Last adaptation to the version: 12.6.1
- Simplified rule in the DNS server network for SSL-VPN and WireGuard connections 04.2024
- Updated to Redesign of the webinterface
- Packetfilter rule Source and destination corrected
- 12.2024
- Position of the section on WireGuard transfer network corrected
- Hint for DNS resolving with WireGuard 10.2024
Introduction
In this scenario, the UTM and clients of a remote site are to be connected to the domain at the main site.
- All DNS requests for the domain to the DNS server, through the VPN tunnel, are forwarded to the main site.
- The UTM shall provide DNS for the clients in the remote site.
- Requests for the domain network shall be forwarded in the VPN tunnel to the DNS server in the main site.
Creating the DNS Relay Zone
Set Firewall as Namesever
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnNetwork 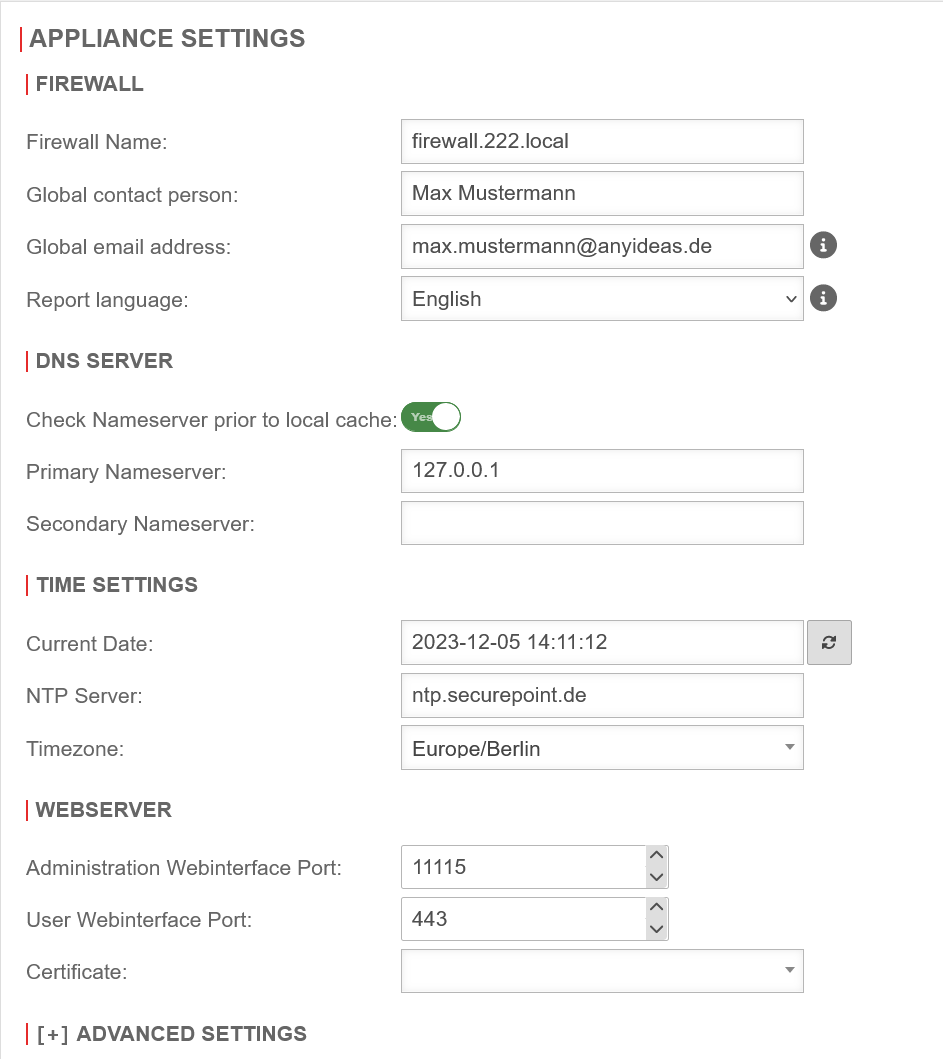 Nameserver IP
The first step is to define the UTM itself as the nameserver of the firewall.
Nameserver IP
The first step is to define the UTM itself as the nameserver of the firewall.
- Configuration under Area Server settings section DNS Server
- Field Primary nameserver set the IP to 127.0.0.1 (localhost) as IP.
- Save with
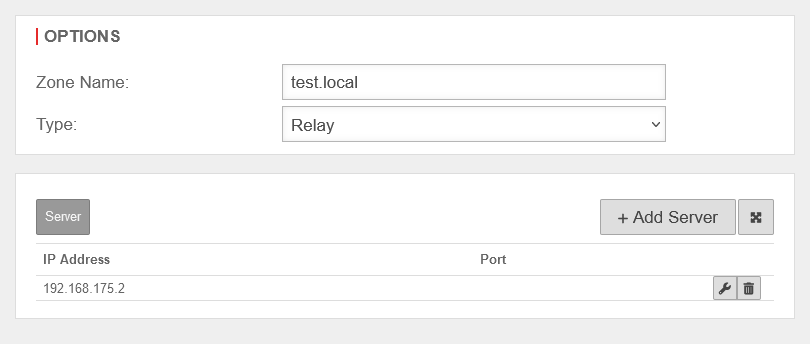
Create DNS Relay
Area Zones
The next step is to create a relay zone.
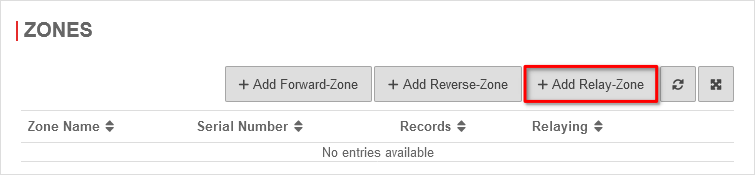
- Open the Zones tab in the Nameserver window.
- Click on the button to create a new relay zone
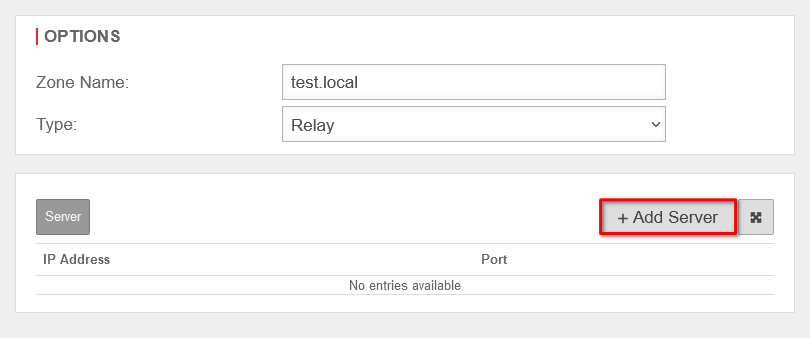
After creating the relay zone, the firewall forwards all requests to the DNS server at the main site on the domain network.
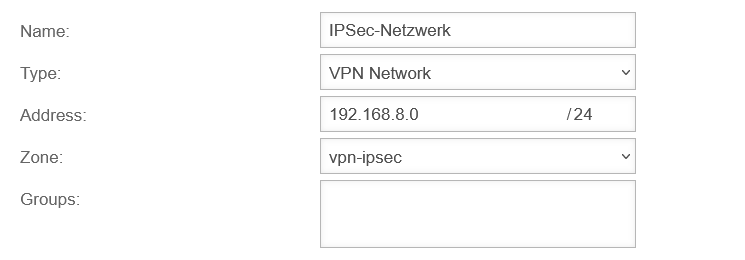
DNS Relay for an IPSec Site-to-Site Tunnel
In order to forward internal domain requests to a remote nameserver that is on an IPSec network, note that by default, all direct requests addressed to external nameservers are sent from the firewall with the external IP. However, a public IP is not routed into an IPSec tunnel.
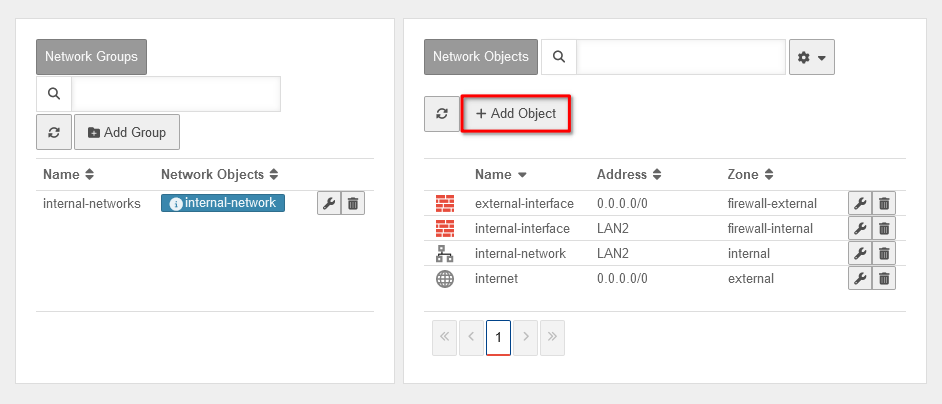
Create network object
The packet filter rules in the Implied rules are automatically activated. This means that no network object is yet available for the IPSec network.
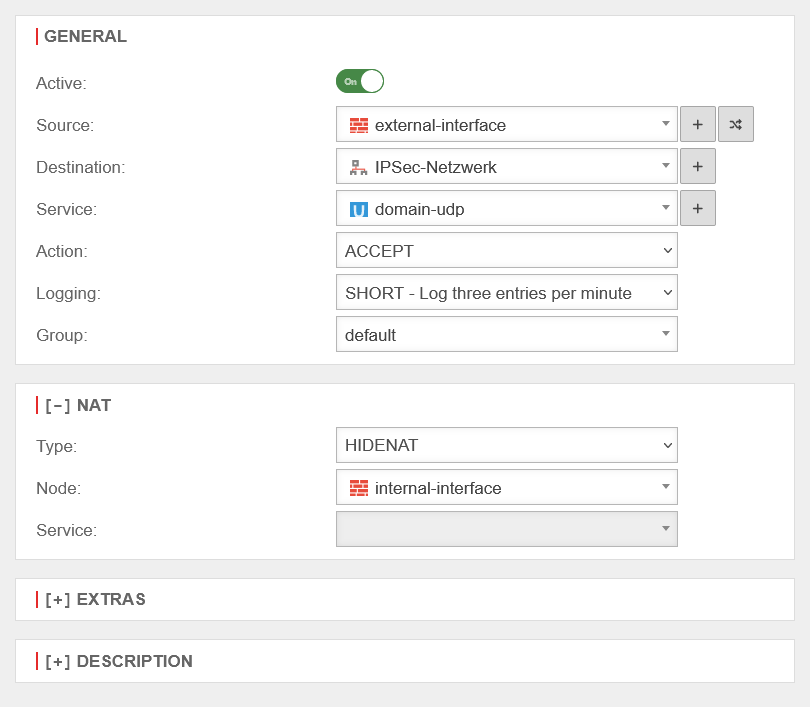
Create rule
The last step is to create a firewall rule with a Hide NAT.
This causes DNS forwarding to also go to the tunnel and not directly to the Internet.
With this rule, all domain UDP requests made through the firewall to the remote nameserver are natted over the IP of the internal interface and can thus be routed into the IPSec tunnel.
DNS Relay for an OpenVPN Site-to-Site Tunnel
In order to forward internal domain requests to a remote nameserver located in an OpenVPN network, note that by default all direct requests directed to external nameservers are send from the firewall with the external IP. However, a public IP is not routed into an OpenVPN tunnel.
Central configuration in the DNS server network
Simplified solution with packet filter rule in the network of the DNS server
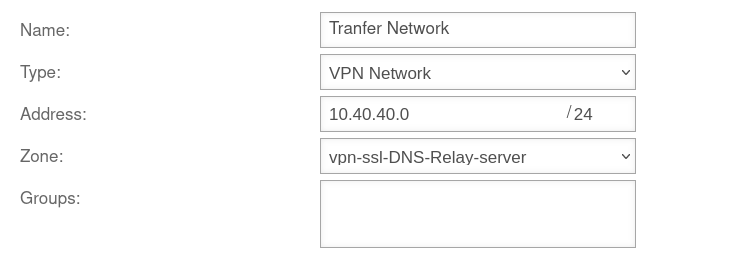
If there are several branch offices, the simplest option is often to release the entire transfer network on the server side. This requires a packetfilter rule on the UTM in the DNS server network.
Creating the network object for the transfer network
UTM im DNS-Server Netzwerk Box Network Objects button
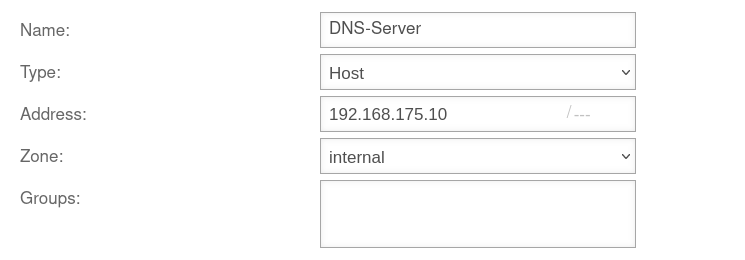
Network object DNS server
A network object for the DNS server (type: Host) should already exist.
If not, it must also be created.
UTM in the DNS server network Box Network Objects button
Create rule
Decentralized configuration on each S2S client
If a central configuration in the DNS server network is not desired or possible, a NAT rule can be created on each S2S client.
Create zone
UTM in the S2S client network
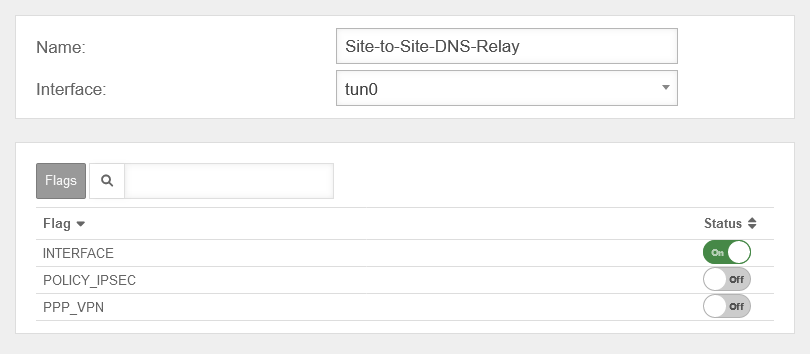
In order to route the DNS requests into the OpenVPN tunnel, a new interface zone must be created on the UTM.
A new zone is created with the button.
Create Open-VPN network objects
UTM in the S2S client network
The packet filter rules in the Implied rules are automatically activated. This means that no network object is yet available for the Open-VPN network.
Create rule
UTM in the S2S client network button
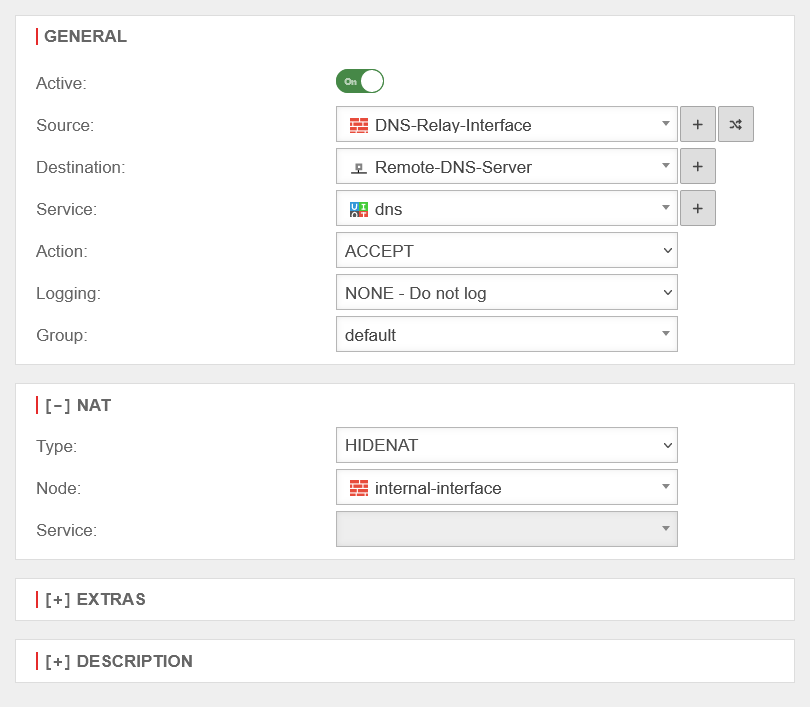
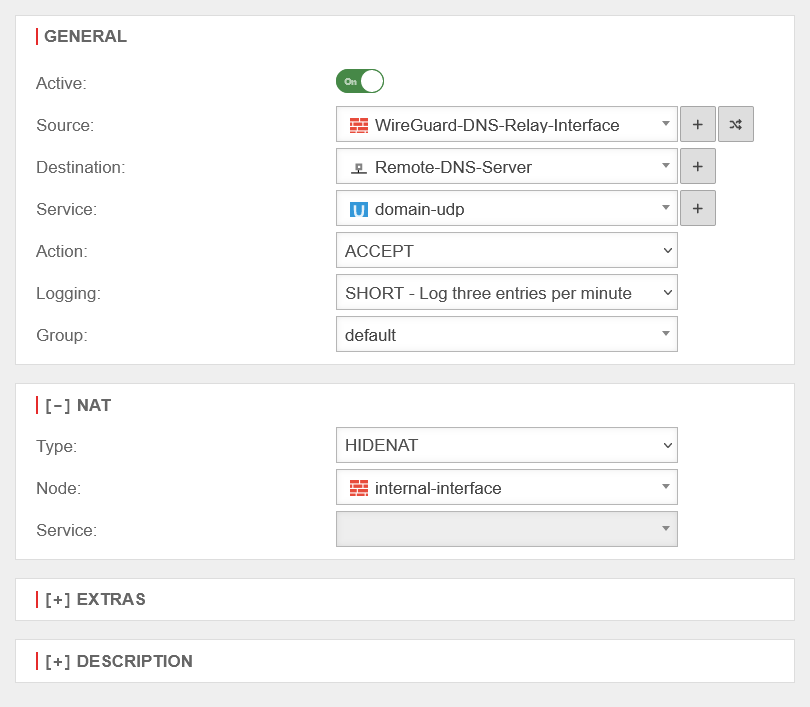
The last step is to create a firewall rule with a Hide NAT.
This causes DNS forwarding to also go to the tunnel and not directly to the Internet.
DNS Relay for a WireGuard Site-to-Site Tunnel
The internal domain requests can also be forwarded to a remote nameserver located in a WireGuard network. The configuration of such a scenario requires an existing WireGuard site-to-site VPN (S2S) connection.
Central configuration in the DNS server network
Simplified solution with packet filter rule in the network of the DNS server
If there are several branch offices, the simplest option is often to release the entire transfer network on the server side. This requires a packetfilter rule on the UTM in the DNS server network.
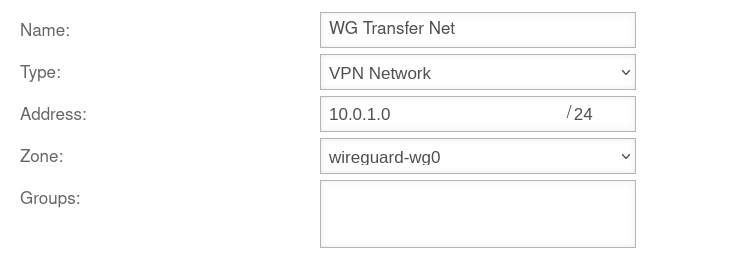
Enable WireGuard transfer network as peer network
UTM im DNS-Server Netzwerk
The IPv4 address of the corresponding WireGuard interface can be looked up or adjusted under button Edit. The network in which this is located is then released as a peer network under button Edit of the corresponding WireGuard peer.
Creating the network object for the transfer network
UTM im DNS-Server Netzwerk Box Network Objects button
Network object DNS server
A network object for the DNS server (type: Host) should already exist.
If not, it must also be created.
UTM in the DNS server network Box Network Objects button
Create rule
UTM in the DNS server network button
|
|
# | Source | Destination | Service | NAT | Logging | Action | Active | ||
| 4 | Accept | On | ||||||||
This packetfilter rule allows the SSL-VPN transfer network and thus all S2S clients on this SSL-VPN tunnel to access the DNS server
notempty
Decentralized configuration on each S2S client
If a central configuration in the DNS server network is not desired or possible, a NAT rule can be created on each S2S client.
Create zone
UTM in the S2S client network
button
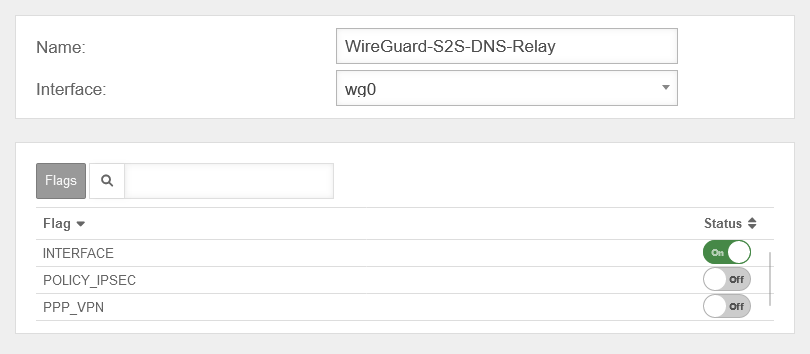
In order to route the DNS requests into the WireGuard tunnel, a new interface zone must be created on the UTM.
Create WireGuard network objects
UTM in the S2S client network
The packet filter rules in the Implied rules are automatically activated. This means that no network object is yet available for the WireGuard network.
Create rule
UTM in the S2S client network button
The last step is to create a firewall rule with a Hide NAT.
This causes DNS forwarding to also go to the tunnel and not directly to the Internet.