- Layout adjustment
- Screenshots updated
Introduction
In this wiki, we want to deal with the case where a road warrior establishes a VPN connection to different destinations at the same time, but they all use the same subnet. Furthermore, the VPN client also receives an address from the same roadwarrior pool from the VPN servers. In this case, the client would of course have the problem that it cannot distinguish between the destinations.
The NAT type NETMAP can help here.
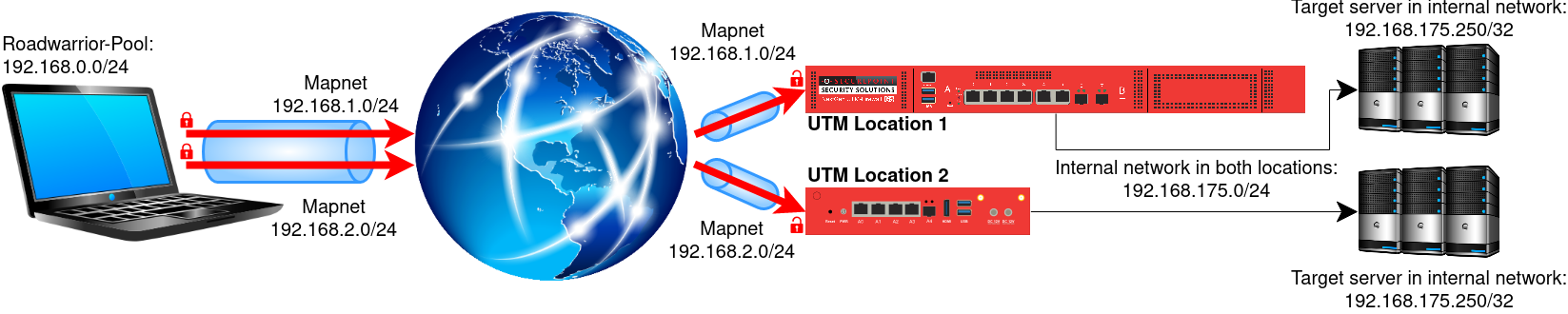
In our example, we assume the following specifications:
| Roadwarrior Pool: | 192.168.0.0/24 |
| Internal network of the locations: | 192.168.175.0/24 |
| Netmap network of the first location: | 192.168.1.0/24 |
| Netmap network of the second location: | 192.168.2.0/24 |
We also assume that the SSL-VPN Roadwarrior connection is already set up and working.
Configuration of the SSL-VPN roadwarrior server with Netmap
Preparations
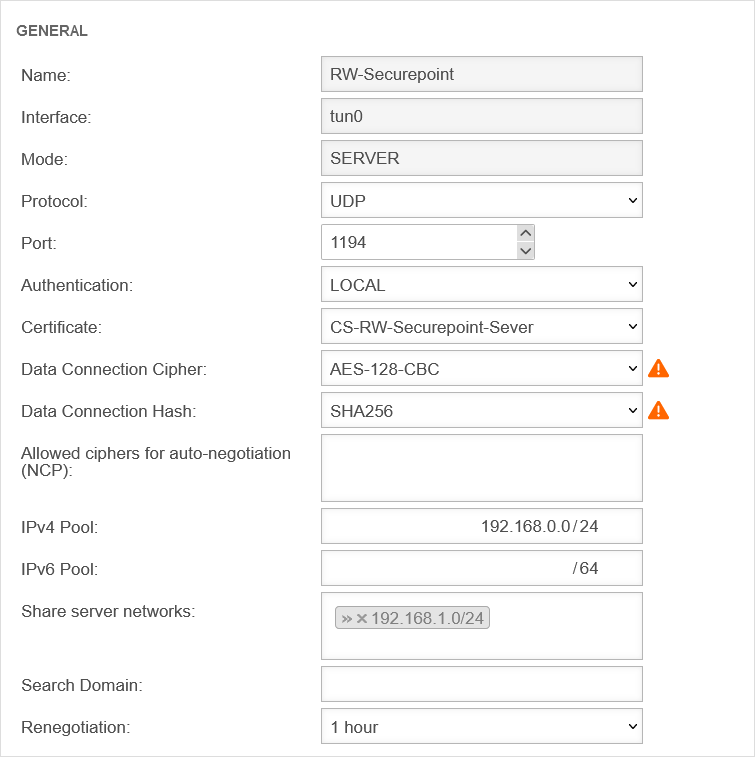
Setting in the SSL-VPN server
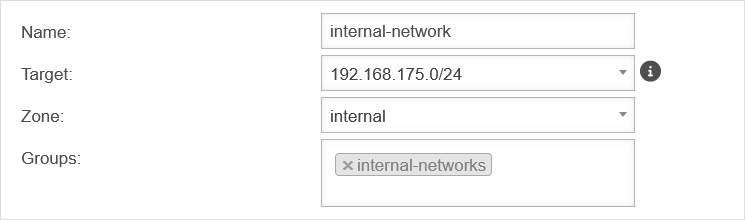
Create network objects
In addition to the existing network object for the Roadwarrior, another one is required for the Netmap network with the following properties in order to create a corresponding packet filter rule:
Packet filter rules
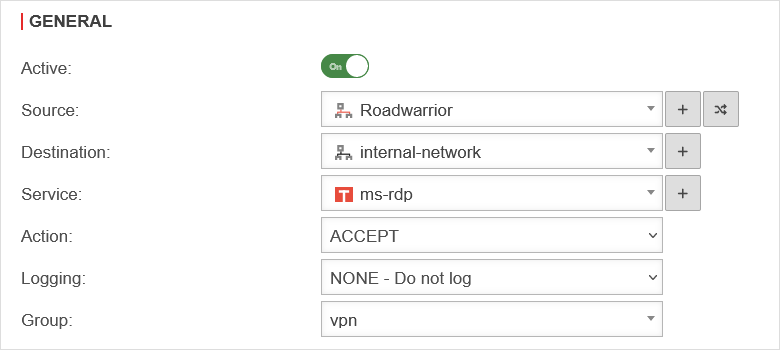
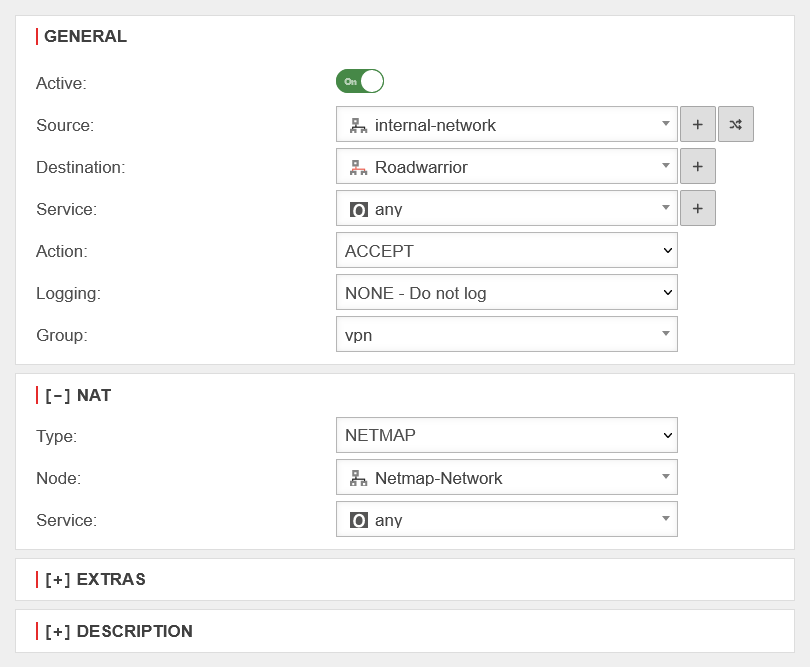
The packet filter overview should now contain the following lines:
| # | Source | Destination | Service | NAT | Action | Active | |||
| 5 | Accept | On | |||||||
| 6 | NM | Accept | On | ||||||
Notes
The VPN client must re-establish the connection so that it also receives the correct subnet.
Access from the client to a host in the internal network then takes place via the IP address 192.168.2.x, as the subnet mask /24 has been defined here. The last octet is therefore the original host IP.
So if we want to address the host with the original IP address 192.168.0.1 in this example, the client must use the IP address 192.168.2.1 to reach it.
The client can only access the hosts in the internal network with IP addresses. A DNS query would result in the original IP of the host being transferred and the client would no longer be able to access it.