notempty
- Hide IKEv1 L2TP. Display only with special activation
- IKEv2 Phase 1 updated
- Copy psk to clippboard
- Note on Config_mode for NCP or Greenbow clients
- Changes in the arrangement of the configuration steps in the assistant (v12.2.4)
- Note for the use of MOBIKE (v12.2.4)
- DHCP configurable for IPSec in phase 2 (v12.2.4)
Introduction
A Roadwarrior connection connects individual hosts to the local network. This allows, for example, a field service employee to connect to the network of the headquarters.
This step-by-step guide shows how to configure an end-to-site connection. The selected connection type is native IPSec with IKEv1.
For native IPSec connections with IKEv1 the client needs a separate program.
Configuration of a native IPSec connection
New connections can be added in the menu Tab Connections with Button
Wizard
Connection Type Step 1 - Connection Type
| |||
| Caption | Value | Description | 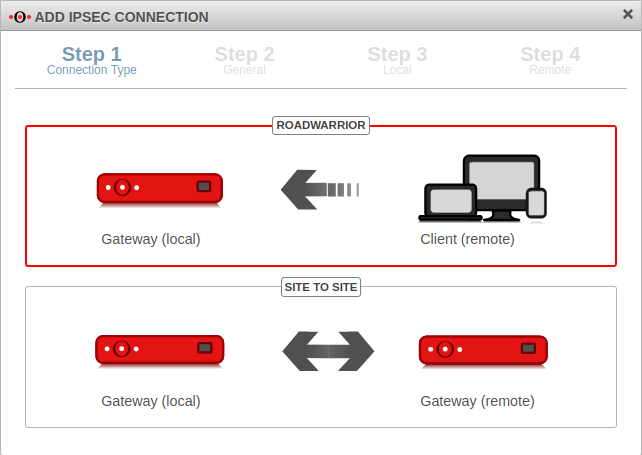 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selection of the connection type | The following connections are available:
|
For the configuration of an E2S / End-to-Site-connection Roadwarrior is to be selected. | |
General Step 2 - General
| |||
| Name: | IPSec Roadwarrior | Name for the connection | 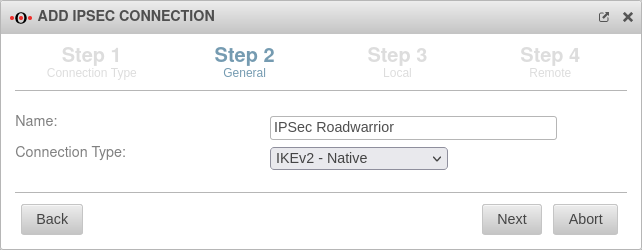 |
| Connection Type: | Possible connection types: notempty New as of: 12.4 The connection type IKEv1 - L2TP can only be selected if L2TP is set to Autostart or explicitly enabled in the admin interface. Enable L2TP under: Tab Hidden functions Enable L2TP: Ja Activate hidden menu buttons: Ctrl + Alt + A Please note which type is supported by the operating system | ||
| notempty In setup step 2, two fundamentally different connection types are available for selection. Depending on whether a connection type of IKEv1, or IKEv2 is selected, the upcoming setup steps 3 and 4 differ:
| |||
Local – IKEv1 Step 3 - Local - IKEv1
| |||
| Local Gateway ID: | The gateway ID is included in the authentication. This can be an IP address, a host name or an interface. Automatically filled in when an X.509 certificate is selected |
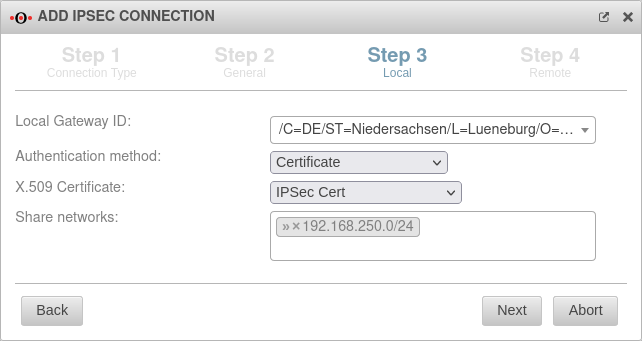 | |
| Authentication method: | A pre-shared key is in use | ||
| An existing certificate is being used | |||
| An existing private RSA key is in use | |||
| Pre-Shared Key: | An arbitrary PSK | ||
| X.509 Certificate: Only for authentication method
|
Selection of a certificate | ||
| Private RSA key: | Selecting an RSA key | ||
| Share networks: Only for IKEv1 - Native |
192.168.250.0/24 | Enable networks for the IPSec connection | |
Local – IKEv2 Step 3 - Local - IKEv2
| |||
| Local Gateway ID: | The gateway ID is included in the authentication. This can be an IP address, a host name or an interface. Automatically filled in when an X.509 certificate is selected |
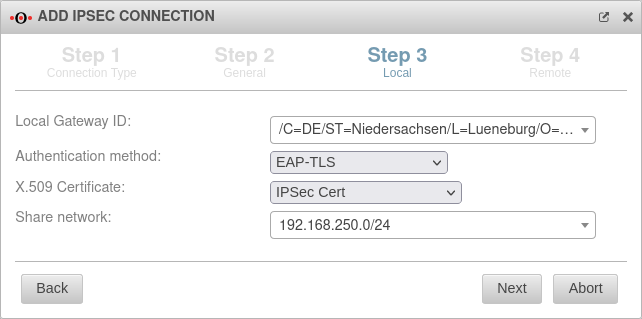 | |
| Authentication method: | A pre-shared key is in use | ||
| An existing certificate is being used | |||
| An existing private RSA key is in use | |||
| Only with IKEv2 | EAP-TLS is used. Required for MSCHAPv2. | ||
| Pre-Shared Key: | An arbitrary PSK | ||
| Creates a very strong key | |||
| Copies the PSK to the clipboard | |||
| X.509 Certificate: Only for authentication method
|
Selection of a certificate | ||
| Private RSA key: | Selecting an RSA key | ||
| Share networks: | 192.168.250.0/24 | Enable networks for the IPSec connection | |
Remote terminal – IKEv1 Step 4 - Remote terminal - IKEv1
| |||
| Public RSA key: Only for authentication method RSA |
The required public RSA key of the remote terminal | 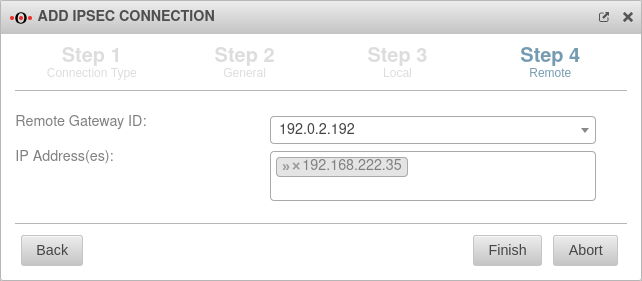 | |
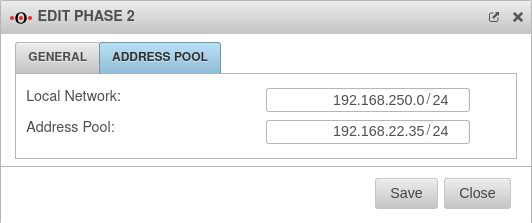
| IP address / pool: Only for IKEv1 - XAuth |
192.168.22.35/24 | IP address, or pool for establishing the IPSec connections | |
| Open user dialog after completion: Only with
|
Yes | Opens the user dialog of the UTM after the wizard is done. For the establishment of this connection the input of user data is necessary. The user needs the necessary rights. | |
| Remote Gateway ID: Only for IKEv1 - Native |
192.0.2.192 or My_Roadwarrior |
If more than one IPSec connection is established, a unique ID should be entered here. The password of incoming connections is validated against the ID of the IPSec connection. If no IP address is specified as ID, further settings must be made for site-to-site connections. | |
| IP Address(es): Only for IKEv1 - Native |
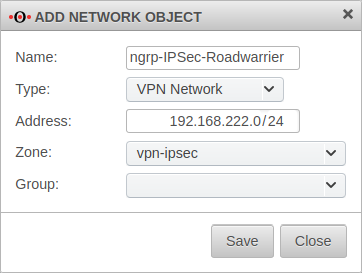
192.168.222.35 | Additional IP address for the Roadwarrior with which the IPSec connection is established.
For this example, after the wizard has finished, the ip-address just dedicated is edited and for the Remote network the value 192.168.222.0/24 is entered. | |
Remote terminal – IKEv2 Step 4 - Remote terminal - IKEv2
| |||
| Public RSA key: Only for authentication method RSA |
The required public RSA key of the remote terminal | 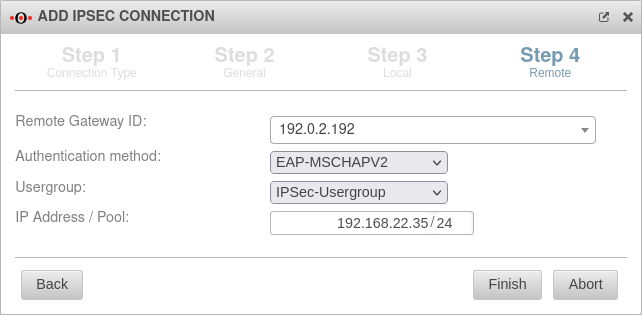 | |
| IP address / pool: | 192.168.22.35/24 | IP address, or pool for establishing the IPSec connections | |
| Authentication method: Only for authentication method
|
An existing certificate is being used | ||
| EAP-MSCHAPV2 is in use | |||
| EAP-TLS is used. Required for MSCHAPv2. | |||
| X.509 Certificate: Only for authentication method
|
The certificate for the remote terminal Two different certificates must be selected for the local and remote side. | ||
| User groups: Only for EAP-MSCHAPv2 |
Selection of the authorized user group. This must be created beforehand. | ||
| Exit the setup wizard with | |||
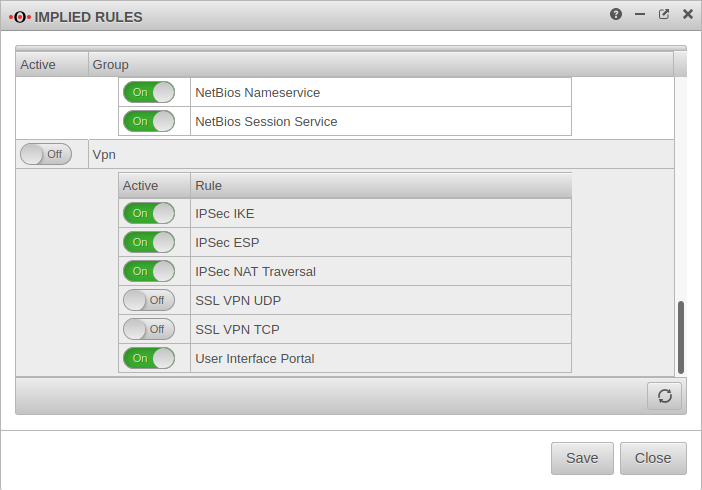
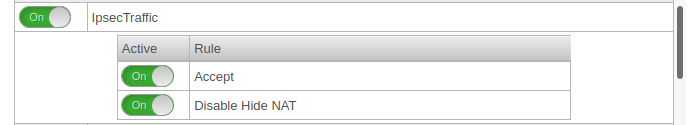
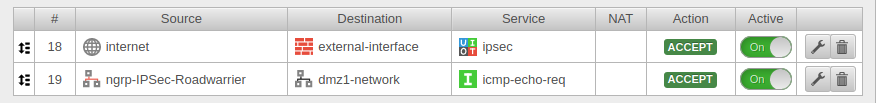
Set of rules
To grant access to the internal network, the connection must be allowed.
Now a connection with a Roadwarrior can be established.
A client may have to be used for this. It must be ensured that the parameters on both sides are identical in all phases of the connection.
Necessary changes, when using an NCP client:
- UTM
- Diffie-Hellman Group (Phase 1)
- DH-Group (PFS) (Phase 2)
or
- NCP- or Greenbow-Client:
- IKE-DH-Group
- NCP- or Greenbow-Client:
- Exchange mode: Main Mode (IKEv1)
- Activate Config_mode
Additional settings
In addition to the settings that have already been set in the wizard, further parameters can be configured:
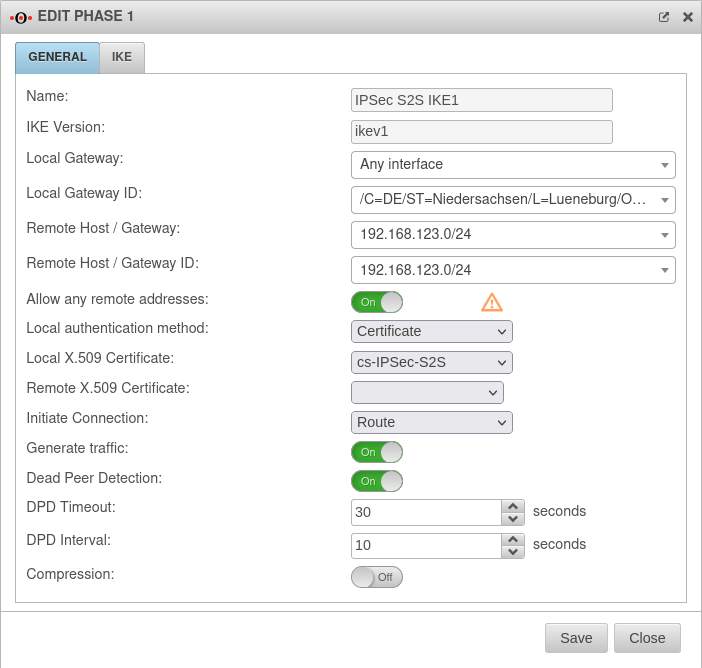
IKEv1
Phase 1 | |||
Tab Connections Button GeneralTab General | |||
| Caption | Value | Description | 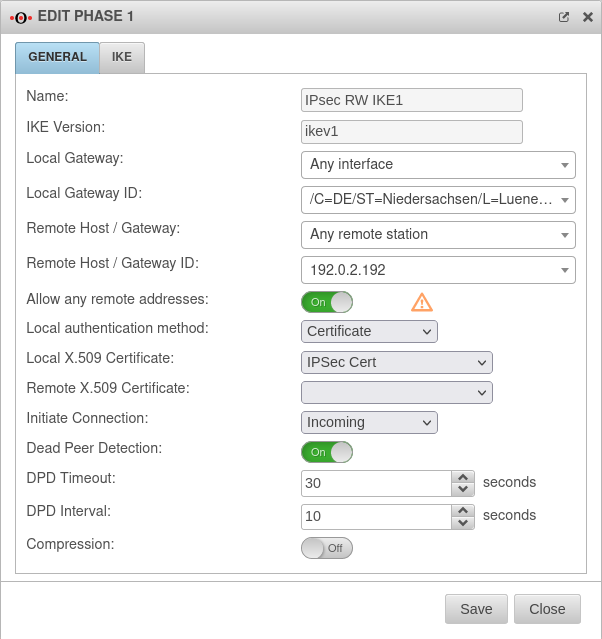 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allow any remote addresses: | On Default |
Disable this option for site-to-site connections with DynDNS hosts if multiple IPsec connections with a priori unknown addresses (DynDNS S2S, Roadwarrior) are configured. | |
| Initiate Connection: |
The tunnel is initiated by the UTM even if no packets are sent. Incoming requests are accepted. | ||
| Default if Remote Host is any | The UTM accepts incoming tunnel requests. No outgoing connection is created. | ||
| Default if Remote Host known | The tunnel is initiated by the UTM only when packets are to be sent. Only set as default value if Any remote station is not selected as Remote Host / Gateway.
| ||
| Deactivates the tunnel | |||
| Dead Peer Detection: | On | Checks at a set interval whether the tunnel still exists. If the tunnel was terminated unexpectedly, the SAs are dismantled. (Only then it is also possible to reestablish a new tunnel). | |
| DPD Timeout: | 30 seconds | Period before the state under Startup behavior is restored. The same values are used here as for regular packets. | |
| DPD Interval: | 10 seconds | Testing interval | |
| Compression: | Off | Compression is not supported by all remote stations | |
Tab IKE Settings that must be identical in the UTM and in the client: IKE | |||
| Caption | Default-Werte UTM | Default-Werte NCP-Client | 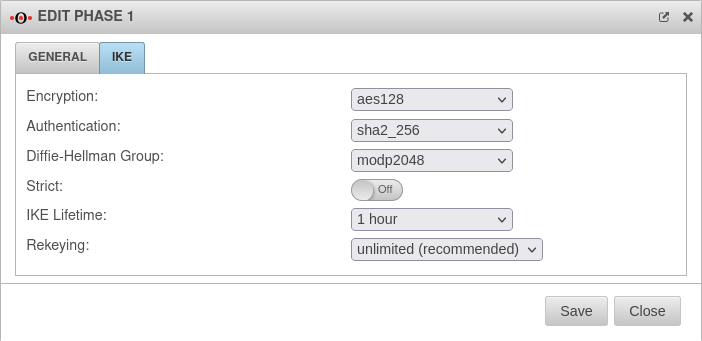 |
| Encryption: | AES 128 Bit | ||
| Authentication: | Hash: SHA2 256 Bit | ||
| Diffie-Hellman Group: | IKE DH-Grupe: DH2 (modp1024) | ||
| Tab IKE More settings: | |||
| Caption | Value | Description | |
| Strict: | Off | The configured parameters (authentication and encryption algorithms) are preferred for connections | |
| On | No further proposals are accepted. A connection is only possible with the configured parameters. | ||
| IKE Life time: | Validity period of the Security Association: Agreement between two communicating entities in computer networks. It describes how the two parties apply security services to communicate securely with each other. When using multiple services, multiple security connections must also be established. (Source: Wikipedia 2022) in phase 1 | ||
| Rekeying: | Number of attempts to establish the connection (initial or after abort). For E2S connections (Roadwarrior), the setting 3 times can avoid endless attempts to connect to devices that are not correctly logged out. | ||
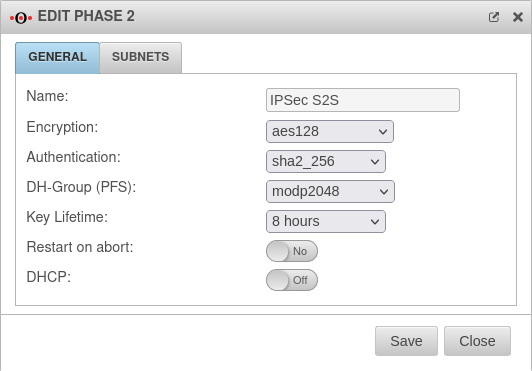
Phase 2 | |||
Tab Connections Button GeneralTab General : Settings that must be identical in the UTM and in the client: | |||
| Caption | Default-Werte UTM | Default-Werte NCP-Client | 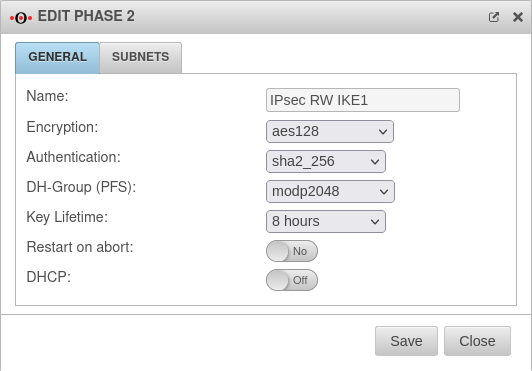 |
| Encryption: | AES 128 Bit | ||
| Authentication: | SHA2 256 Bit | ||
| Diffie-Hellman Group: | IKE DH-Grupe: DH2 (modp1024) | ||
| As of UTM version 12.2.4, there may currently be difficulties with key exchange in phase 2 for DH groups from modp6144. | |||
| Schlüssel-Lebensdauer: | Validity period of the key in phase 2 | ||
| Austausch-Modus | Main Mode (nicht konfigurierbar) | Aggressive Mode (IKEv1) The UTM does not support Aggressive Mode for security reasons. | |
Tab General: More settings | |||
| Restart on abort: | No | If the connection was terminated unexpectedly, activating will restore the state configured under Startup behavior in phase 1. | |
| DHCP: New as of 12.2.4 |
Out | When enabled (On), clients receive IP addresses from a local network. | |
Troubleshooting
Detailed Troubleshooting instructions can be found in the Troubleshooting Guide If an email address should be used as gateway ID, it is necessary to insert a double @@ in front of the ID (mail@... becomes @@mail@...). Otherwise the ID will be treated as FQDN
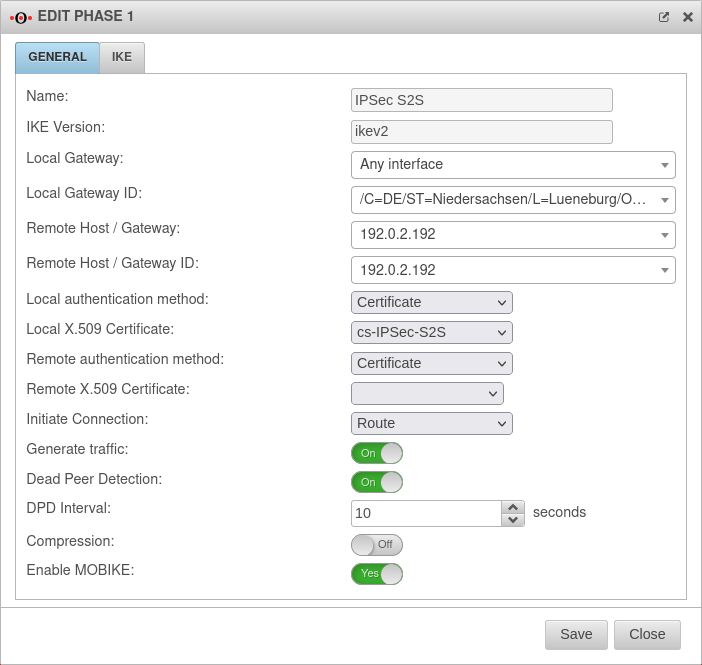
IKEv2

Phase 1 | |||
Tab Connections Button GeneralTab General | |||
| Caption | Value | Description | 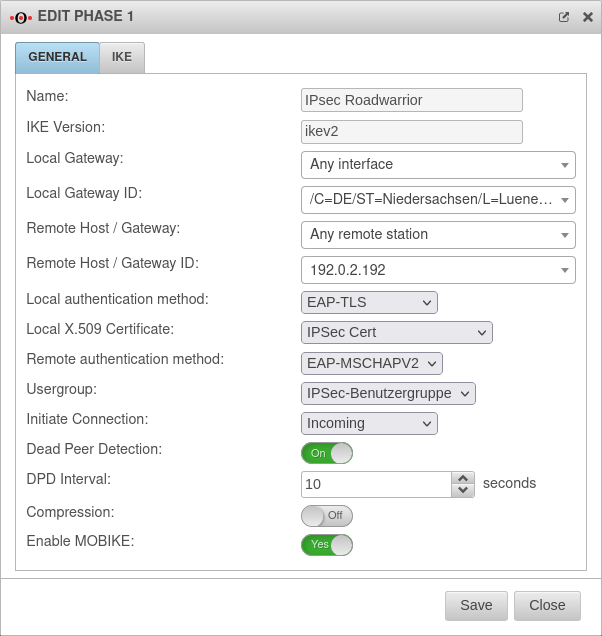 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiate Connection: |
The tunnel is initiated by the UTM even if no packets are sent. Incoming requests are accepted. | ||
| Default if Remote Host is any | The UTM accepts incoming tunnel requests. No outgoing connection is created. | ||
| Default if Remote Host known | The tunnel is initiated by the UTM only when packets are to be sent. Only set as default value if Any remote station is not selected as Remote Host / Gateway.
| ||
| Deactivates the tunnel | |||
| Dead Peer Detection: | On | Checks at a set interval whether the tunnel still exists. If the tunnel was terminated unexpectedly, the SAs are dismantled. (Only then it is also possible to reestablish a new tunnel). | |
| DPD Timeout: | 30 seconds | Period before the state under Startup behavior is restored. The same values are used here as for regular packets. | |
| DPD Interval: | 10 seconds | Testing interval | |
| Compression: | Off | Compression is not supported by all remote stations | |
| Enable MOBIKE: New as of 12.2.4 |
Yes Default |
Used to deactivate the MOBIKE option Deactivation prevents encrypted data from a remote station from being additionally encapsulated in 4500udp, which leads to problems in communication. | |
Tab IKE Settings that must be identical in the UTM and in the client: IKE | |||
| Caption | Default-Werte UTM | Default-Werte NCP-Client | 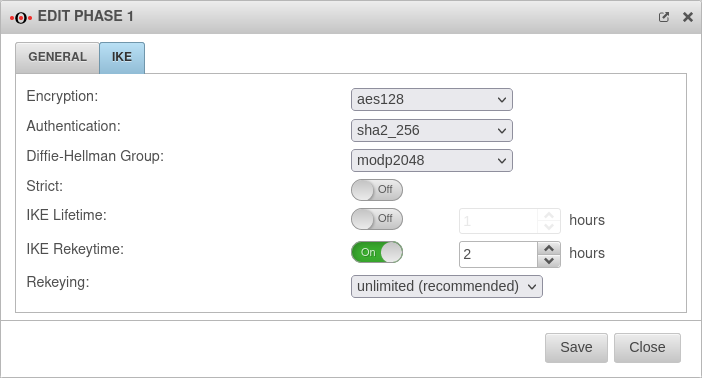 |
| Encryption: | AES 128 Bit | ||
| Authentication: | Hash: SHA2 256 Bit | ||
| Diffie-Hellman Group: | IKE DH-Grupe: DH2 (modp1024) | ||
| Tab IKE More settings: | |||
| Caption | Value | Description | |
| Strict: | Off | The configured parameters (authentication and encryption algorithms) are preferred for connections | |
| On | No further proposals are accepted. A connection is only possible with the configured parameters. | ||
| IKE Life time: | Out Neue Option. Default : Aus 3 hours |
Validity period of the Security Association: Agreement between two communicating entities in computer networks. It describes how the two parties apply security services to communicate securely with each other. When using multiple services, multiple security connections must also be established. (Source: Wikipedia 2022) in phase 1 Can be activated Vorlage:ButtonOn in addition to IKE Rekeytime. Automatically activated when IKE Rekeytime is deactivated. | |
| IKE Rekeytime: New as of: v12.4 |
On 2 hours | The validity period in which the connection is established (initial or after termination) | |
| Rekeying: | Number of attempts to establish the connection (initial or after abort). For E2S connections (Roadwarrior), the setting 3 times can avoid endless attempts to connect to devices that are not correctly logged out. | ||
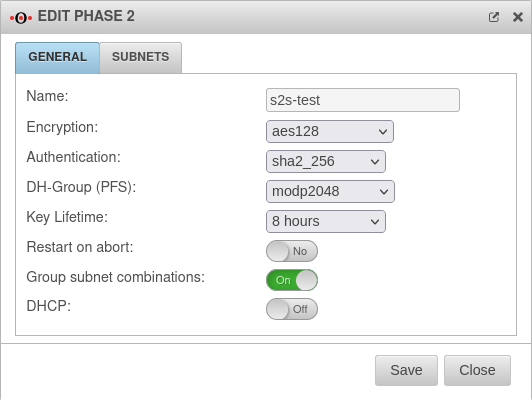
Phase 2 | |||
Tab Connections Button GeneralTab General : Settings that must be identical in the UTM and in the client: | |||
| Caption | Default-Werte UTM | Default-Werte NCP-Client | 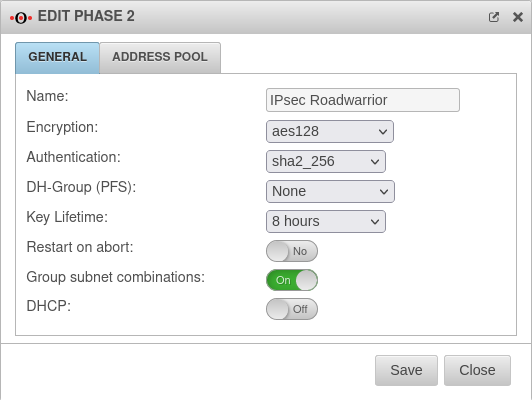 |
| Encryption: | AES 128 Bit | ||
| Authentication: | SHA2 256 Bit | ||
| Diffie-Hellman Group: | IKE DH-Grupe: DH2 (modp1024) | ||
| As of UTM version 12.2.4, there may currently be difficulties with key exchange in phase 2 for DH groups from modp6144. | |||
| Schlüssel-Lebensdauer: | Validity period of the key in phase 2 | ||
| Austausch-Modus | Main Mode (nicht konfigurierbar) | Aggressive Mode (IKEv1) The UTM does not support Aggressive Mode for security reasons. | |
Tab General: More settings | |||
| Restart on abort: | No | If the connection was terminated unexpectedly, activating will restore the state configured under Startup behavior in phase 1. | |
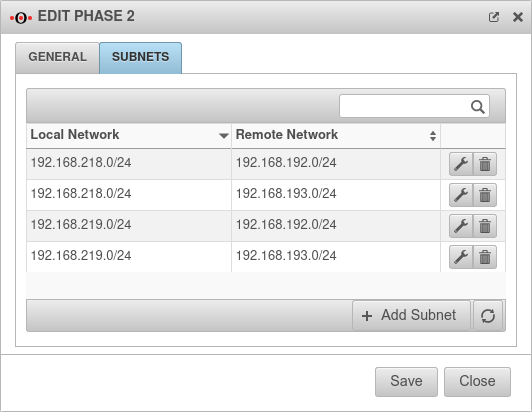
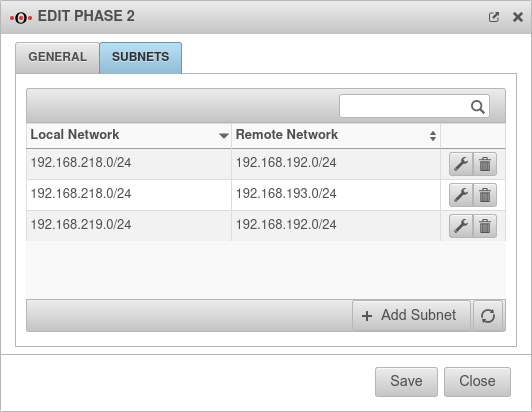
| Group subnet combinations: | Yes |
If more than one network is configured on the local side or at the remote gateway, a separate SA is negotiated for each subnet combination when it is deactivated. This results in numerous subnet combinations and thus many SAs, especially with multiple subnets, and leads to limitations and losses in the stability of the connections due to the design of the IPSec protocol. | |
| DHCP: New as of 12.2.4 |
Out | When enabled (On), clients receive IP addresses from a local network. | |
Troubleshooting
Detailed Troubleshooting instructions can be found in the Troubleshooting Guide If an email address should be used as gateway ID, it is necessary to insert a double @@ in front of the ID (mail@... becomes @@mail@...). Otherwise the ID will be treated as FQDN