IKEv1 Troubleshooting
|
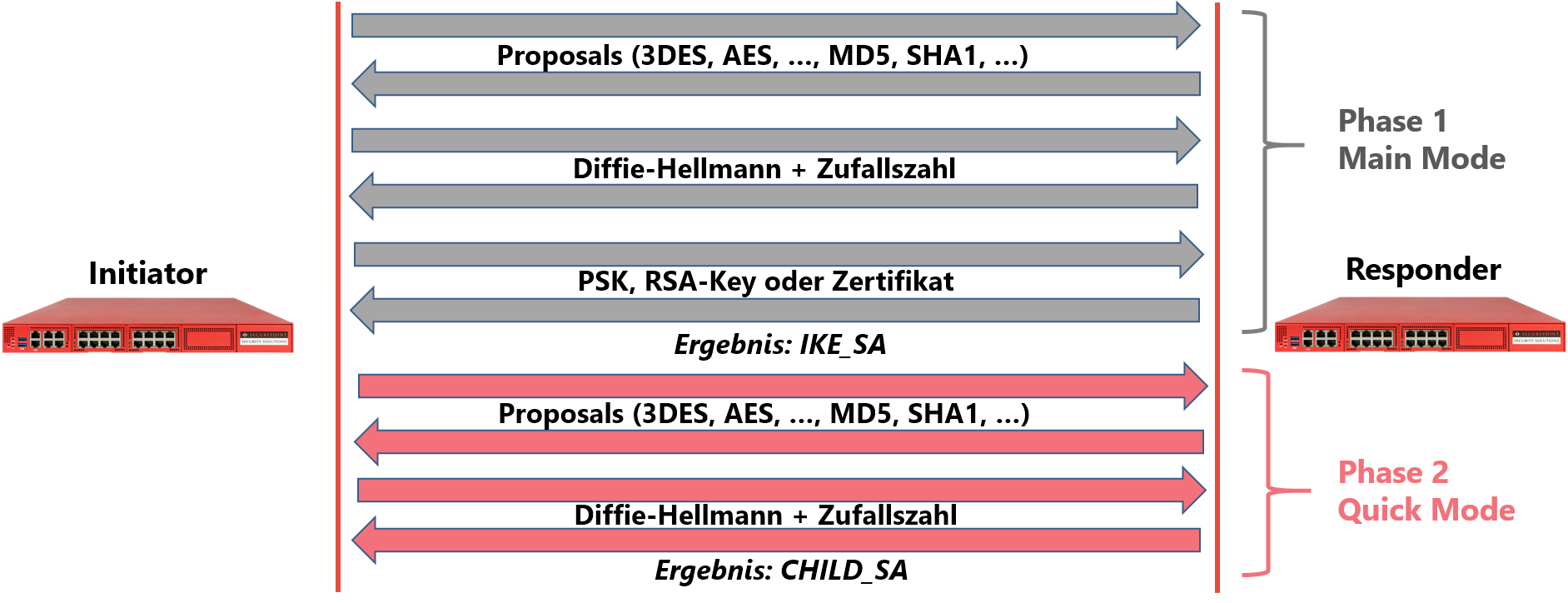
| The establishment of an IPSec connection using IKEv1 takes place in two phases. In phase 1, both gateways are authenticated against each other. This can be done in two different ways: The "Aggressive Mode" or the "Main Mode". The aggressive mode encrypts the Pre Shared Key (PSK) using a simple hash algorithm.
Apart from this PSK, no further identification is provided. This results in the following disadvantages:
- When several remote stations are connected, they cannot be distinguished from each other in phase 1. Therefore, the same PSK must be used in all connections. The probability of being compromised increases with the number of remote stations.
- The simple hash encryption of the PSK makes it vulnerable to dictionary attacks, and more so the simpler it is. Since no other identification feature is provided besides the PSK, such attacks can be carried out by any computer with Internet access.
For these reasons, the aggressive mode of IPSec does not find any use in connection with Securepoint NextGen UTM. Only the secure main mode is used. In addition to the PSK, this requires a further identification feature, the so-called ID. Furthermore, the transmission of the PSK is secured by the Diffie-Hellman key exchange method. This makes it mathematically impossible to intercept a transmitted key. In addition to PSKs, the main mode also allows RSA keys or X.509 certificates for authentication.
|

|
|
|
Phase 1
|
The normal connection setup
|
| If no errors occur in phase 1, this is indicated by an entry in the LiveLog that reports the successful establishment of an IKE_SA. If this entry is found in both the initiator's log and the responder's log, phase 1 has been configured without errors and any configuration error should be looked for in phase 2.
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
10[IKE] IKE_SA Standort_1_2[1] established between 198.51.100.75[198.51.100.75]...198.51.100.1[198.51.100.1]
|
|
|
False proposal
|
If both sides cannot agree on encryption parameters acceptable to both sides, the responder reports this in its livelog.
The initiator gets the message "NO_PROPOSAL_CHOSEN".
|
| Initiator-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
10[IKE] received NO_PROPOSAL_CHOSEN notify error
|
| Responder-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
05[CFG] selecting proposal:
|
| IPSec |
05[CFG] no acceptable ENCRYPTION_ALGORITHM found
|
| IPSec |
05[CFG] selecting proposal:
|
| IPSec |
05[CFG] received proposals: IKE: BLOWFISH_CBC_256 / HMAC_SHA2_512_256 / PRF_HMAC_SHA2_512 / MODP_8192
|
| IPSec |
05[CFG] configured proposals: IKE: AES_CBC_128 / HMAC_SHA2_256_128 / PRF_HMAC_SHA2_256 / MODP_2048, IKE: AES_CBC_128 / AES_CBC_192 / AES_CBC_256 / 3DES_CBC / CAMELLIA_CBC_128 / CAMELLIA_CBC_192 / CAMELLIA_CBC_256 / AES_CTR_128 / AES_CTR_192 / AES_CTR_256 / CAMELLIA_CTR_128 / CAMELLIA_CTR_192 / CAMELLIA_CTR_256 / HMAC_MD5_96 / HMAC_SHA1_96 / HMAC_SHA2_256_128 / HMAC_SHA2_384_192 / HMAC_SHA2_512 / AES_XCBC_96 / AES_CMAC_96 / PRF_HMAC_MD5 / PRF_HMAC_SHA1 / PRF_HMAC_SHA2_256 / PRF_HMAC_SHA2_512 / 256 / AES_XCBC_96 / AES_CMAC_96 / PRF_AES128_CMAC / MODP_2048 / MODP_2048_224 / MODP_2048_256 / MODP_1536 / MODP_3072 / MODP_4096 / MODP_8192 / MODP_1024 / MODP_1024_160 / ECP_256 / ECP_384 / ECP_512 / ECP_224 / ECP_192 / ECP_224_BP / ECP_256_BP / ECP_384_BP_ECP_512_BP , IKE: AES_GCM_8_128 / AES_GCM_8_192 / AES_GCM_8_256 / AES_GCM_12_128 / AES_GCM_12_192 / AES_GCM_12_256 / AES_GCM_16_128 / AES_GCM_16_192 / AES_GCM_16_256 / PRF_HMAC_MD5 / PRF_HMAC_SHA1 / PRF_HMAC_SHA2_256 / PRF_HMAC_SHA2_384 / PRF_HMAC_SHA2_512 / PRF_AES128_XCBC / PRF_AES128_CMAC / MODP_2048 / MODP_2048_224 / MODP_2048_256 / MODP_1536 / MODP_3072 / MODP_4096 / MODP_8192 / MODP_1024 / MODP_1024_160 / ECP_256 / ECP_384 / ECP__521 / ECP_224 / ECP_192 / ECP_224_BP / ECP_256_BP / ECP_384_BP / ECP_512_BP
|
| IPSec |
10[IKE] received proposals inacceptable
|
|
|
Incorrect remote gateway address
|
If the initiator attempts to establish a connection from a gateway address other than the one configured on the responder side, the responder cannot classify this connection. This is reported accordingly in the LiveLog.
The initiator gets the message NO_PROPOSAL_CHOSEN.
|
| Responder-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
11[CFG] looking for an ike config for 198.51.100.75...195.51.100.1
|
| IPSec |
11[IKE] no IKE config found for 198.51.100.75...195.51.100.1, sending NO_PROPOSAL_CHOSEN
|
|
|
Incorrect ID Initiator
|
If the initiator logs in with an identifier (ID) other than the one stored in the responder's configuration, the responder cannot determine a PSK configuration for this connection attempt and reports this accordingly in the LiveLog.
The initiator receives the error message AUTHENTICATION_FAILED.
|
| Initiator-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
09[IKE] received AUTHENTICATION_FAILED error notify
|
| Responder-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
07[CFG] looking for pre-shared key peer configs matching 198.51.100.75...198.51.100.1[blubb]
|
| IPSec |
07[IKE] no peer config found
|
|
|
Incorrect ID Responder
|
| If the responder reports with a different ID than in the initiator's configuration, then this is reported accordingly in the initiator's log.
|
| Initiator-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
05[IKE] IDir 'blubb' does not match to '198.51.100.75'
|
|
|
Incorrect PSK
|
| In contrast to older software versions, there is no clearly readable hint in the log for mismatched PSKs when using IKEv1. Indirectly, the indication of "malformed" packets points to this error.
|
| Initiator-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
15[IKE] message parsing failed
|
| IPSec |
15[IKE] ignore malformed INFORMATIONAL request
|
| IPSec |
15[IKE] INFORMATIONAL_V1 request with message ID 1054289493 processing failed
|
| Responder-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
14[IKE] message parsing failed
|
| IPSec |
14[IKE] ID_PROT request with message ID 0 processing failed
|
|
|
Incorrect RSA key initiator
|
If the initiator of the connection uses a different RSA key than the one set in the responder configuration, authentication cannot take place.
The initiator receives the error message "AUTHENTICATION_FAILED".
|
| Initiator-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
15[IKE] authentication of 'Filiale' (myself) succesful
|
| IPSec |
16[IKE] received AUTHENTICATION_FAILED error notify
|
| Responder-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
14[CFG] looking for RSA signature peer configs matching 198.51.100.75...198.51.100.1[Filiale]
|
| IPSec |
14[CFG] candidate "Standort1_4", match: 1/20/28 (me/other/ike)
|
| IPSec |
14[CFG] selected peer config "Standort1_4"
|
| IPSec |
14[CFG] using trusted certificate "Filiale"
|
| IPSec |
14[IKE] ignature validation failed, looking for another key
|
| IPSec |
14[IKE] no trusted RSA public key found for 'Filiale'
|
|
|
Incorrect RSA key responder
|
| If the responder uses a different RSA key than the one specified in the initiator's configuration, the authentication fails again on the initiator's side. The responder that has already established an IKE_SA is instructed to delete it again.
|
| Initiator-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
16[CFG] authentication of 'Filiale' (myself) succesful
|
| IPSec |
16[IKE] using trusted certificate "Zentrale"
|
| IPSec |
16[IKE] signature validation failed, looking for another key
|
| IPSec |
15[IKE] no trusted RSA public key found for 'Zentrale'
|
| Responder-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
10[CFG] looking for RSA signature peer configs matching 198.51.100.75...198.51.100.1[Filiale]
|
| IPSec |
10[CFG] candidate "Standort1_4", match: 1/20/28 (me/other/ike)
|
| IPSec |
10[CFG] selected peer config "Standort1_4"
|
| IPSec |
10[CFG] using trusted certificate "Filiale"
|
| IPSec |
10[IKE] authentication of 'Filiale' with RSA succesful
|
| IPSec |
10[IKE] authentication of 'Zentrale' (myself) succesful
|
| IPSec |
10[IKE] IKE_SA Standort1_4[1] established between 198.51.100.75[Zentrale]...198.51.100.1[Filiale]
|
| IPSec |
10[IKE] IKE_SA Standort1_4[1] established between 198.51.100.75[Zentrale]...198.51.100.1[Filiale]
|
| IPSec |
10[IKE] scheduling reauthentication in 2593s
|
| IPSec |
10[IKE] maximum IKE_SA lifetime 3133s
|
| IPSec |
13[IKE] received DELETE for IKE_SA Standort_4[1]
|
|
|
Phase 2
|
The normal connection setup
|
| If phase 2 is also configured correctly, the successful establishment of a CHILD_SA is documented in the livelog of both sides.
|
| Initiator-Log & Responder-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
05[IKE] CHILD_SA Zentrale_2{1} established with SPIs ca7520e3_i c562f9d6_o and TS 10.1.10.0/24 === 10.0.0.0/24
|
| IPSec |
05[IKE] CHILD_SA Zentrale_2{1} established with SPIs ca7520e3_i c562f9d6_o and TS 10.1.10.0/24 === 10.0.0.0/24
|
|
|
Incorrect subnet configuration
|
| If the configured subnets (the so-called traffic selectors) do not match in phase 2 of the initiator and responder, no tunnel can be set up on the previously established IKE_SA, i.e., no CHILD_SA is established. This information can be found in the responder's livelog.
|
| Initiator-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
13[CFH] proposing traffic selectors for us:
|
| IPSec |
13[CFG] 10.1.0.0/24
|
| IPSec |
13[CFG] proposing traffic selectors for other:
|
| IPSec |
13[CFG] 11.0.0.0/24
|
| IPSec |
05[IKE] received INVALID_ID_INFORMATION error notify
|
| Responder-Log
|
| Service |
Message
|
| IPSec |
11[CFG] looking for a child config for 11.0.0.0/24 === 10.1.0.0/24
|
| IPSec |
11[CFG] proposing traffic selectors for us:
|
| IPSec |
11[CFG] 10.0.0.0/24
|
| IPSec |
11[CFG] proposing traffic selectors for other:
|
| IPSec |
11[CFG] 10.1.0.0/24
|
| IPSec |
11[IKE] no matching CHILD_SA config found
|
|
|