notempty
Last adaptation to the version: 14.0.1 (01.2025)
- Cloud-verwaltete Paketfilterregeln und Netzwerkobjekte
- Autogenerierte Regeln lassen sich bearbeiten
- Tabellen-Menü zur Layoutanpassung
- Neues Attribut Log Alias (v14.0)
- Buttons for log access (v14.0)
The function and arrangement in the menu has remained identical.
For test purposes, iptables can be replaced by nftables.
system rule_engine set value "nftables"
or
system rule_engine set value "iptables"
Packet filter Description
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewall 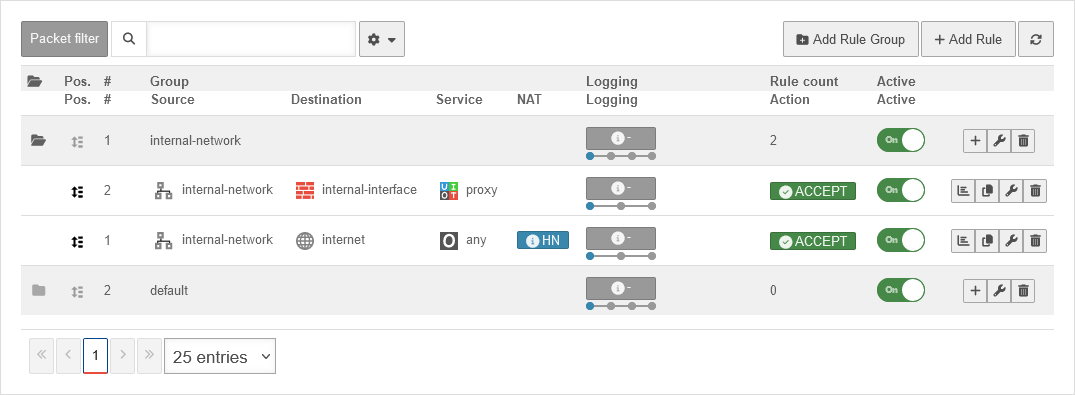 The packet filter controls the data traffic that passes through the UTM.
The packet filter controls the data traffic that passes through the UTM.
- All network packets that pass through the UTM are filtered and only forwarded based on packet filter rules.
- Thereby, it is irrelevant whether the destination address and source address of the packet are in the same network, in another, local network or in the Internet and a local network.
- Based on the source IP, destination IP and service used, the rules are checked from top to bottom.
The sequential number before a rule # indicates the order of rulecreation and is permanently retained. It does not indicate the order in which the rule is processed! - A rule that has been created can be subsequently moved in the order by holding down the mouse button on the icon
 .
.
If the exception rule applies to a package, the specified action is carried out and the packet filter is terminated.
If the exception rule does not apply, the more general rule is then checked.
If this rule then applies, the action specified there is executed.
- Two Network Objects (source / destination).
- One Service
- if applicable, details of the NAT type (Network Address Translation)
- if applicable, Rule Routing
- If applicable, a QoS Profile that regulates the bandwidth made available for certain data packets.
- if applicable, a Time Profile at which the rule is to be applied
- an Action that is to be executed
- details of the Logging
- the assignment to a Rule Group
Packet filter rule
- The basic structure of a rule is :
Source → Target → Service → Action - With copy rulesrules can be copied. The Add Rule dialogue opens with a copy of the respective rule.
- Logging can be changed directly in the overview for individual rules or rule groups (see section Logging ) and notemptywith the button Packetfilter Log for the individual rules or with for all rules.New from v14.0:
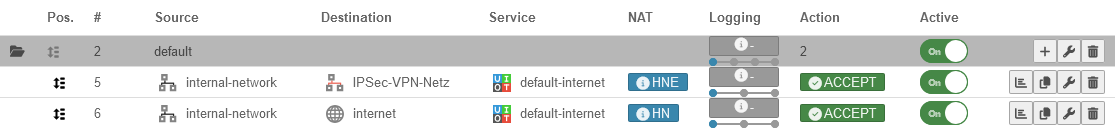
| Typical examples: | # | Source | Destination | Service | NAT | Logging | Action | Cloud | Active | ||
| The Internet should be accessible from the internal network | 7 | HN | Accept | On | |||||||
| The dmz1 network should be accessible for all services from the internal network. | 8 | Accept | On | ||||||||
| A server in the internal network is to be accessible from outside via ssh | 9 | DN ➞ | Accept | On | |||||||
| The Internet should be accessible from the internal network, but no ftp should be enabled! | 10 | Drop | On | ||||||||
| 7 | HN | Accept | On | ||||||||
| Wenn eine Regel über die VPN Konfiguration erstellt wurde, wird dies in der Spalte Cloud-verwaltet mit gezeigt. Diese Regeln können nicht kopiert, bearbeitet oder gelöscht werden. | ACCEPT | On | |||||||||
| ACCEPT | On | ||||||||||
Autogenerated rules
autogenerated
The UTM has autogenerated rules ex works.
These rules initially allow all data traffic into the existing networks and also release the proxy and DNS services of the respective interface for internal networks
Sie müssen unbedingt angepasst oder durch individualisierte Regeln ersetzt werden!
notempty
The visibility of the autogenerated rules can be controlled in the drop-down menu with this switch: On Show auto-generated rules Default
Packet filter Rule Settings
Only after that will the rules be applied!
/ →
| notempty New as of v14.0 | |||
GeneralGeneral
| |||
| Caption | Value | Description | UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewallPacket filter 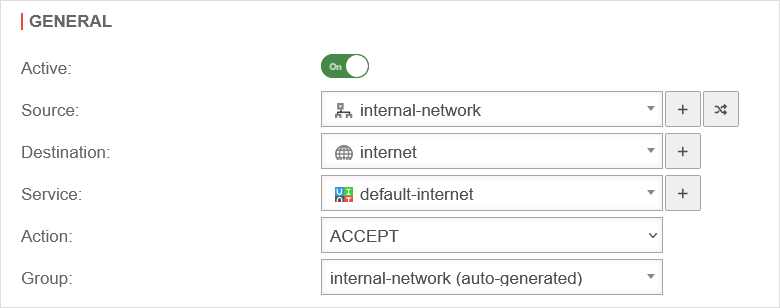 Packet filter rule settings General Packet filter rule settings General
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Active: | On | Only when activated is this rule checked | |
| Source: | Network object or user group that is permitted as the source of the data package. | ||
| Destination: | Network object or user group that is permitted as the destination of the data packet. | ||
| Service: | Desired service with stored port (see tab Services) | ||
| Netzwerkobjekt add / Dienst add | Adds a network object or service | ||
| Switch network object | Exchanges the network objects Source and Destination | ||
Action:Action |
ACCEPT Forwards the package | ||
| DROP The package is dropped | |||
| REJECT An ICMP packet is sent to the sender indicating that the port is not available. In the LAN, reject rules can prevent clients from having to wait for a timeout. | |||
| QOS Allows you to specify a Quality of Service profile that limits the bandwidth for data packets to which this rule applies. Configuration of the QoS profiles in the Area Profile menu. | |||
| STATELESS Allows connections regardless of status | |||
| Group: | default | Packet filter rules must be assigned to a group. This makes it easier to keep track when adding to the set of rules. In addition, rule groups can be activated or deactivated with a switch notempty New as of v12.7.0 | |
LogLog
| |||
Logging:Logging |
Specifies how extensively the application of the rule is logged. notempty New as of v12.7.0 |
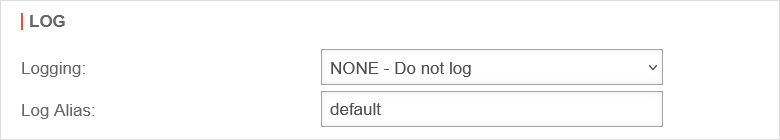 | |
| No logging (default) | |||
| Logs the first entries per minute | |||
| Logs all entries | |||
Log Alias:Log AliasnotemptyNew as of v14.0 |
default | Kurzer (maximal 10 Zeichen langer) Alias für die Paketfilterregel, der im Log statt der Id angezeigt wird. | |
NAT[ - ] NAT
|
Network Address Translation is the conversion of IP addresses used in a network to another IP address from another network. Typically, all internally used private IP addresses are mapped to one or more public IP addresses. | ||
| Type: | No NAT is performed | ||
| With Full Cone NAT, the same port is set for the sender as for the recipient. However, IPs other than the originally addressed IP are also permitted as senders. This can be helpful with VOIP. |  | ||
| Also called Source NAT. Hides the original IP address behind the IP address of the interface used. The standard case is data traffic from an internal network with private IP addresses to the Internet. |
 | ||
| HideNAT Exclude is usually used in connection with IPSec VPN connections. This ensures that data packets for the VPN remote terminal are routed through the VPN tunnel with the private IP address. Otherwise, these would be masked with the public WAN IP address like all other packets in the direction of the Internet and, since they are sent with a private destination address, would be discarded at the next Internet router. See also the Wiki article HideNAT Exclude. |
  | ||
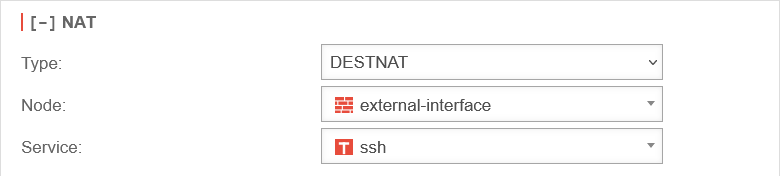
| Destination NAT is usually used to offer several services on different servers under one public IP address. For example, if you want to access the SSH service (port 22) of the server (198.51.100.1/32) from the Internet via the public IP address of the eth0 interface with port 10000, the rule would have to be created as shown opposite. The associated network objects and the service on port 10000 must be created for this. |
 | ||
| NetMap is used to connect two identical subnets with each other. Using auxiliary networks (mapnet), which are not set up on either of the remote sites to be connected, these connections can be created collision-free without completely changing the subnet on either side. Instructions for connecting two networks can be found in a dedicated Wiki article NetMap |
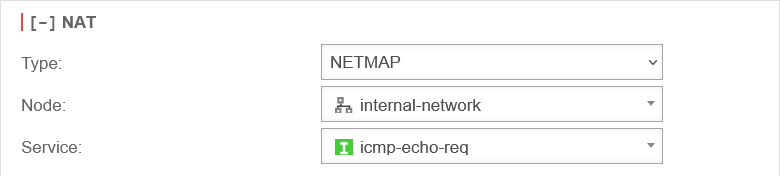 | ||
| Network object: | The IP address of this network object is then used as the sender IP of the data packets in the target network. As a rule, this should be the interface whose IP address is known to the target network so that reply packets can also be correctly delivered. | ||
| Service: | Uses the selected service in the local destination network. This value is often (but by no means always) identical with the service above it in the data source package for which the rule is checked. Type is selected as or . | ||
Extras[ - ] Extras
| |||
Rule RoutingRule Routing |
wan0 | In the [ - ] Extras section, the Rule Routing field is used to specify, based on rules, which route IP packets should take.In the example opposite, all VOIP packets are routed via the wan0 interface. If access to the Internet is via a router connected to an ethernet interface, this can be entered manually. |
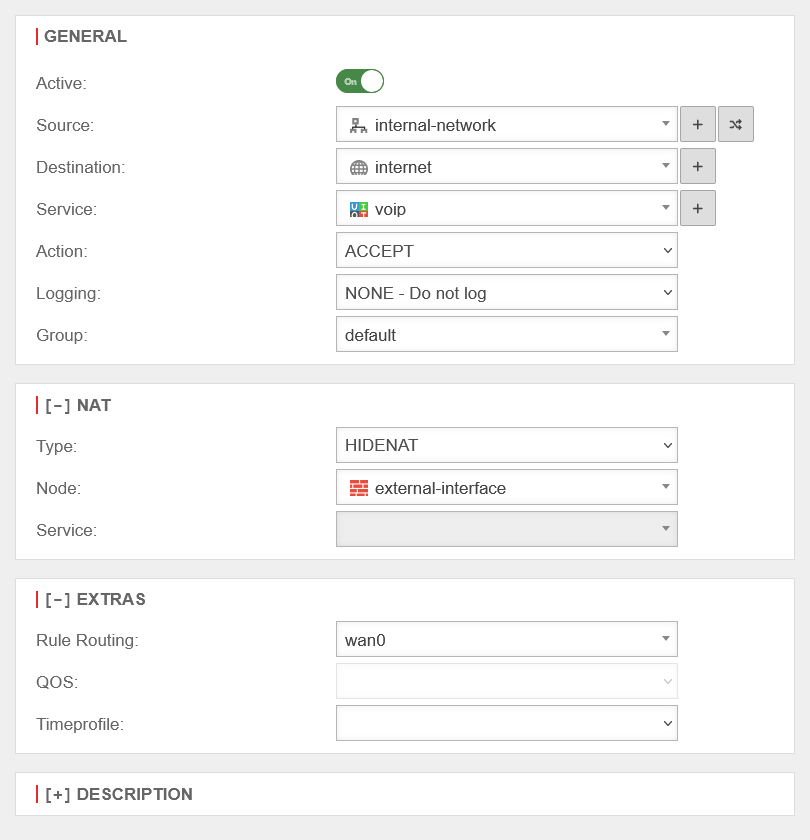 |
QoSQOS |
Allows you to specify a Quality of Service profile that limits the bandwidth for data packets to which this rule applies. Configuration of the QoS profiles in the Area Profile menu. Action . | ||
| Time profile | Restricts the validity of the rule to a previously defined time profile. See section Time Profiles. | ||
Description
|
Show extended rule info On | Alternative text that can be displayed instead of the rule details. The alternative texts are displayed with the button |
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewall 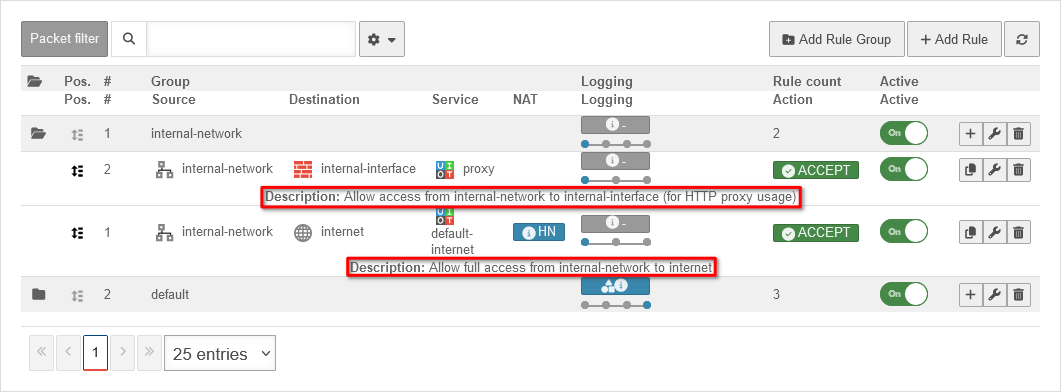 Rule description in plain text Rule description in plain text
|
notempty After editing or adding a rule, the rulebook must be updated. Only after that will the rules be applied! / → | |||
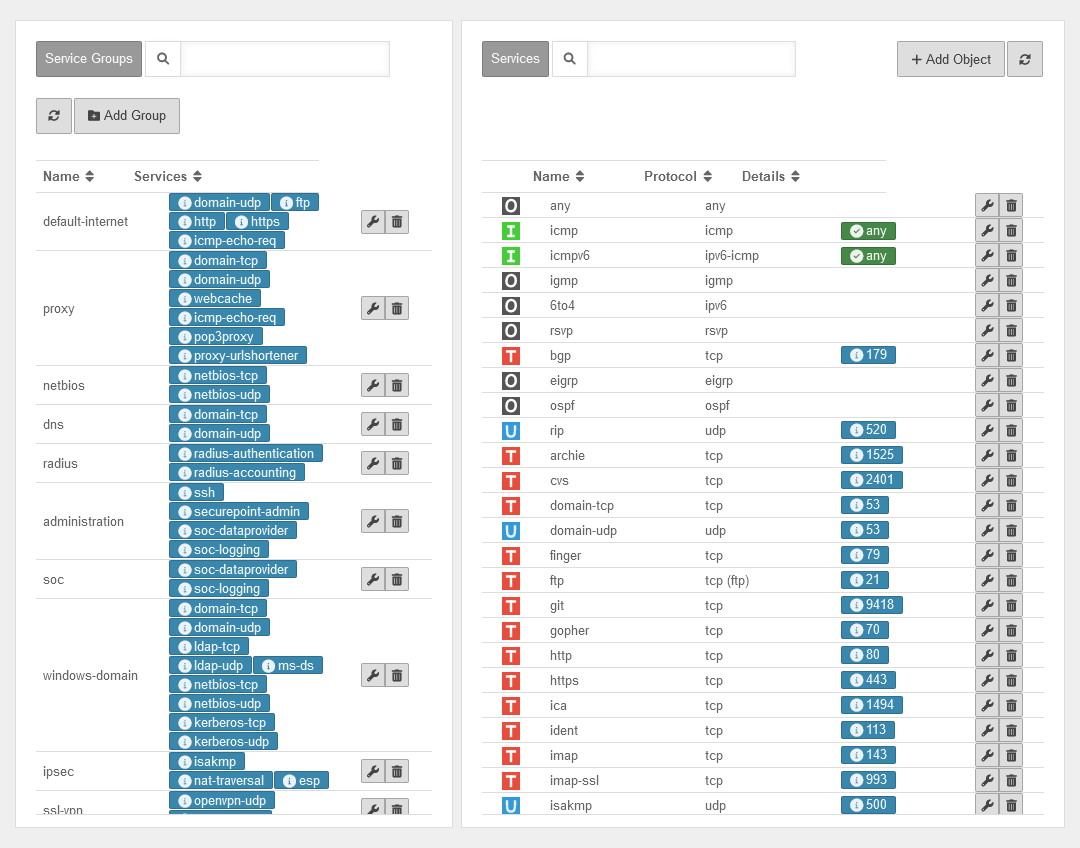
Network objects
| button | Description | UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewall 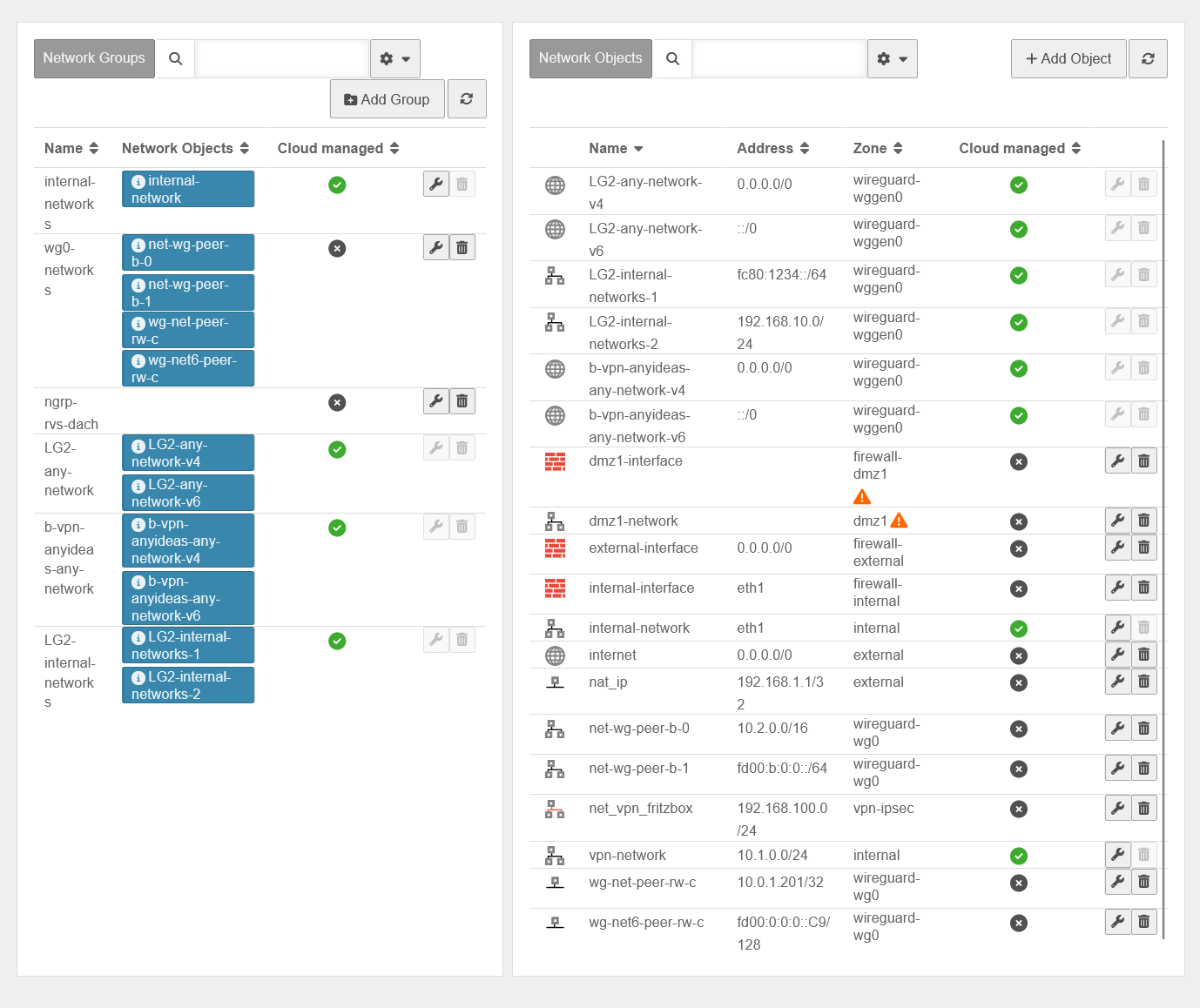 Tab Network Objects Tab Network Objects
|
|---|---|---|
| Edit | Opens the network group or network object for editing | |
| Delete | Deletes the network group or network object. The deletion must be confirmed once again | |
| Creates a new network group to which network objects can be added immediately | ||
| Show GeoIP objects On When disabled Off: Hides GeoIP objects to improve readability. | ||
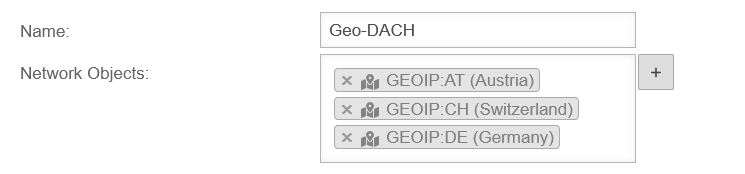
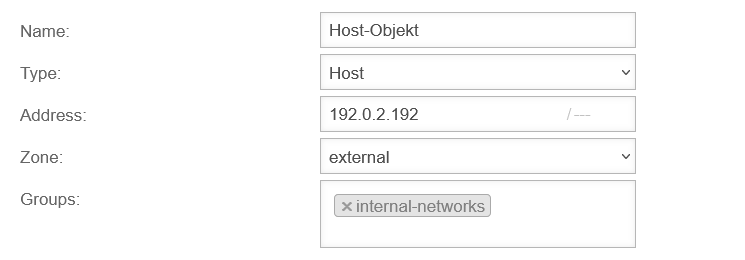
Network objects contain :
Network objects are mainly needed to create packet filter rules, but they are also used in the HTTP proxy. The members of a network group are displayed as labels. v14.0 | ||
Services
Add / edit services
If a service does not exist, it can be created with .
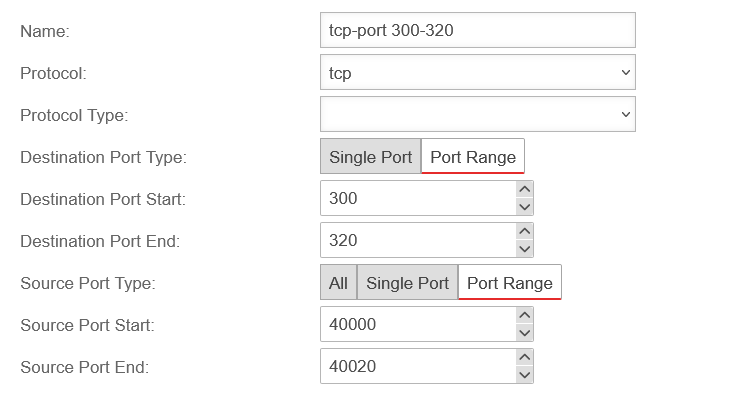
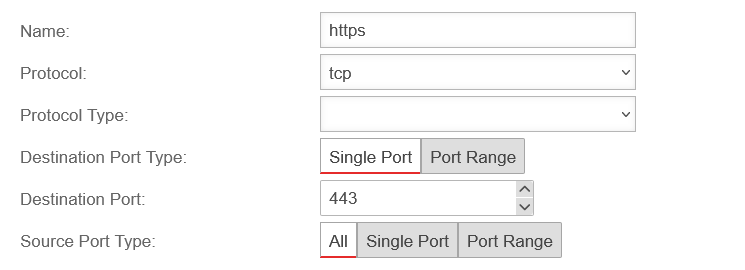
Depending on the protocol used, further settings can be made:
- Ports (TCP and UDP)
- Packet types (ICMP)
- Protocol type (gre)
Service groups
Services can be grouped together in service groups. Here, too, there are already predefined groups that can be added to and changed. Detailed display by clicking on the button .
notemptynotempty
Example: The group default-internet contains, for example, the services:
| Icon | Name | Protocol | UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewallServices 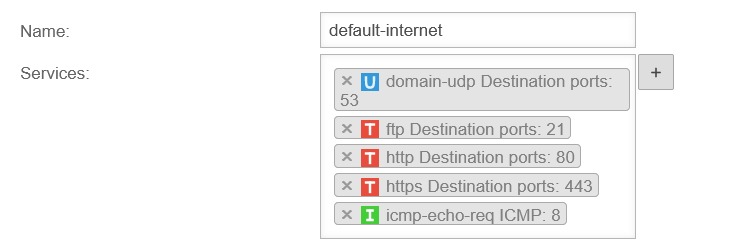
| |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| domain-udp | udp | Port 53 | ||
| ftp | tcp (ftp) | Port 21 | ||
| http | tcp | Port 80 | ||
| https | tcp | Port 443 | ||
| icmp-echo-req | icmp | Pakettyp 8 | ||
Add/remove service from a service group
- Clicking in the click box selects the desired service and thereby adds it.
- Clicking the button creates a new service and then adds it to the service group.
- A service is removed from the service group by clicking on ✕.
Time profiles
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewall 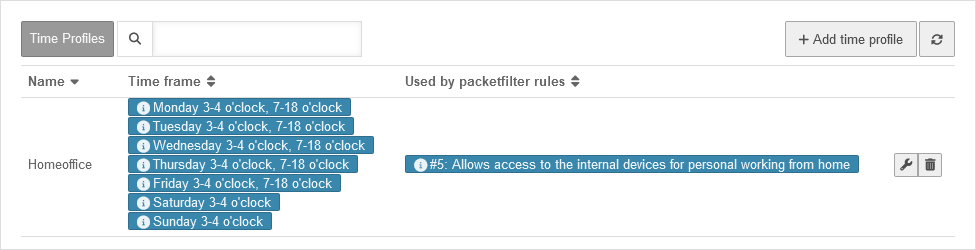 Time profiles overview
Time profiles are used to activate packet filter rules only at specified times. They can be configured under
Time profiles overview
Time profiles are used to activate packet filter rules only at specified times. They can be configured under
In the example shown, the profile applies daily between 3:00 am and 3:59:59 am and on weekdays from 7:00 am to 5:59:59 pm. This can be seen in the table under time window.
Under Used in packet filter rules, the IDs are listed together with the descriptions of the packet filters for which this time profile is set up. The packet filter can also be edited by clicking on the corresponding entry.
The Name column shows an assigned name that should describe the time profile.
Create time profiles
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewallTime profiles 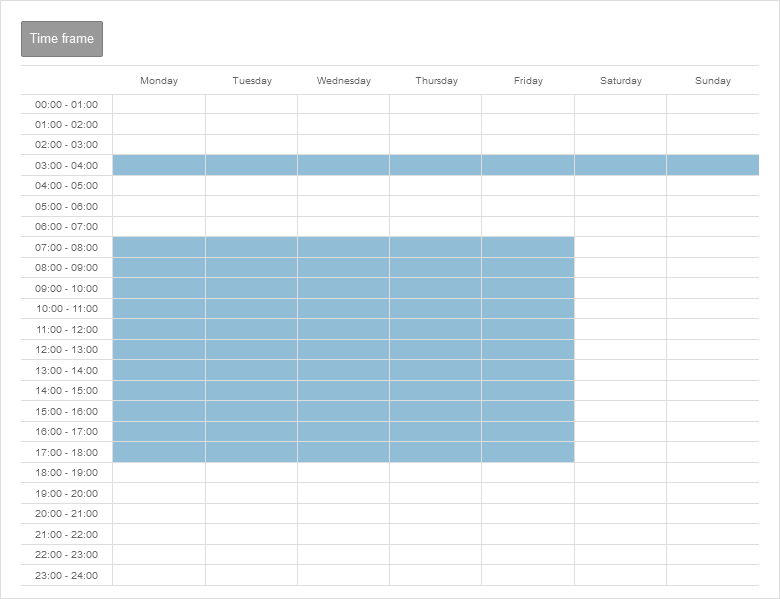 Add time profile
Add time profile
- Create a time profile under button .
- Select times
- Individual fields or time ranges can be selected by clicking the mouse
- Several fields and time ranges can be selected by holding down the mouse button
- Accept the time settings with the button Save and close