New article: 12.2024
notemptyThis article refers to a Beta version
Preliminary remark
The example uses the service group default-internet.
In real configurations, this group must, of course, be adjusted. If necessary, a new service group is recommended.
A rule with any should only be used if all involved networks and devices are 100% trustworthy and compromise can be ruled out.
Prerequisite
- Configured S2S VPN
- Configured S2E connection
| RW Transfer-Netz | 192.168.192.0/24 |
|---|---|
| VPN Server Internal Network | 192.168.175.0/24 |
| S2S Transfer-Netz | 192.168.190.0/24 |
| VPN Client Internal Network | 192.168.174.0/24 |
Example scenarios
Connect SSL-RW to S2S server side
Enter transfer networks
For this, the RW transfer network is entered on the S2S server side in the Server Network release:
- VPN Server
S2S Server edit desired connection in the General section, Globally release server networks: »192.168.192.0/24 - And the S2S client network is entered in the RW Network release:
VPN Server
RW Server edit desired connection in the General section, Release server networks: »192.168.174.0/24In a previous version, the transfer network was incorrectly entered here
- Restart the service to fully apply changes and push routes:
VPN Server
the application SSL VPN stop and then start
Create packet filter rules
Connect SSL-RW on the S2S client side
Enter transfer networks
Die Transfernetze müssen auf den UTMs hinterlegt werden:
- Hierzu wird das RW-Transfernetz auf der S2S-Serverseite in die Client Netzfreigabe eingetragen:
VPN Server
S2S Server Client-Gegenstellen gewünschten Client bearbeiten Clientnetzwerke freigeben: »192.168.192.0/24
- Restart the service to fully apply changes and push routes:
VPN Server
the application SSL VPN stop and then start
Create packet filter rules
SSL-RW via IPSec-S2S
Enter transfer networks
- First, enter the local network at location B, which the road warrior should ultimately be able to access, in the RW tunnel.
Location A
RW Server Edit desired connection Area General Share server networks globally: »192.168.175.0/24
- Next, a network object is created for the local network at location B (behind the IPSec connection).
Location A
button
Name: Target Network Location B
Important:
Therefore, no VPN network may be selected here!
- Restart the service to fully apply changes and push routes:
Location A
the application SSL VPN stop and then start
Edit phase 2
- In phase 2 of the connection, the SSL Roadwarrior IP address must be entered as a subnet.
Location A | Location B
Area Connections Edit phase 2 of the desired connection → Subnets section button
- Location B
If there is no administrative access to the remote location, an additional HideNat rule must be created at the local Location A.
There are separate instructions for this own instructions. Please note: The local location here is “Location B”!
Create packet filter rule
| In addition, the following packet filter rules must be created. The wiki article on
Reaching IPSec S2S destinations with SSL VPN may be useful here. | ||||||||||
| # | Quelle | Target | Service | NAT | Logging | Action | Active | |||
| ACCEPT | On | |||||||||
| ACCEPT | On | |||||||||
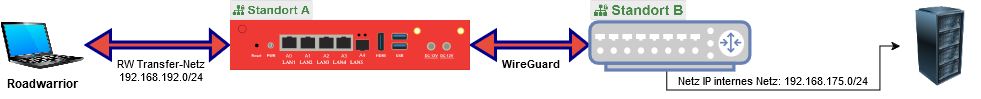
SSL-RW via WG-S2S (SP to SP)
The SSL-RW is located at site A and wants to access a device at site B.
Enter transfer networks
Location A
- First, the local network from location B, which the road warrior should ultimately be able to access, is entered in the RW tunnel.
RW Server Edit desired connection Area General Share server networks globally: »192.168.175.0/24 - Restart the service to fully apply changes and push routes:
the application SSL VPN stop and then start
- In addition, the SSL-RW transfer network is entered into the WireGuard server networks at location A.
Edit desired connection Share server networks globally: »192.168.192.0/24 - Then Wiregard
Location B
- At location B, the SSL-RW transfer network is also entered—but in the WireGuard Peer networks.
Peers Edit desired peer Share peer networks: »192.168.192.0/24 - Then Wiregard
Create packet filter rules
SSL-RW via WG-S2S (SP to external)
The SSL-RW is located at site A and wants to access a device at site B.
Enter transfer networks
- First, the local network from location B, which the road warrior should ultimately be able to access, is entered in the RW tunnel.
RW Server Edit desired connection Area General Share server networks globally: »192.168.175.0/24 - Restart the service to fully apply changes and push routes:
Location A
the application SSL VPN stop and then start - In addition, the SSL-RW transfer network is entered into the WireGuard server networks at location A.
Edit desired connection Share server networks globally: »192.168.192.0/24
Create packet filter rules
| # | Quelle | Target | Service | NAT | Logging | Action | Active | ||
the remote station (location B) |
HN with internal interface |
ACCEPT | On |