Last adaptation to the version: 12.6.0
- Updated to Redesign of the webinterface
notemptyThis article refers to a Beta version
Introduction
The zone concept defines through which interface an object (host or network) reaches the NextGen UTM.
To achieve this, it is bound to an interface in the network configuration, and in the rule set to a network object.
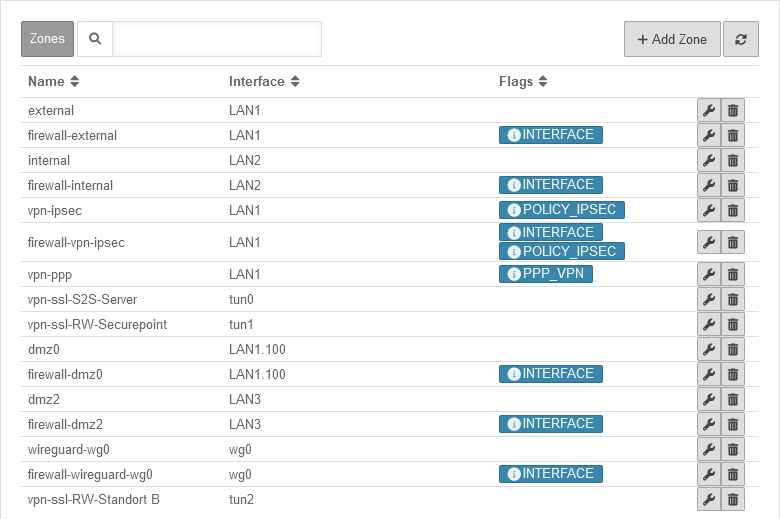
The zone concept
Create a new zone
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnNetworkZone Configuration 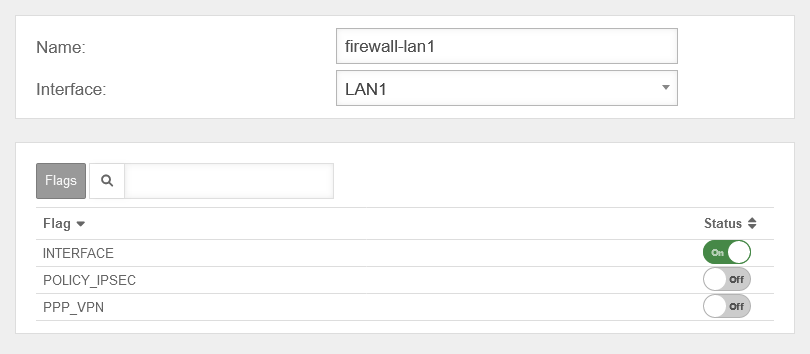 Add zone
Add zone
A new zone is created under by clicking the button.
A zone can be created only without, or with an already created interface.
The zones
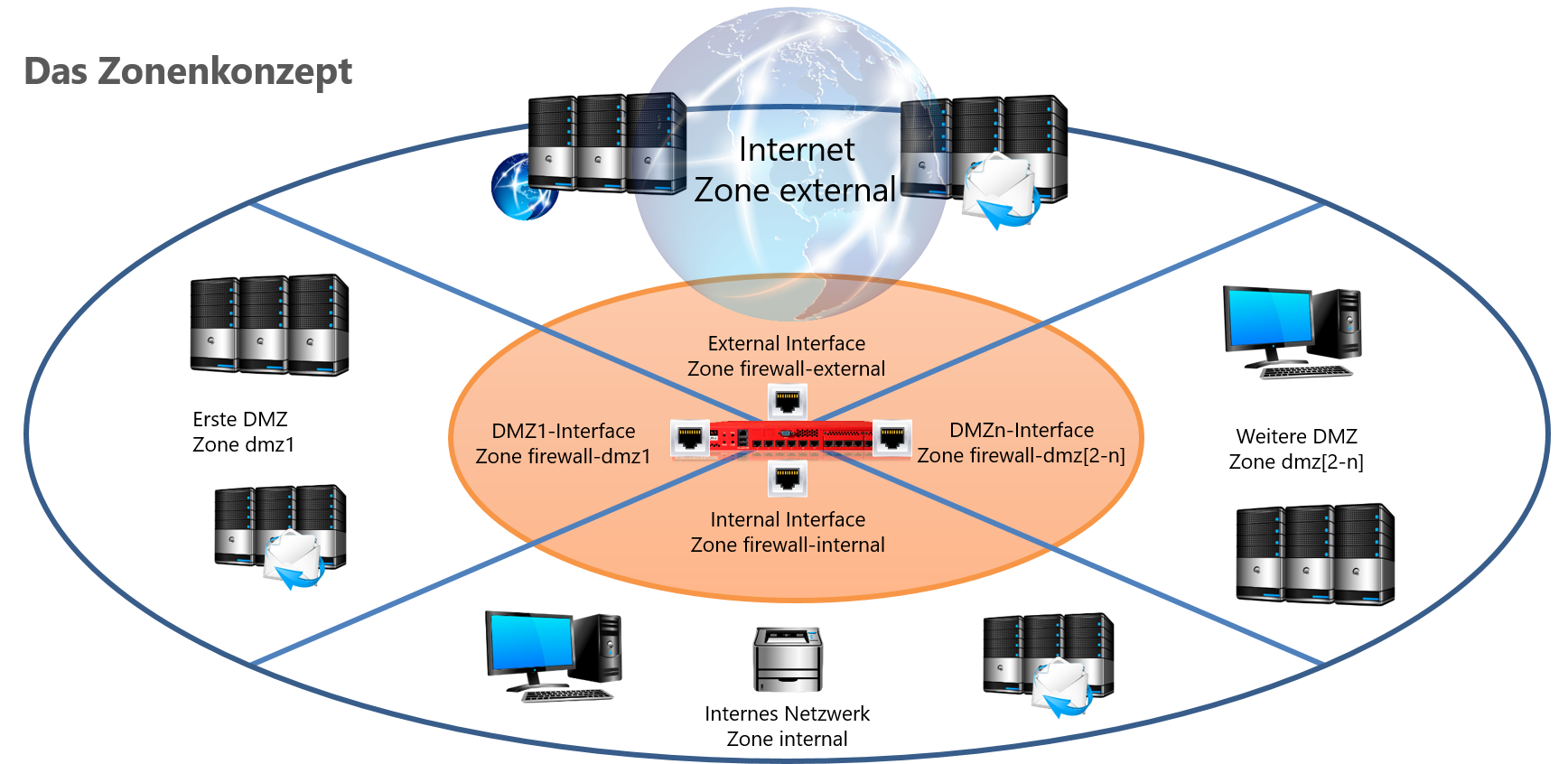
We distinguish between network, interface and VPN zones:
- Network zones distinguish the network segments, each of which is located behind an interface of the firewall.
- Interface zones distinguish the interfaces via which the different network zones are connected.
- VPN zones distinguish different networks that are connected via VPN connections.
The type of a zone is controlled by flags, which are defined when the zone is created.
The distinction for the user is simplified by naming conventions (interfaces: prefix "firewall-", VPN: prefix "vpn-").
By linking an object in the rule set to the interface via the zone, it is possible to ensure that a port filter rule only takes effect if not only the source, destination and service match the rule, but the connection is also made via the correct interfaces.
This prevents all attacks that involve IP spoofing. The assignment of an object to an interface is done by binding the zone to the interface on the one hand and the assignment of the network object to a zone on the other hand.
Examples:
Internal Network: internal
Internal Interface: firewall-internal
External Interface: firewall-external
Internet: external
Mailserver: internal
Webserver in the 1st DMZ: DMZ1
Remote IPSec subnet: vpn-ipsec
'Why is it necessary to distinguish between these different zones?"
Here is an example of a port filter rule:
If, for example, "www.ttt-point.de" is now entered into the browser, name resolution takes place before this connection is established.
Is the firewall DNS server is on the network, the workstation sends the DNS request to the firewall's internal interface.
This request must be allowed with a port filter rule:
Flags
IPv6
For new installations, IPv6 zones are no longer added. Existing zones also remain when upgrading firmware or importing a configuration.