| Enable a service via the firewall |
Enable a service via the firewall, e.g. an internal server that should be accessible via the Internet
|
 The rule wizard of the packet filter The rule wizard of the packet filter
|
| Port forwarding |
Set up port forwarding
|
| Enable a service on the firewall |
Release a service that is offered by the UTM itself, such as a VPN or proxy server
|
|
|
Step 2: Source
|
|
The second step is to determine the source.
It establishes the connection.
This is either
- an address (IP address, network or interface)
- an interface (e.g. LAN4)
- an existing network object
|
Set address
|
| Caption |
Value |
Description
|
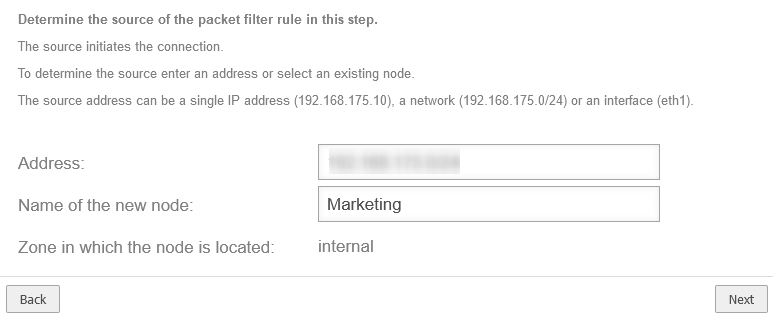 Set the source address, e.g. the network 10.1.20.0/24
|
| Address: |
192.168.175.10
10.1.20.0/24 |
Enter a single IP address or a network
|
Existing network object:
Display only for ‘'already assigned’' IPs or networks |
Technology (10.1.20.0/24) |
The correct network object is entered automatically
|
Name of the new network object:
Display only for ‘'not yet’' otherwise assigned IPs or networks: |
Marketing |
Assign a unique name for the new network object
|
| Zone in which the network object is located: |
internal |
The zone of the network object is displayed automatically
|
| Click on Next
|
|
|
Determine interface
|
| Address: |
LAN3 |
Enter interface Pay attention to correct capitalization!
|
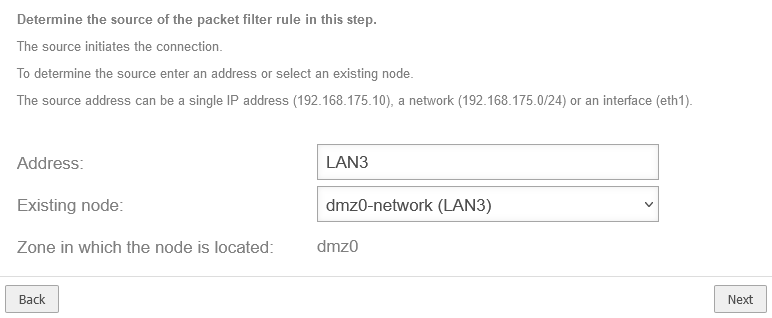 Enter an interface such as LAN3 as the address
|
| Existing network object: |
dmz0-network (LAN3) |
The correct network object is entered automatically
|
| Zone in which the network object is located: |
dmz0 |
The zone of the network object is displayed automatically
|
| Click on Next
|
|
|
|
|
Select network object
|
| Address: |
LAN4 |
The address is entered automatically after selecting the ‘'Existing network object’'
|
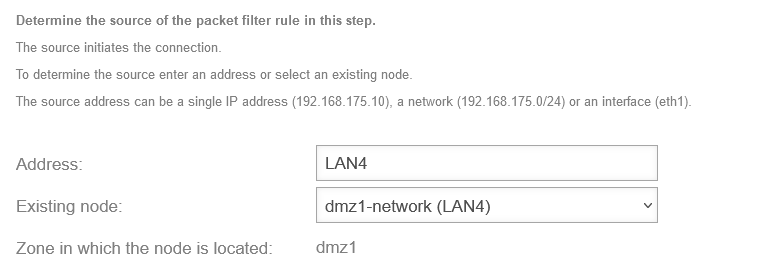 Select an existing network object such as ‘'dmz1-network (LAN4)’'
|
| Existing network object: |
dmz1-network (LAN4) |
Select an existing network object
|
| Zone in which the network object is located: |
dmz1 |
The zone of the network object is displayed automatically
|
| Click on Next
|
|
|
Step 3: Destination
|
Set address
|
| Address: |
192.168.175.10
192.168.175.0/24 |
Enter a single IP address or a network
|
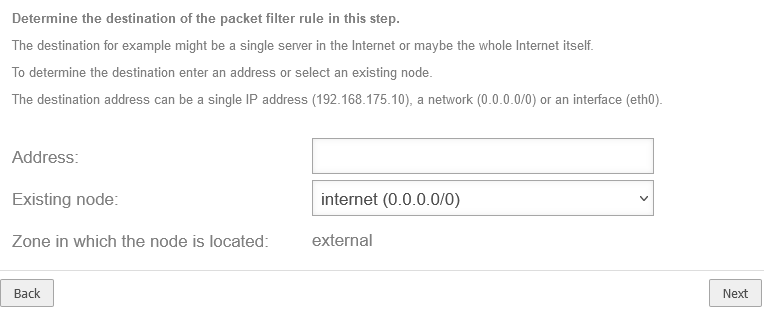 The target is the entire Internet
|
Existing network object:
Display only for ‘'already assigned’' IPs or networks |
internet (0.0.0.0/0) |
The correct network object is entered automatically
|
Name of the new network object:
Display only for ‘'not yet’' otherwise assigned IPs or networks: |
Marketing |
Assign a unique name for the new network object
|
| Zone in which the network object is located: |
internal |
The zone of the network object is displayed automatically
|
| Click on Next
|
|
|
Determine interface
|
| Address: |
LAN2 |
Enter interface Pay attention to correct capitalization!
|
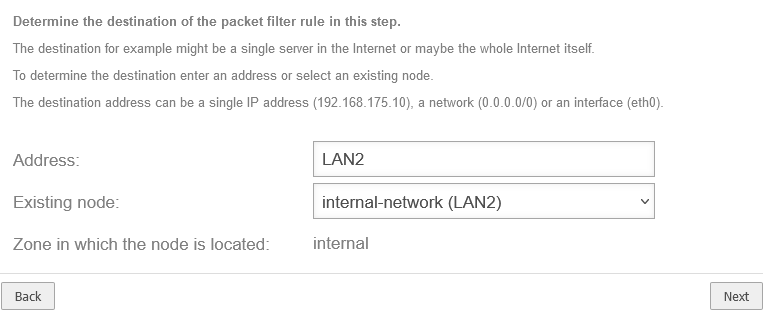 LAN 2 entered as interface
|
| Existing network object: |
internal-network (LAN2) |
The correct network object is entered automatically
|
| Zone in which the network object is located: |
internal |
The zone of the network object is displayed automatically
|
| Click on Next
|
|
|
Select network object
|
| Enable a service via the firewall and Port forwarding
|
| Address: |
192.168.1.0/24 |
The address is entered automatically after selecting the ‘'Existing network object’'
|
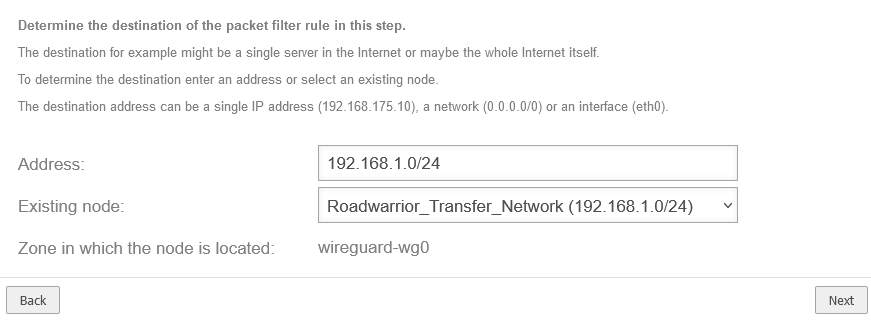 The destination here is ‘'Roadwarrior_Transfernetz’'
|
| Existing network object: |
Roadwarrior_Transfernetzwerk (192.168.1.0/24) |
Select an existing network object
|
| Zone in which the network object is located: |
wireguard-wg0 |
The zone of the network object is displayed automatically
|
| Click on Next
|
|
|
|
|
| Enable a service on the firewall
|
| Existing network object: |
external-interface (0.0.0.0/0) |
Where possible, the UTM automatically configures the destination
|
 The ‘'external-interface’' target was set
|
| If no suitable destination has been configured: Determine the destination yourself or alternatively select another service
|
| Zone in which the network object is located: |
firewall-external |
The zone of the network object is displayed automatically
|
| Click on Next
|
|
|
Step 4: Service
|
|
The fourth step is to determine the service you want to use. There are two ways to do this:
- Select the service directly
- Enter the corresponding port or port range
|
Select Service
|
| Port |
21 |
The name of the port is automatically entered after selecting the ‘'Existing service’'
|
 Select a Service
|
Protocol of the service
Only displayed for services with a protocol |
tcp |
Select ‘'tcp’' or ‘'udp’'
|
Existing service
Only displayed for existing services |
ftp |
Select Service
|
Name of the new service
Only displayed for protocols without an existing service |
gopher-udp |
Name the new service
|
| Click on Next
|
|
|
| Enter the destination port or the port range directly
|
| Port |
70 |
Enter the destination port or the port range directly
|
 Enter a destination port
|
Protocol of the service
Only displayed for services with a protocol |
tcp |
Select ‘'tcp’' or ‘'udp’'
|
Existing service
Only displayed for existing services |
gopher |
Service is entered automatically
|
Name of the new service
Only displayed for protocols without an existing service |
gopher-udp |
Name the new service
|
| Click on Next
|
|
|
Step 5: Configuration
|
| Action |
ACCEPT - Allow connection |
The rule allows one action
|
 The configuration of the newly created rule
|
| DROP - Discard connection (source is not notified) |
The rule discards an action without notifying the user
|
| REJECT - Reject connection (source is notified) |
The rule prevents an action with a notification to the user
|
| QoS and Stateless modes can only be configured manually.
|
| Logging |
NONE - Do not log |
It is not protoled
|
| SHORT - Log three entries per minute |
Limited logging with up to 3 entries per minut
|
| LONG - Log everything |
Everything is logged.
Should only be used for debugging purposes!
|
| Rule group |
internal-network |
Select a rule group
|
|
|