notempty
- Ping check host becomes Ping check IP
Functionality
Procedure of a fallback
A regular ping check is used to test the availability of a connection. The target to be pinged (ping-check IP), the time interval (interval) and the number of attempts (threshold) can be specified individually.
If the ping-check IP is not reached in the set time, it is assumed that the line is down. The fallback is initiated:
- The default route is changed to the fallback interface
- The changed default route is not displayed in the network configuration.
However, in the Tab Routing Table menu you can see the updated default route. - The zones of the main line interface are moved to the fallback interface The move of the zones is not displayed in the UI
- If a DYNDNS is configured, it will now be executed on the fallback interface
- A ping check will still be executed on the main line interface
- A notification is sent by the Alerting Centre
Failback procedure
If the ping check on the main line interface is successful again, a failback is performed. The fallback is "unwound":
- The default route is changed to the interface of the main line
- The zones of the fallback interface are moved back to the interface of the main line
- If a DYNDNS is configured, it will now be executed on the main line interface again.
- A notification is sent by the Alerting Centre
Incoming connections
If certain services are available from the Internet, they may not be available after a switch to the fallback.
This can be circumvented to a certain extent by using DynDNS, but there are limits - depending on the type of fallback line:
- The IP of the fallback line must not be a private IP (usually happens with LTE connections)
The connection to the Unified Security Console (USC) is also possible with a private IP - Incoming connections must use a DynDNS name.
- Applications particularly affected:
- Mailrelay
- IPSec and SSL VPN connections
- Sharing for administrative access
- Port forwarding (network objects are not moved as well)
- Reverse Proxy
Outgoing connections
- Outgoing connections, from applications on the UTM or local network, that are bound to an IP should be configured to a private IP that is still available on fallback.
- Particularly affected applications:
- HTTP proxy
- Mailrelay
Preparations
Connection of the UTM in the local network
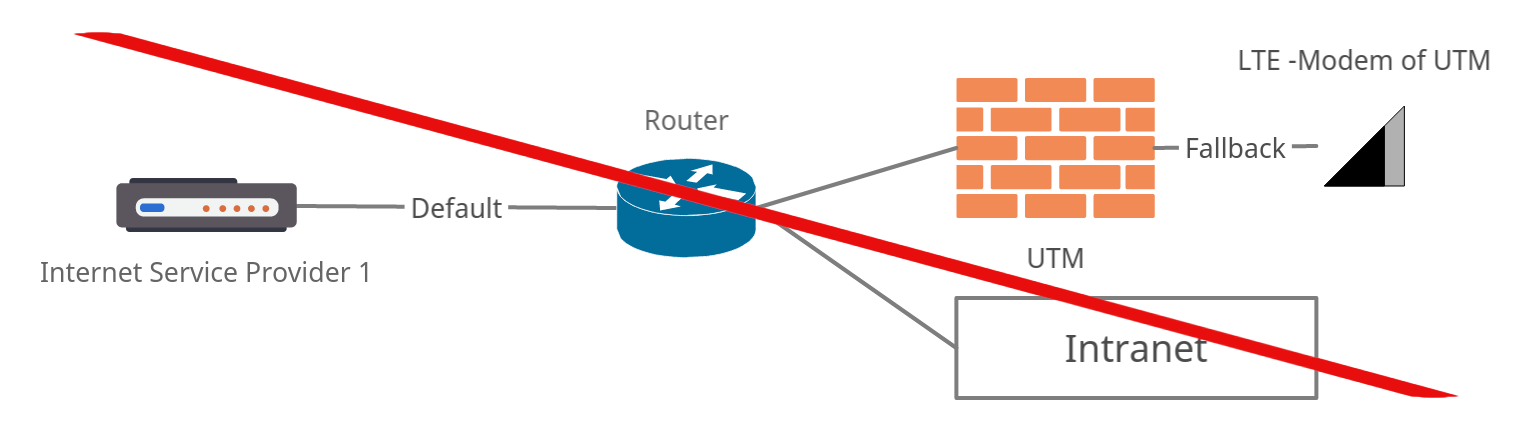
In the event of a fallback, all zones of the interface over which the ping-check IP is checked are moved.
If there is a network on the same interface over which this check takes place, this entire network is also no longer accessible in the event of a fallback.
- The UTM is on a local network behind a router that provides default Internet access
- The UTM serves as a cloud connector only for certain applications, for example
- The LTE interface of the UTM is to serve as a fallback
- The UTM now checks the ping-check IP via the default Internet access and determines that it cannot be reached
- All zones of the UTM that are located on the interface to the router of the default Internet access are then moved to the LTE interface
- However, the UTM is then no longer accessible, since this was also the access to the local network.
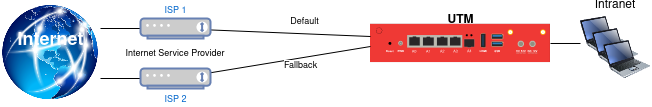
Different connections to the Internet
PPPoE (wan) interfaces
- Access is via PPPoE (wan) interfaces.
Fallback with the same provider
In this case, network IPs and router IPs could overlap.
The solution here is the use of a router between the network access and the UTM, which sets up a transfer network and natts the connection in the process.
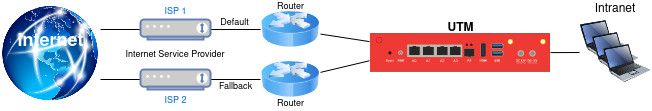
Ethernet (LAN) interfaces
- The default line and / or the fallback line is accessed via another router (e.g. a Fritzbox or a Speedport).
Edit Ethernet interfaces
Configuration of the fallback
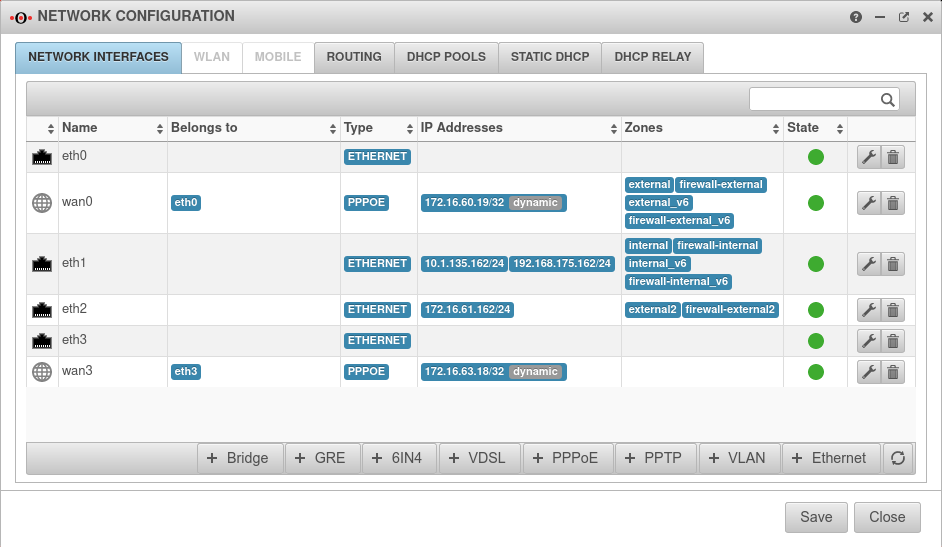
Configuration network interfaces
Configuration under Tab Network interfaces
- The network should be configured in such a way that the external zones (external, firewall-external and the VPN zones) are located on the primary interface.
- On the fallback interface (in the example
wan3) no zones are allowed to be present.
If necessary, under Tab Network Objects button change the interface name from e.g. LAN1 or eth0 to 0.0.0/0.
Routing
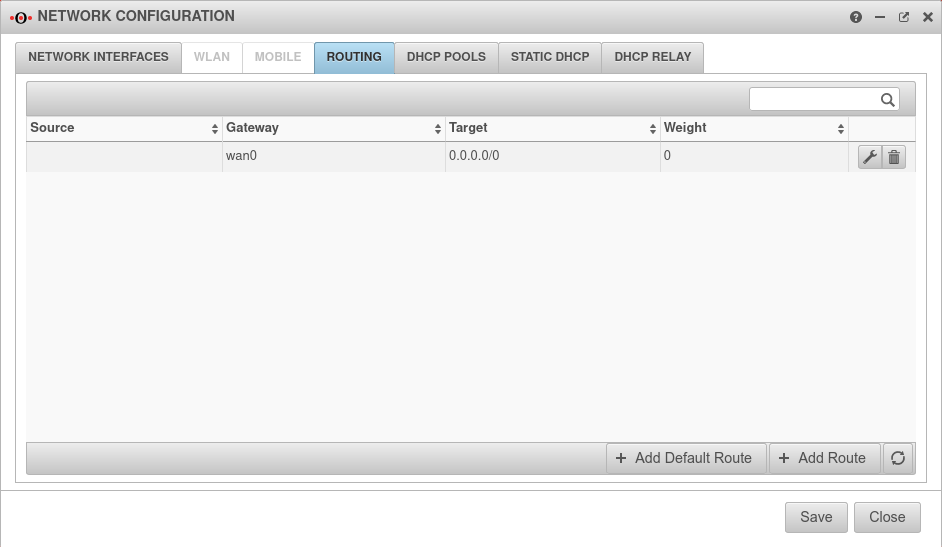
Exactly one Default route over the default line is on the Firewall required .
In the example wan0
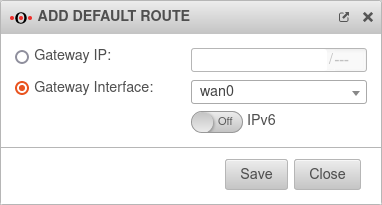
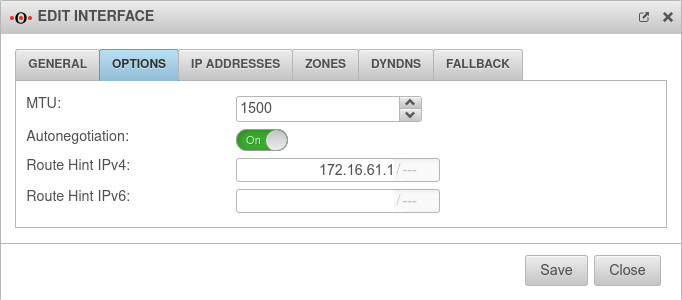
Fallback
Configuration under Tab Network Interface Button of the relevant interface, tab Fallback
Configure the interface of the default line
| Caption | Value | Description | 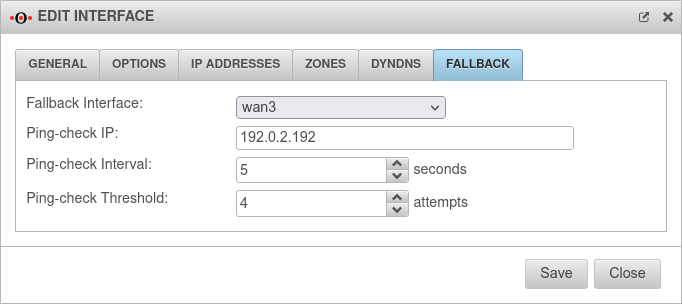 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fallback interface: | |
Interface to switch to in case of malfunction. | |
| Ping-check IP: |
192.0.2.192 Example IP must be replaced |
A host of your choice that is to be pinged, thus checking the availability of the network. | |
| Ping-check Intervall: | 5 Seconds | The "break" between pings. | |
| Ping-check Threshold | 4 Versuche | Number of consecutive pings allowed without a response before the fallback is triggered. | |
Notes on the application
A restriction regarding hostnames in the list of the administration in connection to fallback no longer exists.