source network for which the server is to be made accessible. | ||
| Goal | Network object of the target server (created previously as described above, if necessary). | ||
| Service | Service that occupies the desired port. Here port 443 → https If an individual port is required, it must be selected with the button to be newly created as a service. For more information, see the Packet Filter article, Services section. | ||
| Action | The action must be set to Accept. | ||
[-] Nat
| |||
| Type | A single host should be addressed | ||
| Network object | The external interface is selected as the network object (or the network object that holds the external IP over which the port is to be forwarded). | ||
| Service | Service that occupies the desired destination port. If a different port is to be used here than for the source service and this is not already created as a service object, this must be created before . | ||
| Save and close | Saves the settings and closes the dialog | ||
Create firewall rules for the Hide-NAT
For the server to answer the request to the public IP in the correct way, a Hide-NAT rule must now be created.
With this rule, the IP of the requesting computer is hidden behind the IP of the firewall.
This is necessary since otherwise the request would arrive at the server with the internal IP of the computer and it would then attempt to deliver the response internally and not via the firewall.