Last adaptation to the version: 12.6.0
- Updated to Redesign of the webinterface
notemptyThis article refers to a Beta version
Introduction
Eine Bridge (Netzwerkbrücke) verbindet zwei physikalische Netzwerke zu einem gemeinsamen Netz.
Die so zusammengeschlossenen Schnittstellen haben eine IP und die IP-Adressen der angeschlossenen Geräte liegen im selben Subnetz.
notemptyDie Firewall darf nicht über diejenige Schnittstelle administriert werden, die zu einer Bridge hinzugefügt werden soll!
Die Verbindung zum Admin-Interface fällt weg, sobald die IP-Adresse von der Schnittstelle entfernt wird, über die gerade auf die UTM zugegriffen wird.
Wenn alle verfügbaren internen Schnittstellen zu einer Bridge hinzugefügt werden (z. B. A1 und A2 bei einer Black Dwarf), muss der Zugriff auf die Firewall von außen über A0 erfolgen.
Lösung: Eine Forward-Zone im Nameserver der UTM einrichten. Dafür muss die UTM als Nameserver für die internen Clients konfiguriert sein. Dann verweist die externe URL, die von Intern aufgerufen wird, direkt auf den Internen Ziel-Server.
Eine Anleitung zum einrichten der Forward-Zone befindet sich unter Forward-Zone im Nameserver Wiki.
Prepare administration access
- Identify an interface on the firewall that should not be bridged.
- In the menu Area Network interfaces IP Addresses note down or assign existing IP address of this interface (e.g. 10.0.10.1/24 or 10.10.10.193/29).
- Find a free IP address from the corresponding network.
- Add this IP address or the entire associated network (e.g. 10.0.10.0/24 or 10.10.10.192/29) in the menu Area Administration and authorize it for administration.
- Establish access on the selected interface via this IP address or this network (e.g.: 10.0.10.1:11115 or 10.10.10.193:11115).
Prepare interfaces
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnNetworkNetwork configuration 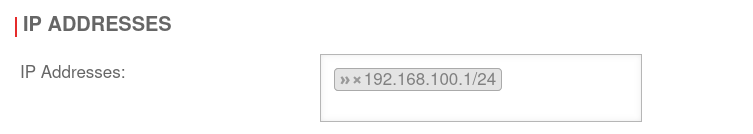 Removing IP address
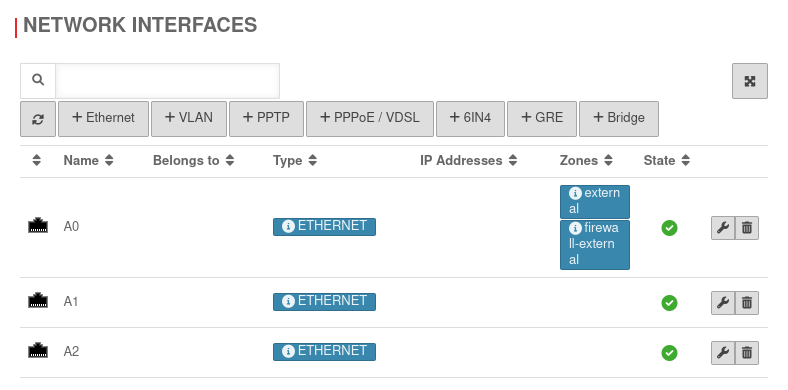
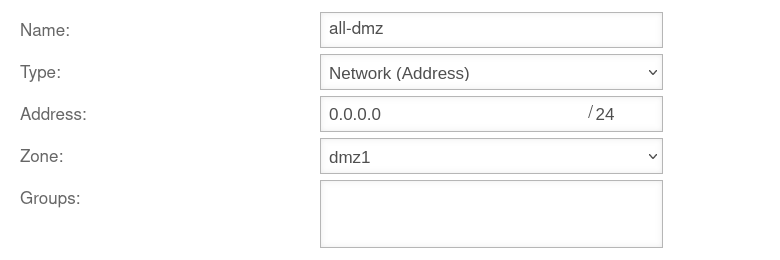
First, remove all IP addresses from the interfaces to be used for the bridge.
Removing IP address
First, remove all IP addresses from the interfaces to be used for the bridge.
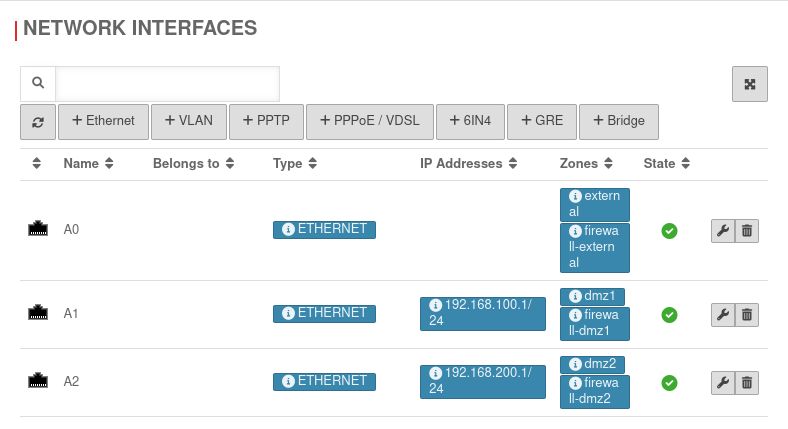
Menu → in the corresponding interface → Tab IP Addresses.
Remove IP addresses. In the example »192.168.100.1/24 by clicking on
Under no circumstances may the IP address be removed which is used for the current access!
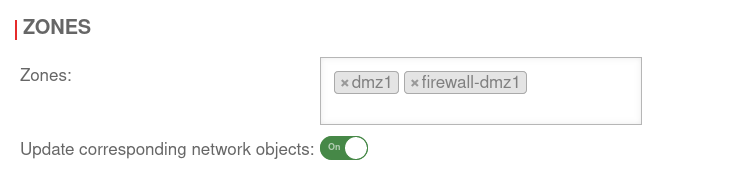
In the second step, all zones are removed from the interfaces to be used for the bridge.
Menu → in the corresponding interface → Tab Zones.
Remove the zones by clicking on . In the example »dmz1 »firewall-dmz1.
Then Save.
Under no circumstances may the zone be removed which is used for the current access!
Create a Bridge
In the example, the interfaces A1 and A2 are to be combined to a DMZ.
Start the wizard in the menu Area Network interfaces button .
Step 1Step 1
| |||
| Caption | Value | Description | UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnNetworkNetwork configuration 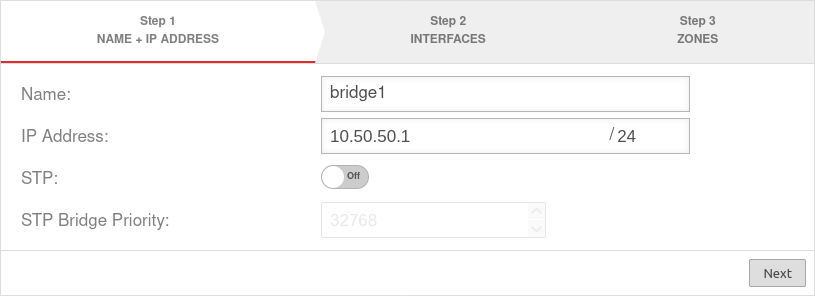 Assistant step 1 Assistant step 1
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Name: | bridge0 | Name of the bridge interface | |
| IP address: | 10.50.50.1/24 | Example-IP address of the bridge interface | |
| STP: | Off | In addition, the Spanning Tree Protocol can be activated. The Spanning Tree Protocol prevents parallel connections in networks with multiple switches and thus avoids unwanted circular packets | |
| STP Bridge Priority: | 32768 | ||
| Next step | |||
Step 2Step 2
| |||
| Interfaces: | »A1 »A2 | Interfaces that are to be combined. Available interfaces can be selected in the click box. | 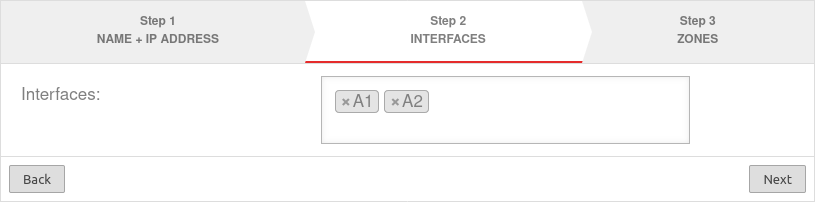 |
| Next step | |||
Step 3Step 3
| |||
| Zones: | »dmz1 »firewall-dmz1 | Zones that are to be linked with the bridge interface. In our example dmz1 and firewall-dmz1. |
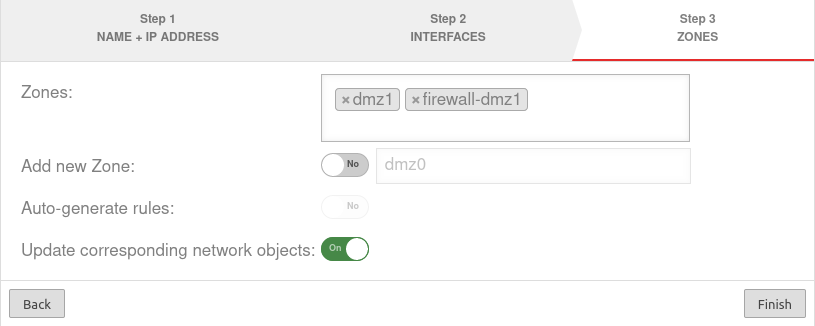 |
| Add new zone: | Off dmz2 | If activated, a new zone can be added to the bridge alternatively or additionally. | |
| Generate Rules: | Off | Packetfilter rules are automatically created for the new zone. These rules first allow any network traffic of the bridge to the internet (any rules) and must be replaced unconditionally by customized rules! | |
| Update associated network objects: | On | If activated, all network objects whose zone is assigned to another interface and which have specified an interface as the target are now assigned the new bridge as the target. | |
| Completes the bridge setup. | |||
| Configured bridge | UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnNetwork 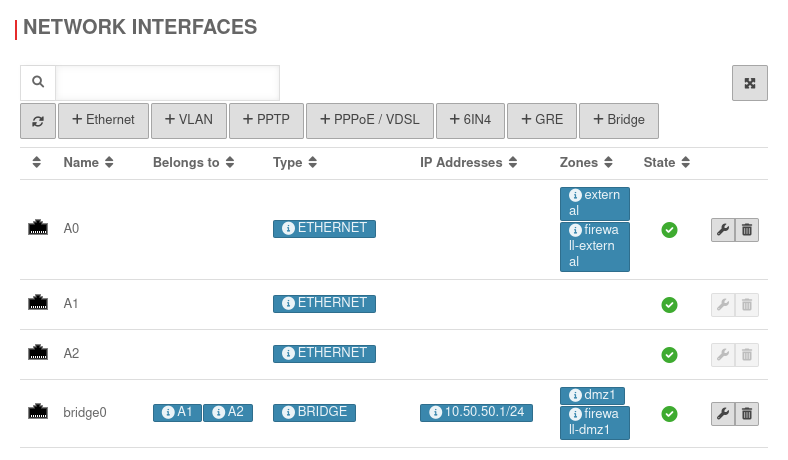 Configured bridge Configured bridge
| ||
Set up packetfilter rule
A packetfilter rule is required to allow network traffic between the interfaces belonging to the bridge.
A new network object is created for this purpose.
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewallPacketfilter 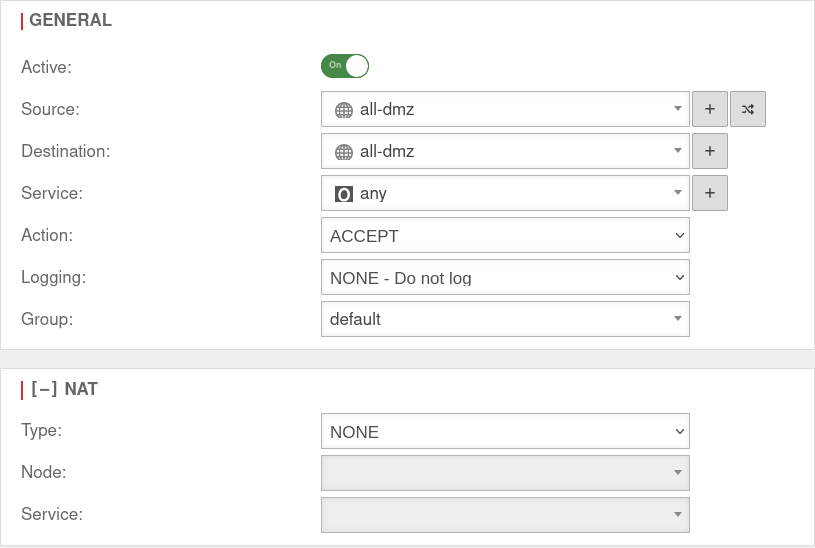 Packetfilter rule for the bridge
Packetfilter rule for the bridge
Finally, only the packetfilter rule with the network object just created has to be created.
At this point a any-rule may actually be used so that the interfaces can communicate completely with each other.
| # | Source | Destination | Service | NAT | Action | Active | |||
| 4 | Accept | On |
Network traffic to other networks (internal or external) should then be restricted by rules that work with the network objects that are mapped to the bridge zone.
Example rule to release only ftp services from the DMZ
| # | Source | Destination | Service | NAT | Action | Active | |||
| 4 | HNE | Accept | On |
The bridge setup is completed with .