Last adaptation to the version: 12.6.4
- Updated to Redesign of the webinterface
Introduction
HTTP/HTTPS requests are intercepted and processed by the HTTP proxy when Transparent Mode is enabled. (
For https requests, SSL interception must also be enabled.)
The HTTP proxy does not have to be configured in the client's settings.
If the HTTP/HTTPS server (destination of the HTTP/HTTPS request) can be reached via a VPN connection, these connections must be excluded from transparent mode, or the HTTP/HTTPS proxy must be adapted for the use of the VPN connection. This can be done either via an exception rule for transparent mode, or by setting the outgoing IP address of the HTTP/HTTPS proxy.
Scenario 1: Transparent exception rule
Area Transparent Mode button
If a VPN connection is to be excluded from transparent mode, a rule is added in the Transparent Mode tab.
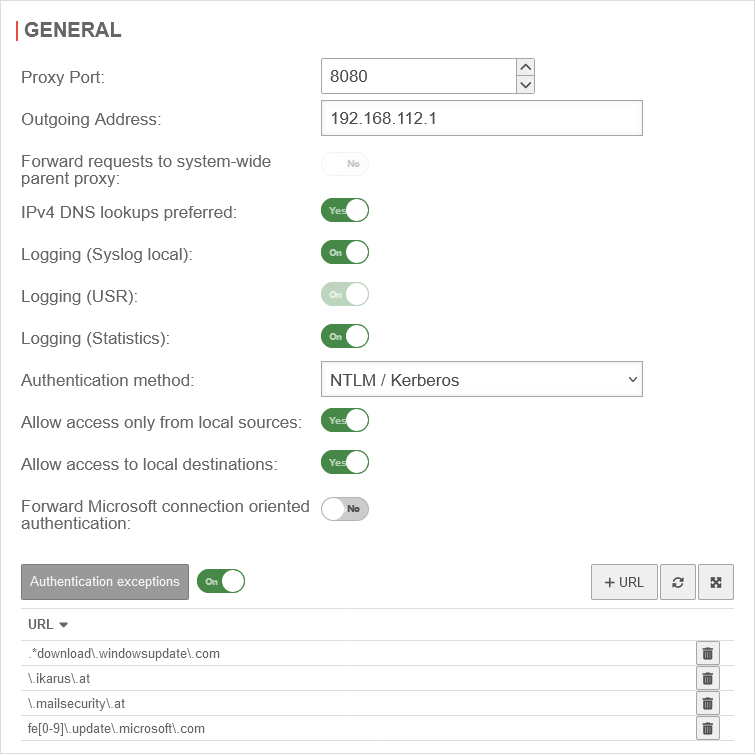
Scenario 2: Outbound proxy address
If the HTTP proxy is to be customized for use with the VPN connection, go to Area General.
Under
Advantages and disadvantages of both scenarios
Scenario 1: Transparent exception rule
Advantages:
- HTTP traffic is routed, the network of the remote terminal sees the IP address of the client
Disadvantages:
- The virus scanner in the HTTP proxy is not used for this connection
Scenario 2: Outbound proxy address
Advantages:
- The HTTP request can be scanned by the virus scanner for malicious code
Disadvantages:
- The network of the remote terminal only sees the IP address of the proxy.
- If there are rule and / or source routes for the network, the HTTP proxy is also affected by them