notempty
notempty
notempty Dieser Artikel bezieht sich auf eine nicht mehr aktuelle Version!
notempty
Der Artikel für die neueste Version steht hier
Zu diesem Artikel gibt es bereits eine neuere Version, die sich allerdings auf eine Reseller-Preview bezieht
Adaptation of the firewall to the UMA
Last adaptation to the version: 3.3
New:
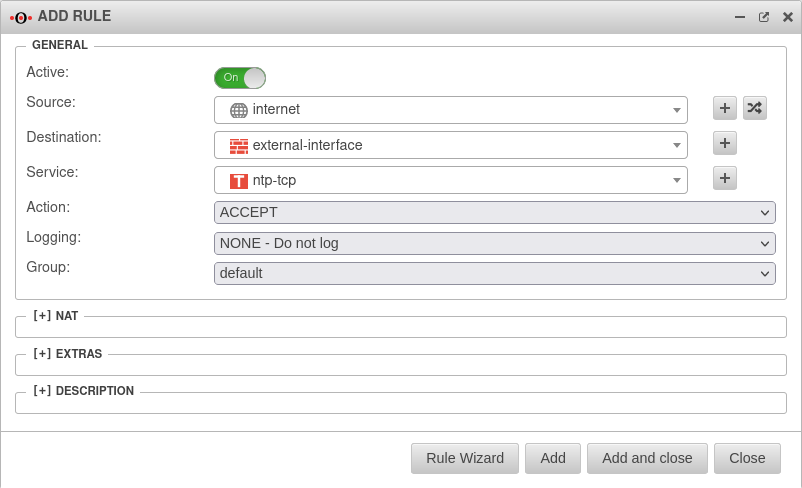
- Additional ports required: Port 123 (ntp) and Port 443 (for retrieval).
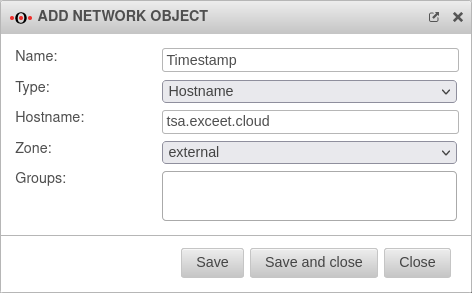
- Release: tsa.exceet.cloud for Timestamp
- Layout adjustment
notempty
This article refers to a Resellerpreview
Introduction
Introduction
In order to implement the UMA, the firewall must be adapted. The firewall must be configured to receive email, check spam, filter for viruses, and forward to the internal mail server.
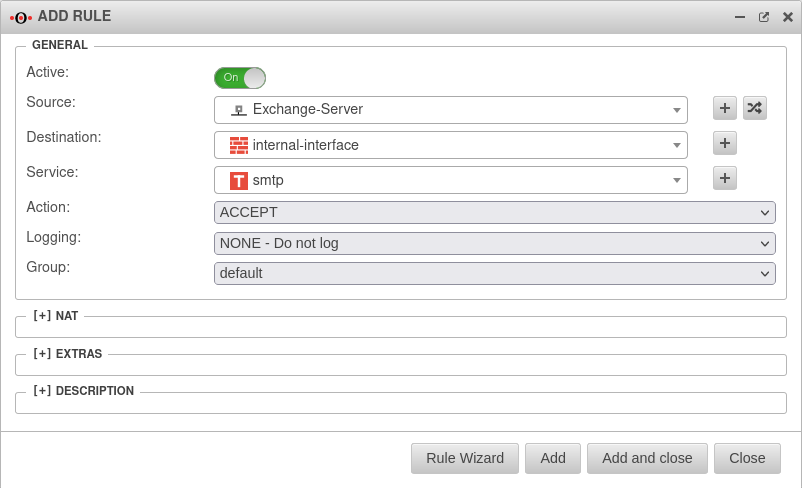
Im Beispiel wird von einem Exchange-Server ausgegangen.
Details on the administration of the firewall can be found in corresponding Wiki articles. The setup on a UTM is described here.
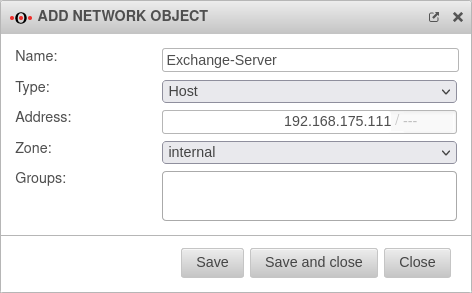
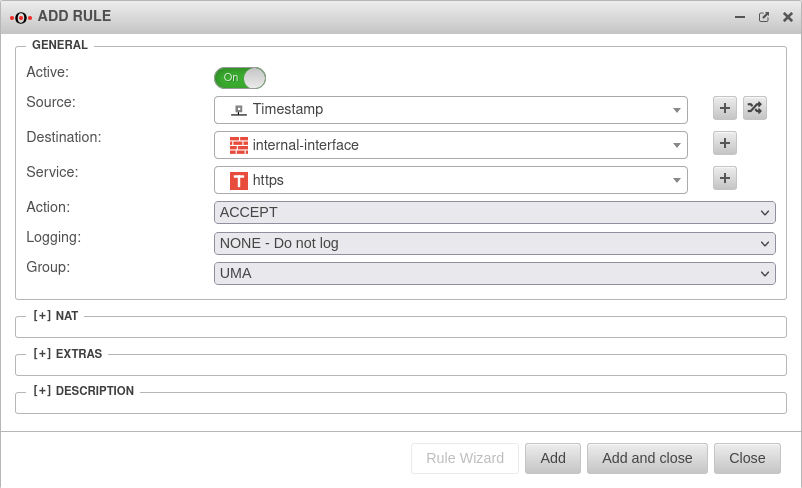
Creating the network objects and firewall rules for SMTP
Creating the network objects and firewall rules for SMTP
Configure the mail relay
Configure the mail relay
| . In order for incoming mail to be properly scanned for viruses, filtered for spam, and then forwarded to the internal mail server, the next step is to configure the mail relay. | |||||
| In the General tab, a postmaster email address is entered and the maximum email size for incoming emails and emails to be sent is specified. | 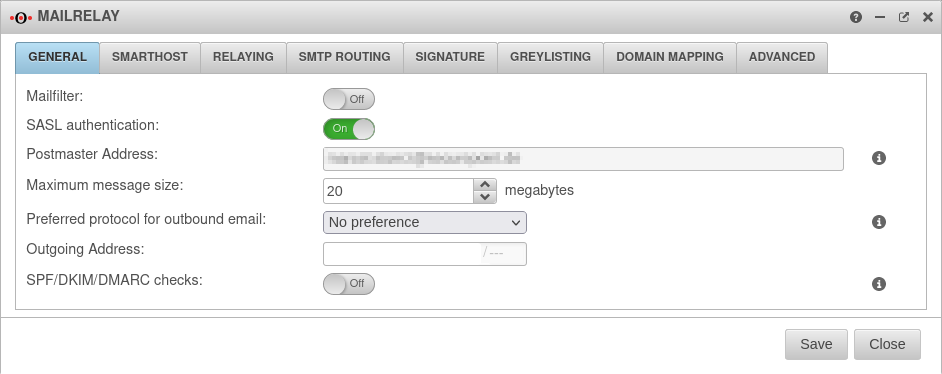 | ||||
RelayingRelaying
| |||||
| In the Relaying tab, the button adds two domains. | |||||
| Caption | Value | Description | 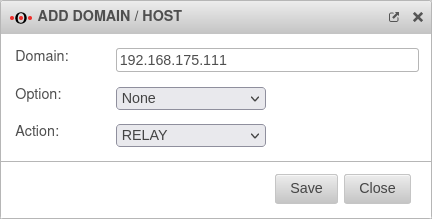 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domain: | 192.168.175.111 | The IP address of the mail server | |||
| Option: | No option is selected | ||||
| Task: | Select this action For accepting emails with the IP of the mail server. | ||||
| Domain: | mydomain.de | The domain of the mail server | 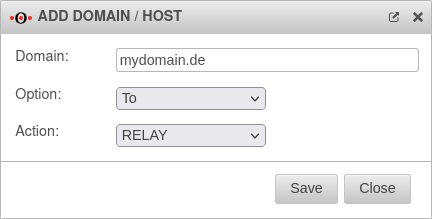 | ||
| Option: | Select this option The entry of the domain with the To option allows accepting all emails of the entered domain in the recipient. | ||||
| Task: | Select this action | ||||
SMTP RoutenSMTP Routen
| |||||
| In the SMTP Routes tab, the button creates a new SMTP route. | |||||
| Caption | Value | Description | Datei:UMA3.3 Anwendungen Mailrelay SMTP-Routene-en.png | ||
| Domain: | mydomain.de | Enter the selected domain | |||
| Mailserver: | 192.168.175.111 | Enter the IP address of the mail server This route specifies that all incoming emails are forwarded to the internal server. | |||
| Under Settings Check email address: can be selected.
| |||||
| |||||
| In the Advanced tab, under Greeting Pause the Status: is activated On.
|
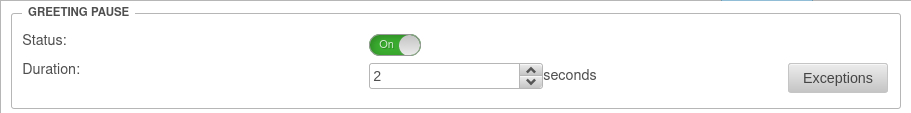 | ||||
| |||||
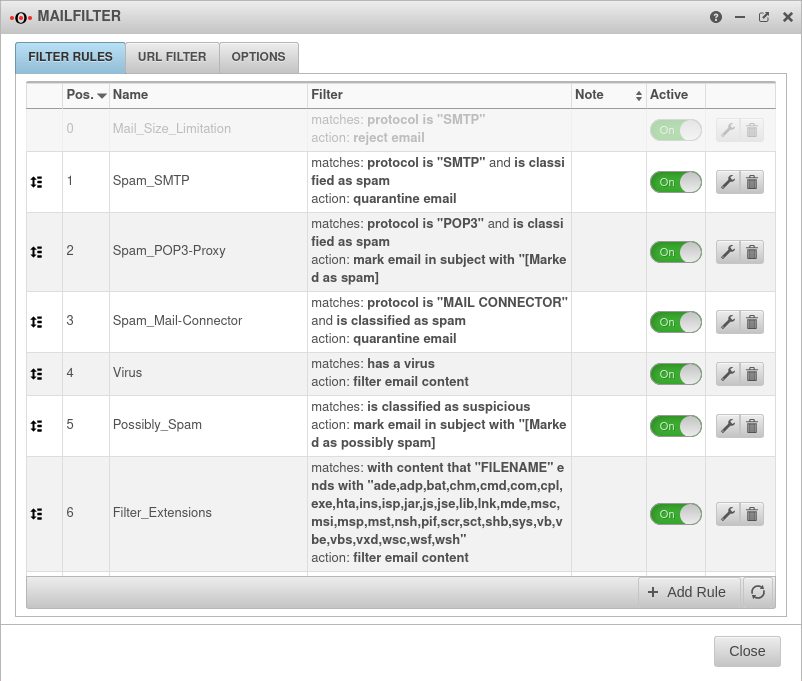
Customize the mail filter
Customize the mail filter