Last adaptation to the version: 12.6.0
- Updated to Redesign of the webinterface
notemptyThis article refers to a Beta version
Introduction
The automatic or user-defined bandwidth management can be edited under .
Only one mode can be used at a time.
Depending on the application, it makes sense to select one of the two modes.
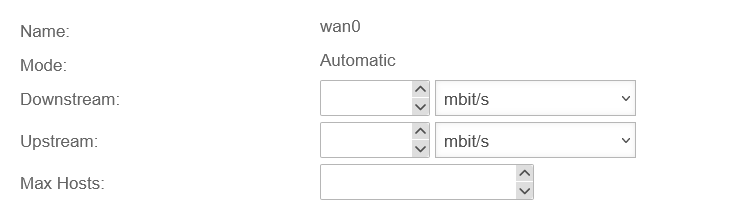
Mode: Automatic
In the "Automatic" mode, the prioritization information of the data packets is evaluated.
In addition, a bandwidth management can be done in this mode, where the maximum outgoing or incoming bandwidth can be set.
The note Recommended is located on the interface where the zone external is located. By clicking Edit the interface can be edited.
Once the settings have been saved, the data packets are now automatically classified on the basis of the ToS (Type of Service) or DSCP (Differentiated Services Code Point) information. The priority of the individual data packets is therefore determined by the applications.
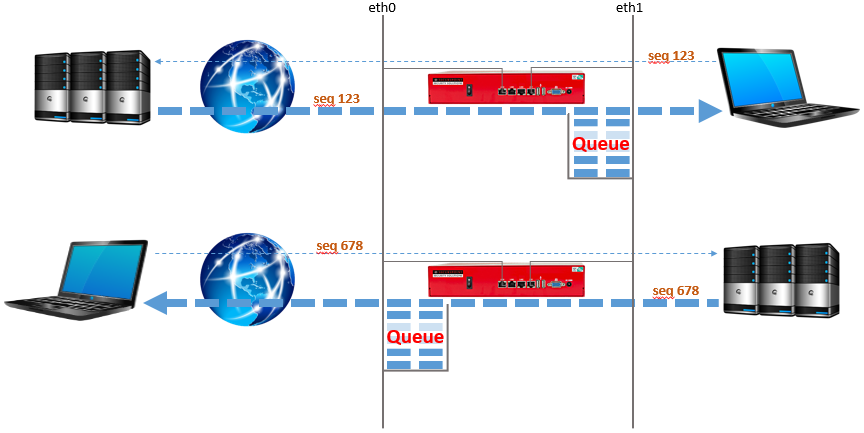
The traffic is split into three queues:
- High Priority
- Normal Priority
- Low Priority
The queues are then processed with different priority.
The allocation is based on the following criteria:
| Priorität: | ToS-Feld: |
|---|---|
| High (Minimum delay) | 0xb8, 0x10 |
| Low (Maximum data throughput) | 0x08 |
| Normal | Everything else |
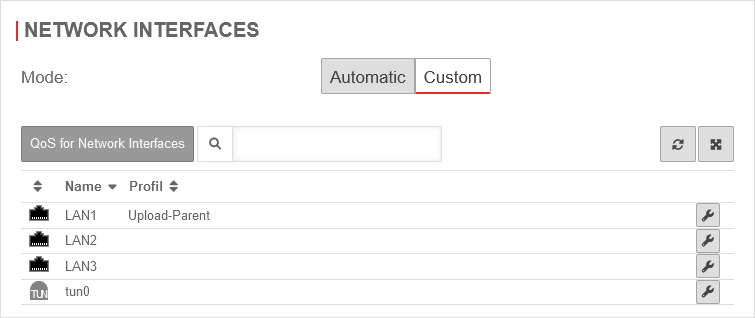
Mode: User-defined
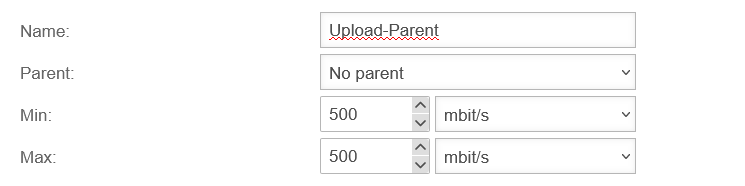
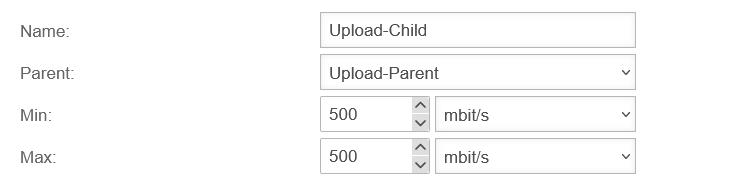
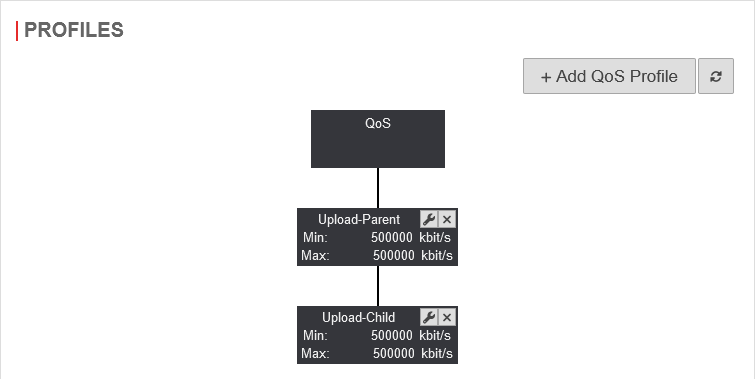
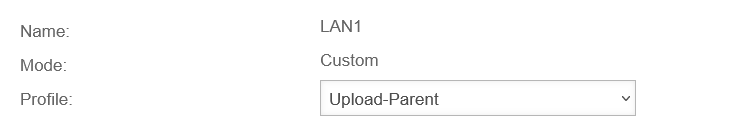
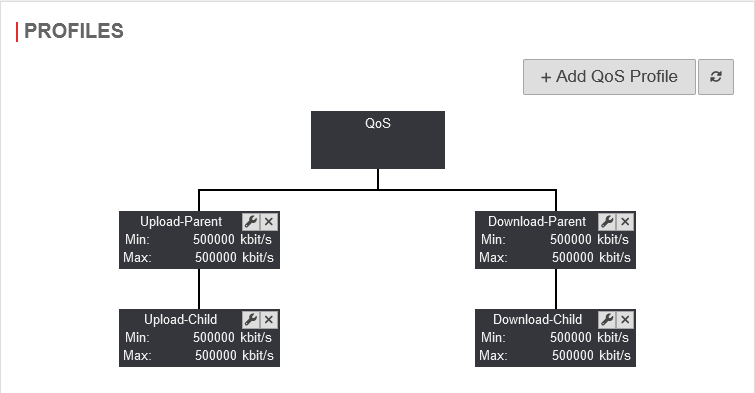
In " User-defined" mode, the bandwidth can be managed with the help of parent and child profiles. It is also possible to limit the bandwidth in the portfilter rules for specific services.
It is important that this is the actual bandwidth and not the data specified by the provider with the addition "up to". After all, the actual available bandwidth can be subject to strong fluctuations depending on the time of day, so the values that the provider specifies as the minimum available bandwidth must be entered here.
Profiles
Packetfilter rules
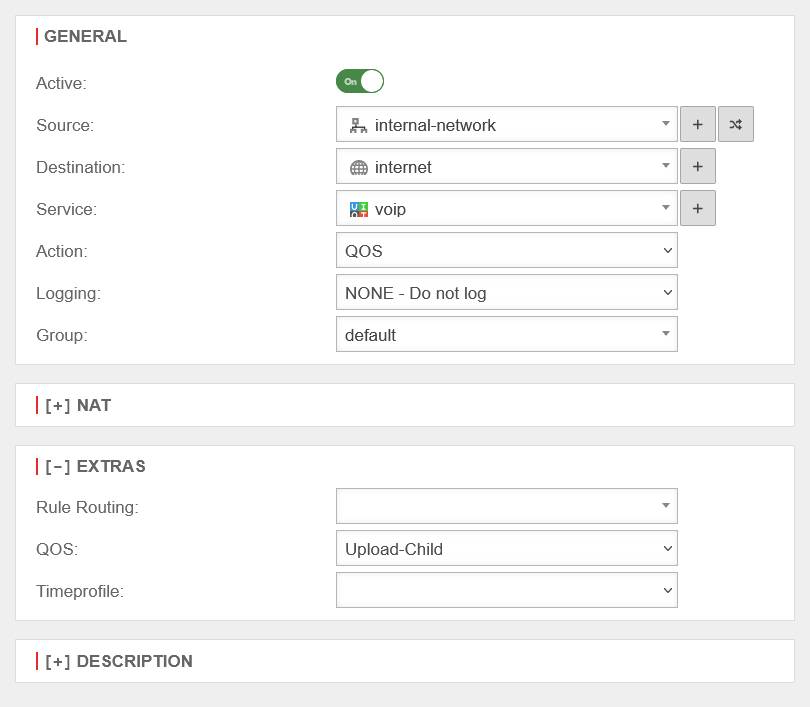
Finally, click button to create a suitable packetfilter rule.
A packet filter rule is required, which for QOS always has "internal-network" as the source and "internet" as the destination.
The packet filter rules for download and upload, if available, then look as follows:
| # | Source | Destination | Service | QoS | Action | Active | |||
| On | |||||||||
| On | |||||||||
In any case, additional packetfilter rules must be created or exist to allow traffic between source and destination with the required ports.
Help for this can be found under Packetfilter.