Setting up a UTM with the installation wizard
Last adaptation to the version: 14.0.1 (01.2025)
New:
notemptyThis article refers to a Beta version
Prefaces
- Usually, the installation wizard appears during the initial setup of the UTM.
This checks whether a configuration already exists that is marked as the boot configuration. (Status )
If this is not the case, the wizard opens automatically. - It is not advisable to start the installation wizard later, as other settings made in the meantime may be overwritten.
Installation wizard
Step 1 - General
| Caption | Value | Description | UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnConfiguration management 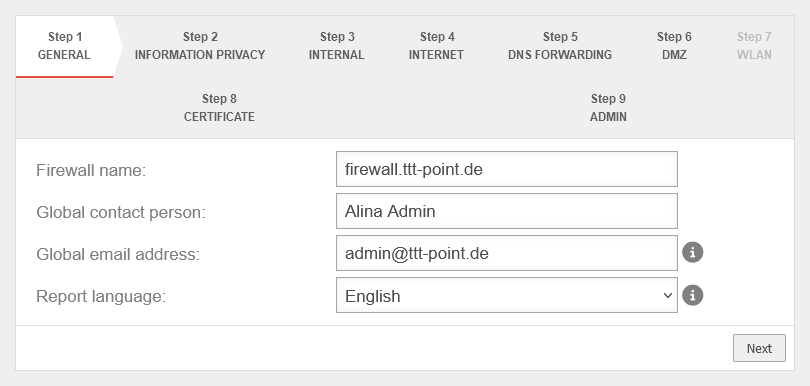 Step 1 Step 1
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Firewall Name: | firewall.ttt-point.local | This is about how the UTM responds to requests. For example, if the mail relay is to be used, it may be useful to enter the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the mail exchange (MX) here so that other mail servers can match it via the reverse resolution of the PTR Resource Record (PTR). This setting is made in the Authentication → AD/LDAP Authentication → tab Settings Appliance Account entry. | |
| Global contact person: | Alina Admin | In this field, the name of the administrator or the organization is entered, which is later specified in the UTM error messages for questions. | |
| Global email address: | admin@ttt-point.de | Important system messages are sent to this email address. | |
| Language of reports: | Language in which the reports and system messages are sent | ||
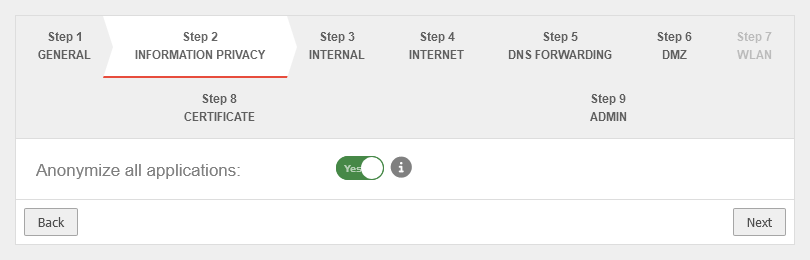
Step 2 - Privacy | |||
| Anonymize all applications | Yes | When activated (default), the appliance's applications are anonymized in accordance with the GDPR. Under anonymization can also be activated individually for each application. |
 |
Step 3 - Internal | |||
Without WLAN moduleWithout WLAN module
| |||
| Internal firewall IP address: | The IP address of the internal interface ( A1 / eth1 / LAN2 - depending on the hardware and software used |
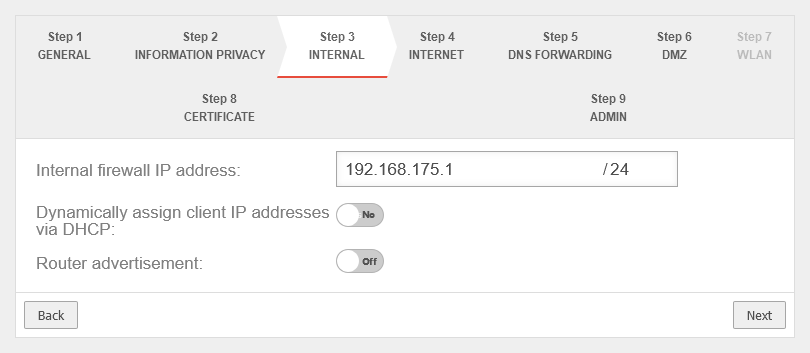 | |
| Dynamically assign Client IP Addresses via DHCP: | No | When enabled Yes, the UTM works as a DHCP server: All clients in the internal network receive an IP address via DHCP. This sets the UTM as the default gateway and DNS server for the clients. | |
| Router Advertisement: | Off | If the UTM has received an IPv6 prefix, it can advertise the subnet via router advertisement in the network segment behind the interface. (See article IPv6 Prefix Delegation) | |
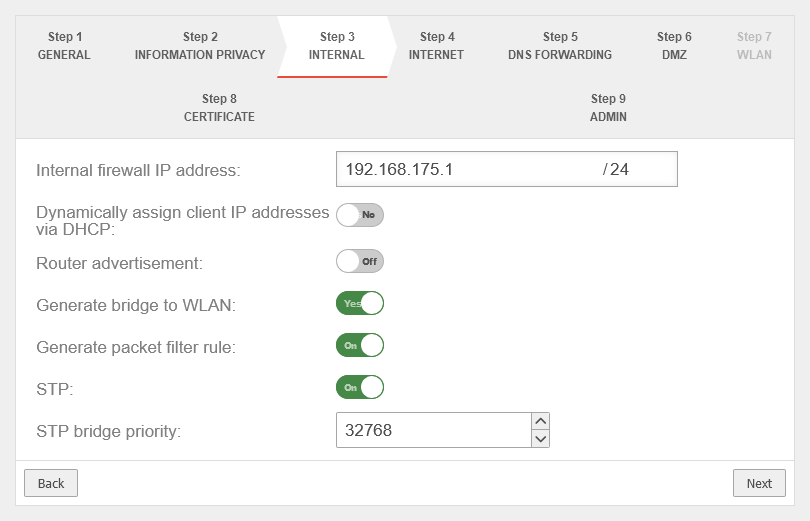
With WLAN module With WLAN module
| |||
| Internal firewall IP address: | The IP address of the internal interface ( A1 / eth1 / LAN2 - depending on the hardware and software used |
 | |
| Dynamically assign Client IP Addresses via DHCP: | No | When enabled Yes, the UTM works as a DHCP server: All clients in the internal network receive an IP address via DHCP. This sets the UTM as the default gateway and DNS server for the clients. | |
| Generate WLAN Bridge: | No Default |
Creates a bridge so that this network and the WLAN are on the same network. | |
| Generate portfilter rule: Shown when Generate WLAN Bridge is enabled |
No | When activated, a port filter rule is automatically generated | |
| STP: Shown when Generate WLAN Bridge is enabled |
Off | When activated, STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is used | |
| STP Bridge Priority: Shown when Generate WLAN Bridge is enabled |
32768 Default |
The priority of the STP Bridge is set | |
Step 4 - InternetThis is where the Internet connection is configured on the external interface (A0 / eth0 / LAN1 - depending on the hardware and software used The following variations are available: | |||
Connection type PPPoE / VDSL Connection type:
| |||
| With this type, an ADSL or SDSL modem is connected to the external interface ( A0 / eth0 / LAN1 - depending on the hardware and software used | |||
| Username: | (Shares ISP) | The login information is provided by the ISP (Internet Service Provider). | 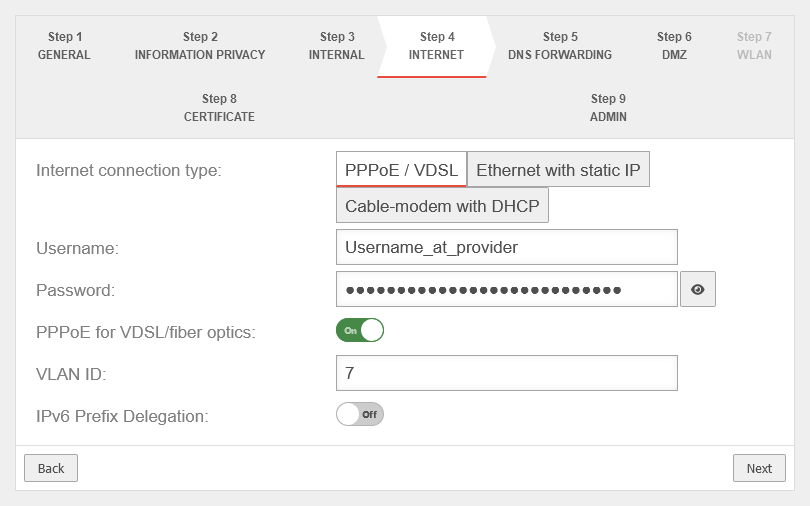 |
| Password: | (Shares ISP) | ||
| PPPoE for VDSL/fiber optics: | Off | Check the box if PPPoE is connected via a VDSL modem or via fibre. | |
| VLAN ID: Shown when PPPoE for VDSL/fiber optics is enabled |
7 | The VLAN ID is usually specified by the network operator | |
| IPv6 Prefix Delegation: | Off | Allows an IPv6 network assigned by the Internet Service Provider to be split into /64 networks and assigned to individual interfaces via Router Advertisement. Example: Network assigned by ISP: 2001:0db8:aaaa:bb::/56 Networks distributed at internal interfaces via router adviertisement: 2001:0db8:aaaa:bb00::/64 2001:0db8:aaaa:bb01::/64 | |
| notempty The option Use DNS server of the provider has been moved to step 5 | |||
Connection type Ethernet with static IP Connection type:
| |||
| With this connection type, a router is connected to the external interface ( A0 / eth0 / LAN1 - depending on the hardware and software used | |||
| External IP address: | The IP address of the external interface ( A0 / eth0 / LAN1 - depending on the hardware and software used The external interface receives an IP address via DHCP by default, provided a DHCP server is available in the external network. |
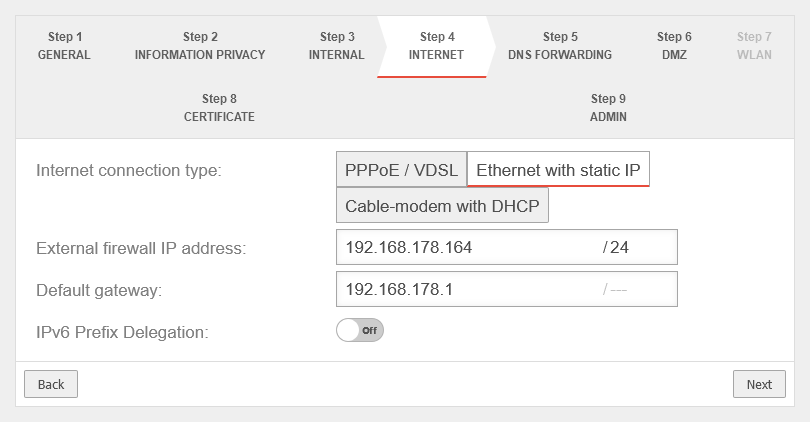 | |
| Default Gateway: | IP address of the default gateway for the UTM so that it knows which is the closest router for all networks that are not on an internal interface: As a rule: the Internet. | ||
| IPv6 Prefix Delegation: | Off | Allows an IPv6 network assigned by the Internet Service Provider to be split into /64 networks and assigned to individual interfaces via Router Advertisement. Example: Network assigned by ISP: 2001:0db8:aaaa:bb::/56 Networks distributed at internal interfaces via router adviertisement: 2001:0db8:aaaa:bb00::/64 2001:0db8:aaaa:bb01::/64 | |
Connection type Cable modem with DHCP Connection type:
Originally mostly devices that cable providers provided to their customers. | |||
| Also with this connection type, a router is connected to the external interface ( A0 / eth0 / LAN1 - depending on the hardware and software used |
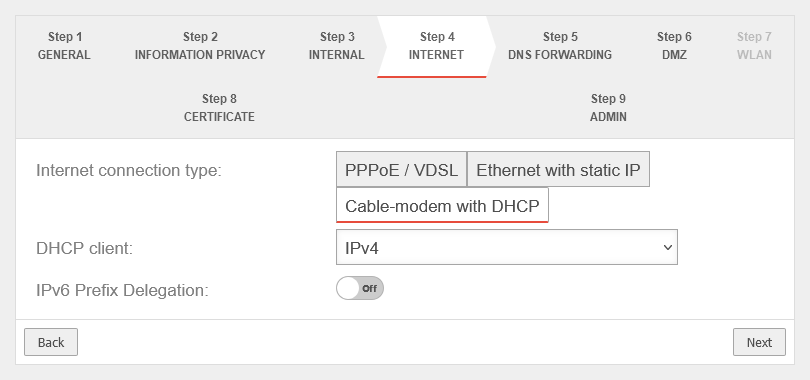 | ||
| DHCP Client: | Selection with which protocol the interface receives IP addresses from the preceding router with DHCP server. | ||
| Use the provider's DNS server: | Off | When activated, the provider's DNS server is used. | |
| IPv6 Prefix Delegation: | Off | Allows an IPv6 network assigned by the Internet Service Provider to be split into /64 networks and assigned to individual interfaces via Router Advertisement. Example: Network assigned by ISP: 2001:0db8:aaaa:bb::/56 Networks distributed at internal interfaces via router adviertisement: 2001:0db8:aaaa:bb00::/64 2001:0db8:aaaa:bb01::/64 | |
Connection type LTE / others Connection type:
| |||
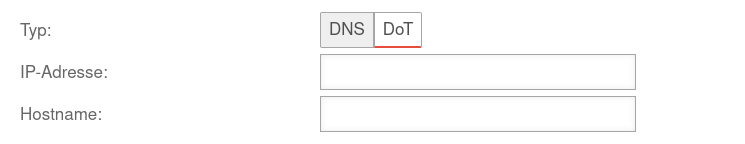
Step 5 - DNS ForwardingnotemptyNew step from v14.0.1 The DNS forwarding of the name server can be configured here. There are the same options as under Area DNS Forwarding. For more detailed information, see the Nameserver article. | |||
notempty New in the installation wizard from v14.0.1 |
Adds DNS Forwarding. It is possible to select classic DNS or DNS over TLS (DoT). Further information in the Article on DNS forwarding in the nameserver. |
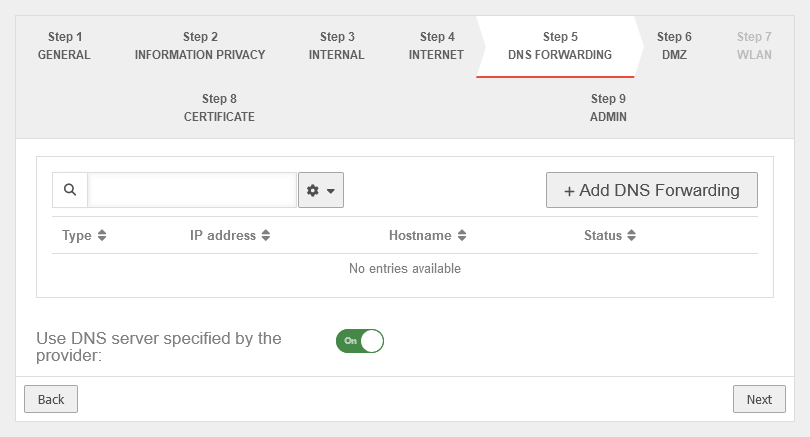 | |
| Use the provider's DNS server: | On | When activated, the provider's DNS server is used. | |
Step 6 - DMZConfiguration of a second internal network, often referred as Demilitarized Zone: Usually a network that is separate from the internal network. | |||
| DMZ IP address: | The IP address of the interface A2 and the subnet mask (as CIDR notation) for the DMZ network. | 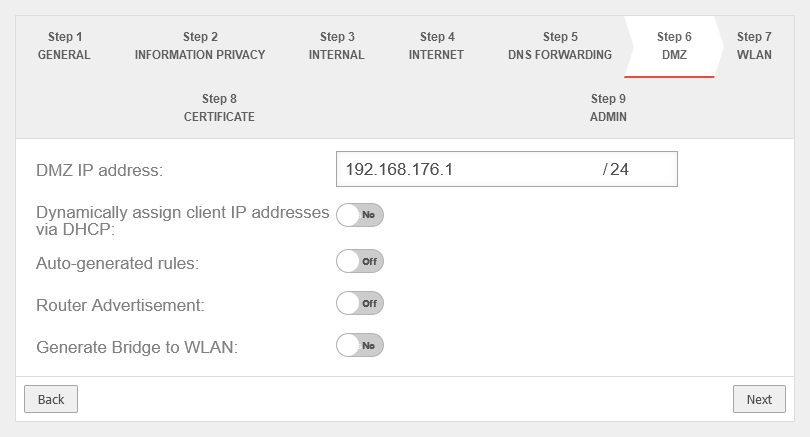 | |
| Assign the IP addresses to the clients in this network via DHCP: | No | When enabled Yes, the UTM works as a DHCP server: All clients in the DMZ network receive an IP address via DHCP. This sets the UTM as the default gateway and DNS server for the clients. | |
| Autogenerated rules: | No | Port filtering rules can be automatically created for this network, allowing traffic to the Internet on the interface to the external interface ( A0 / eth0 / LAN1 - depending on the hardware and software used Likewise, rules are created that also allow traffic from the internal network into the DMZ network. notempty These any rules are intended for testing purposes and should be disabled and replaced with well-defined rules in production mode. | |
| Router Advertisement: | No | If the UTM has received an IPv6 prefix, it can advertise the subnet via router advertisement in the network segment behind the interface. (See article IPv6 Prefix Delegation) | |
| Generate WLAN Bridge: Only if a WLAN module is present |
No | Creates a bridge so that this network and the WLAN are on the same network. | |
Step 7 - WLANThis step appears only if in the used hardware has a WLAN module installed. | |||
| WLAN IP address: Not in bridge mode |
The IP address of the WLAN interface (wlan0) and the subnet mask (as CIDR notation) for the WLAN network. In bridge mode, the setting from the internal network in which bridge mode was activated is used here. |
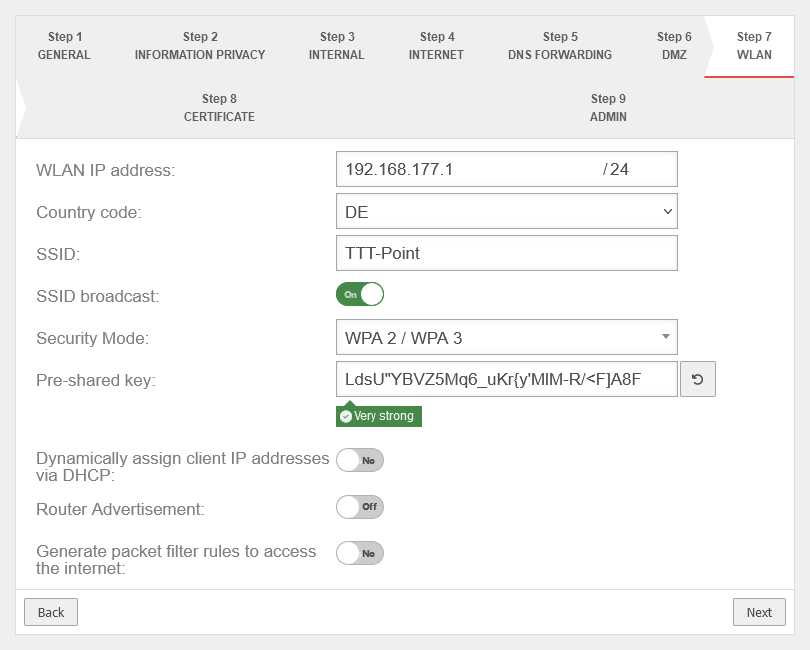 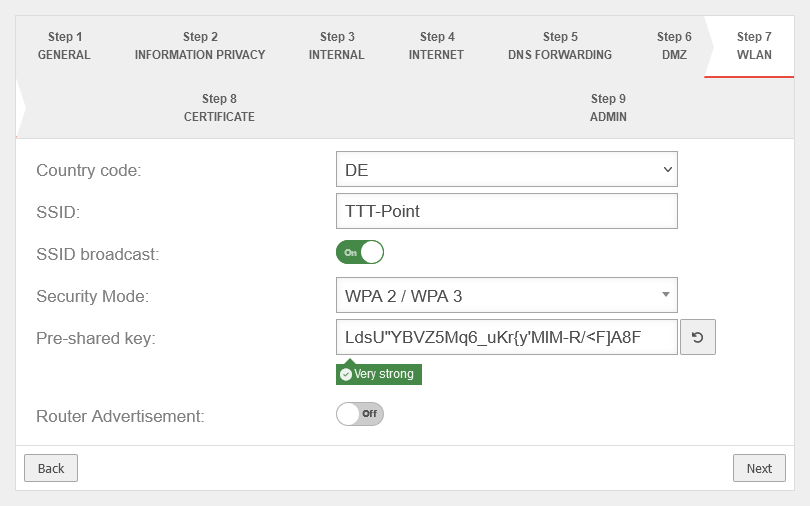 | |
| Country code: | The country code is used to determine which frequencies and which signal strengths may be used. The frequencies used and the transmission power can be found in a Wikipedia article. | ||
| SSID: | TTT-POINT | The Service Set Identifier (SSID) is the name under which the WLAN network is presented to the clients. This must be entered in any case. | |
| SSID Broadcast: | On | This option can be used to define whether the WLAN network can be seen by every client or whether the transmission of the SSID should be suppressed. (Off) | |
| Security Mode: | WPA | Is considered unsafe and only exists for backwards compatibility. (TKIP is used as encryption method) | |
| WPA2 | Standard with enhanced security AES128 is used as encryption method: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WPA2 | ||
| WPA3 | Standard with highest available level of security AES256 and SAE are used as encryption methodes: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/WPA3 | ||
| Pre-Shared Key: | Don'tcopythis:Ei)#W~X$… | The base station and mobile device must have the same PSK (≙password). The security of the encryption depends directly on the length and complexity of the PSK! | |
| Automatically generates a very strong PSK | |||
| Assign the IP addresses to the clients in this network via DHCP: Not in bridge mode |
Off | When enabled, the UTM works as a DHCP server: All clients in the WLAN network receive an IP address via DHCP. This sets the UTM as the default gateway and DNS server for the clients. In bridge mode, the setting from the internal network in which bridge mode was activated is used here. | |
| Router Advertisement: | No | If the UTM has received an IPv6 prefix, it can advertise the subnet via router advertisement in the network segment behind the interface. (See article IPv6 Prefix Delegation) | |
| Generate rules for Internet access: Not in bridge mode |
Off | Port filtering rules can be automatically created for this network, allowing traffic to the Internet on the interface to the external interface ( A0 / eth0 / LAN1 - depending on the hardware and software used notempty These any rules are intended for testing purposes and should be disabled and replaced with well-defined rules in production mode. In bridge mode, the setting from the internal network in which bridge mode was activated is used here. | |
Step 8 - Certificate | |||
| Generate CA and server certificate: | Yes Default |
If Yes is enabled, a CA and server certificate will be generated. |
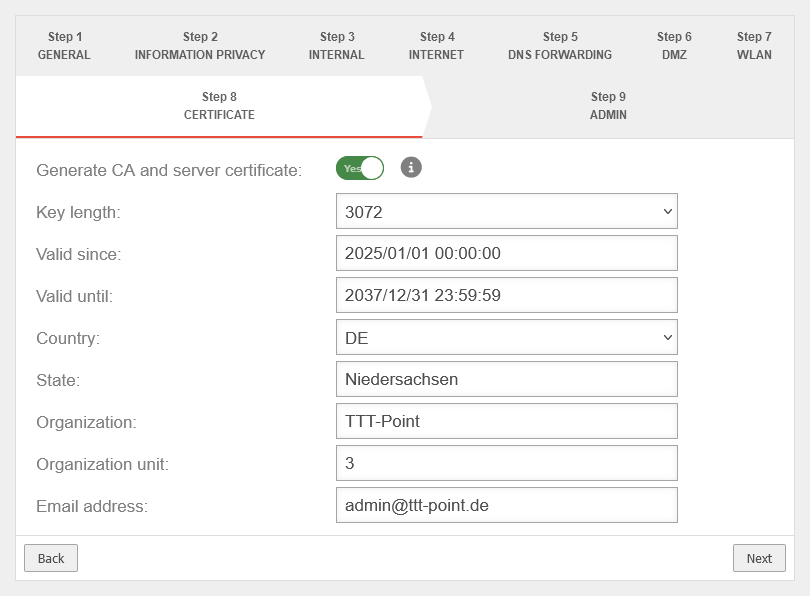 |
| Key length: | Select the bit length of the key | ||
| Valid since: | 2024/01/01 00:00:00 | ||
| Valid until: | 2037/12/31 23:59:59 | ||
| Country: | Detailed information is used to identify who issued the certificate | ||
| State: | Lower Saxony | ||
| Organization: | TTT Point | ||
| Department: | Support | ||
| Email address: | admin@ttt-point.de | ||
Step 9 - Administrator | |||
| User | admin | The username admin cannot be changed at this point | 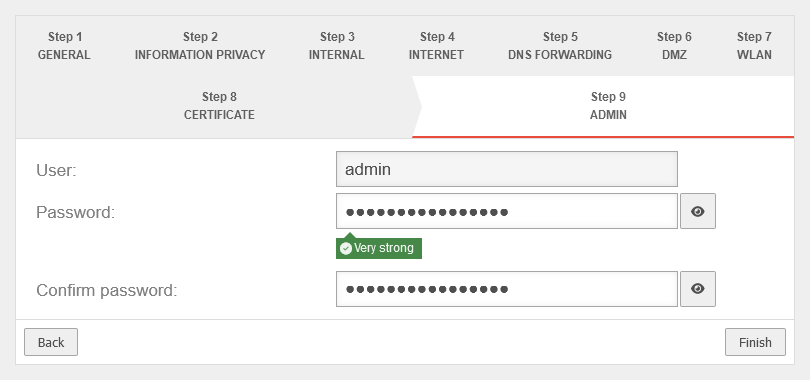 |
| Password: | •••••••••••••• |
Passwords must meet the following criteria:
| |
| Confirm password: | •••••••••••••• | ||
| |||
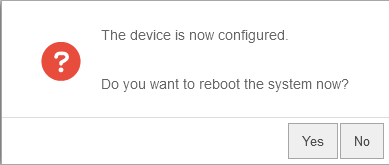
Reboot
| |||
| Do you want to reboot the system now? | In order for the configuration changes to be applied, the respective services must be restarted in the correct order. This is achieved by a reboot of the device. |
 | |
| notempty If your own IP address was changed to reach the admin interface of the UTM and the default was changed in Step 3 - Internal, the internal interface of the UTM is now located in this network. For further configuration, the IP address of your own computer must then be changed again. See the [1] | |||
Configure interfacesnotemptyNew as of v12.7.0 | |||
| Do you want to configure the interfaces now? | This message appears if not all existing interfaces are configured correctly. However, it is recommended to do this to prevent possible problems. The button opens the network configuration directly. | 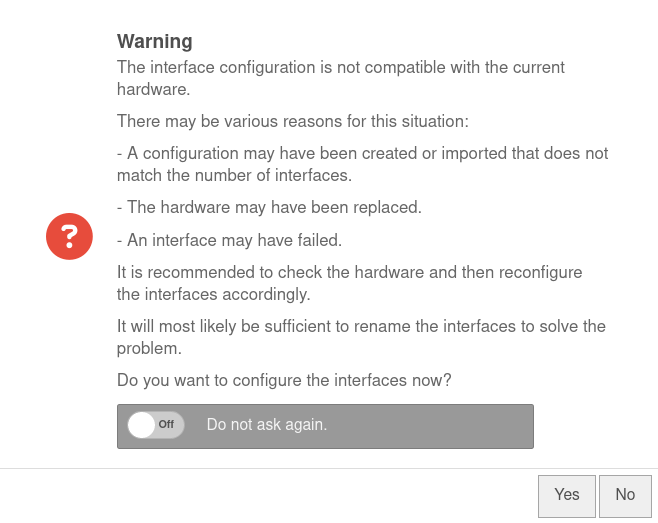 | |
| Do not ask again | Off | If this message is not desired, it can be set here so that it is not displayed again the next time you log in. | |