Last adaptation to the version: 12.6.0
- Updated to Redesign of the webinterface
Introduction
If the same subnets are used on both sides of a VPN connection, it is normally not possible to set up this connection.
In addition, it can happen that the same networks are set up behind different remote peers.
With the NAT type NETMAP and auxiliary networks (map network) that are not set up on any of the remote peers to be connected, these connections can still be set up without completely changing the subnet on one of the sides.
NATing complete subnets with NETMAP
Open .
Preparations
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewallNetwork object 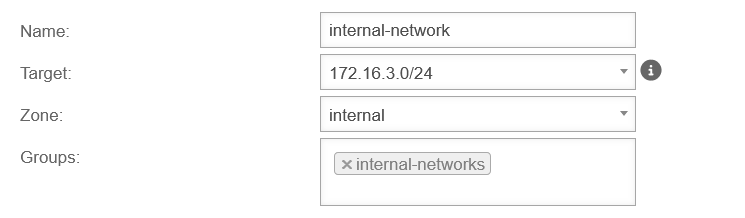 Convert network object to address
Head office & Branch office
Convert network object to address
Head office & Branch office
notempty
No interfaces may be selected to define the network object.
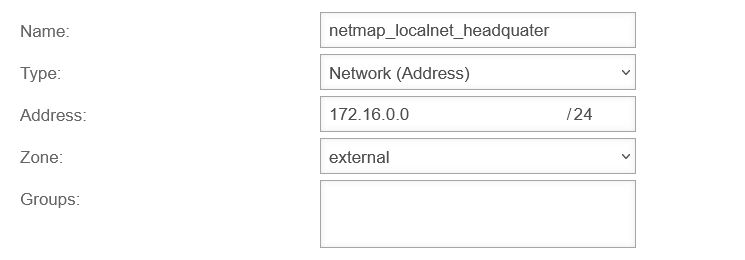
The network object of the internal network must be checked and, if necessary, the network IP of the internal network to be mapped must be entered as target:.
In this example, the network 172.16.3.0/24 is used on both sides.
Initial conditions
Head office and branch have the same subnetwork
In this case, the mapping must be set up on both sides of the connection.
| Local network | Public IP | Netmap | |
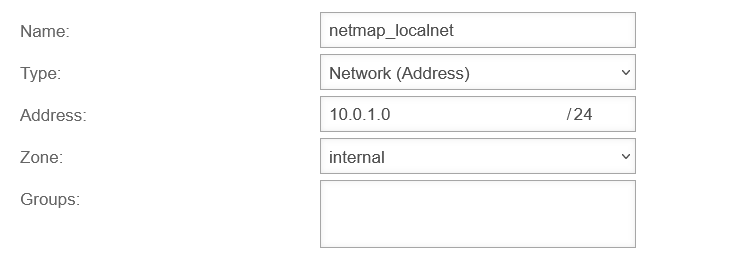
| Head office: | 172.16.3.0/24 | 192.0.2.192 | 10.0.1.0/24 |
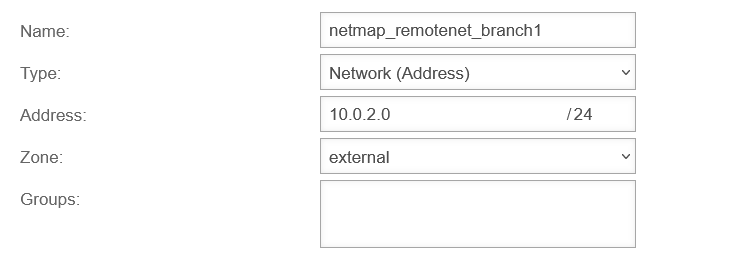
| Branch office: | 172.16.3.0/24 | 192.0.2.193 | 10.0.2.0/24 |
Create VPN connection
Head office Head office
| |
| Create an IPSec site to site VPN connection, as described in the Wiki in the menu with the button.
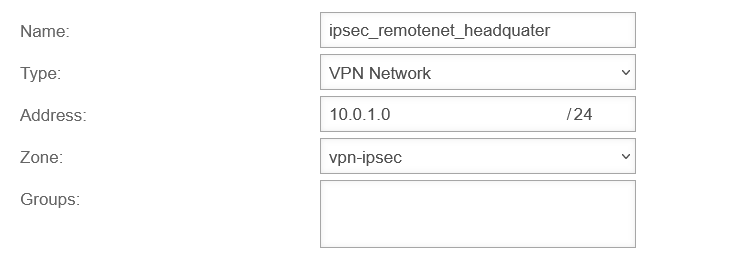
Here »10.0.1.0/24 |
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnVPNIPSec 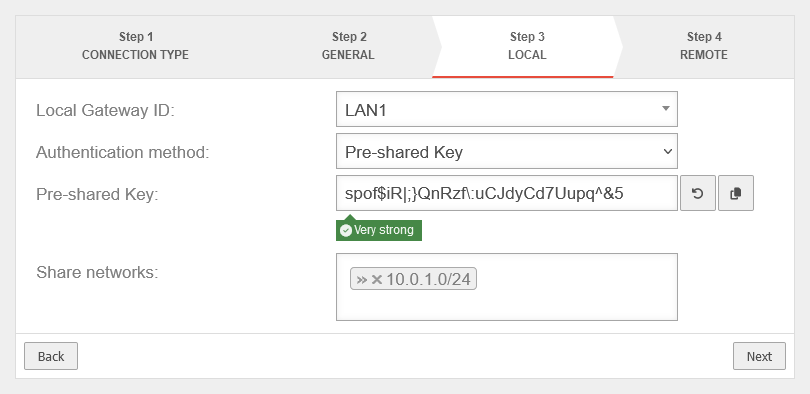 Head office Step 3 with local map network of the head office Head office Step 3 with local map network of the head office
|
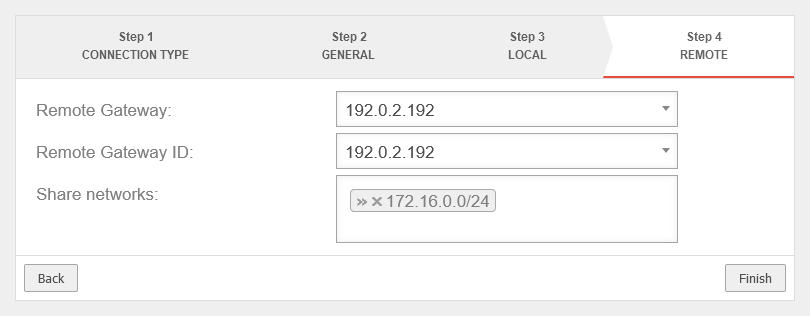
and the remote map network of the branch is required as the shared network. Here»10.0.2.0/24 (Replace with default network IP for the branch, if necessary.) |
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnVPNIPSec 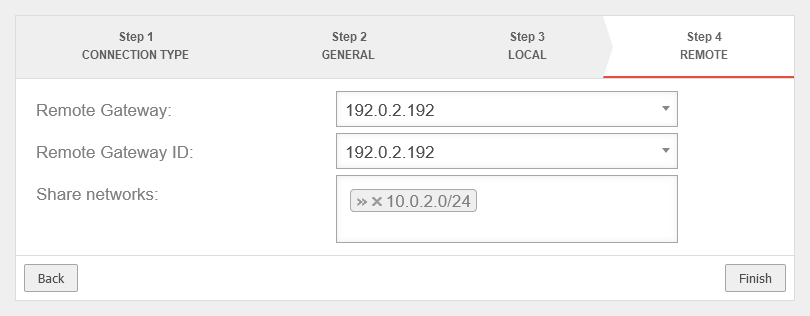 Head office Step 4 with remote map network of the branch office Head office Step 4 with remote map network of the branch office
|
Branch office Branch office
| |
| Create an IPSec site to site VPN connection, as described in the Wiki in the menu with the button.
Here »10.0.2.0/24 (Replace with default network IP for the branch, if necessary.) |
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnVPNIPSec  Branch office Accessibility of hosts of the remote station Branch office Accessibility of hosts of the remote station
|
and the remote mapnetwork of the head office is required as the shared network. Here »10.0.1.0/24 |
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnVPNIPSec 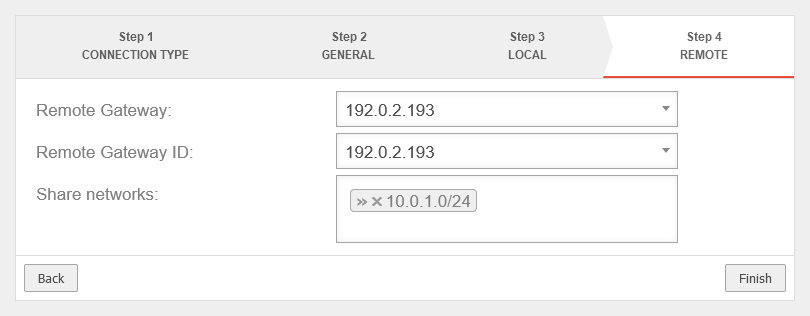 Branch office Step 4 with remote map network of the head office Branch office Step 4 with remote map network of the head office
|
Create network objects for transfer net
Create a NETMAP rule
| There must be two packet filter rules must be created on each side, which perform the mapping outbound and inbound. | |||
Head office Head office
| |||
| On the side of the Head office for outgoing mapping | UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewallPacket filter 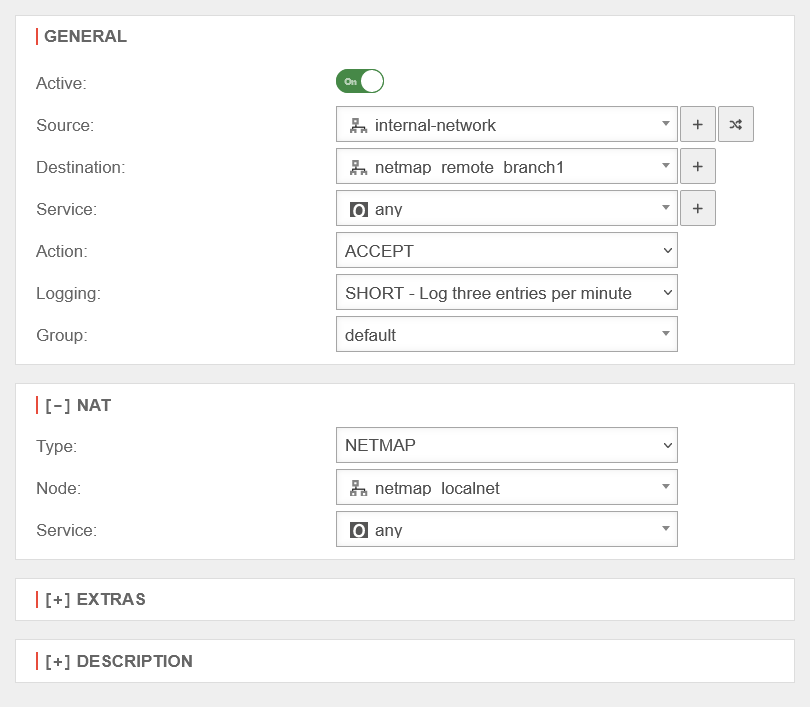 Head office NETMAP packet filter rule Head office NETMAP packet filter rule The mapnet cannot be selected as a network object if it is still associated with an interface instead of an IP address.
| ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Source: | |||
| Destination: | Map network of the branch | ||
| Service: | Exceptionally, an any rule makes sense here | ||
| Action: | |||
[ – ] NAT
| |||
| Type: | |||
| Network object: | Map network of the head office | ||
| Service: | Exceptionally, an any rule makes sense here | ||
| On the side of the Head office for incoming mapping | |||
| Source: | Map network of the branch | ||
| Destination: | |||
| Service: | Exceptionally, an any rule makes sense here | ||
| Action | |||
[ + ] NAT |
notempty No NAT of the type NETMAP is needed for this anymore | ||
Branch office Branch office
| |||
| On the side of the Branch office for outgoing mapping | UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewallPacket filter 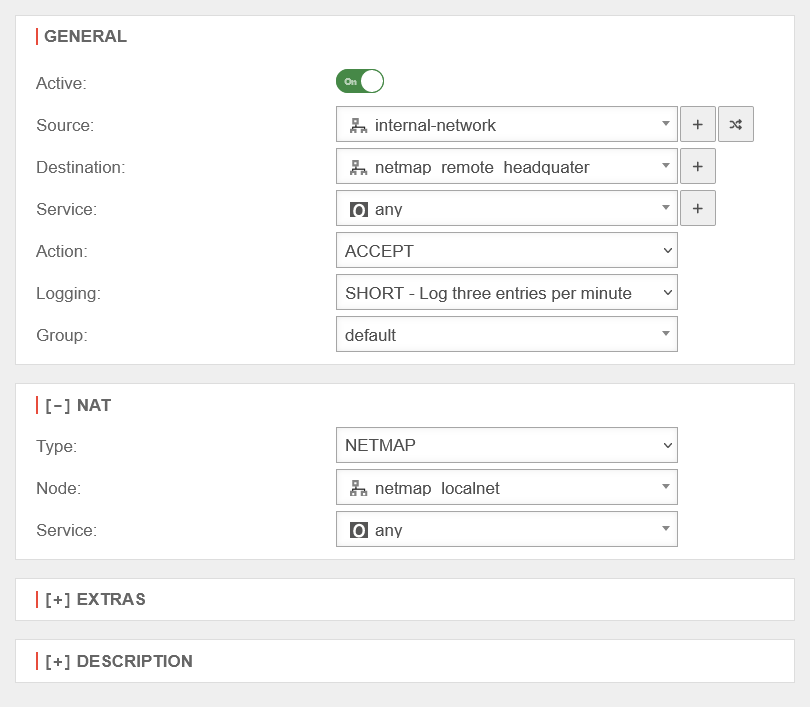 Branch office NETMAP packet filter rule Branch office NETMAP packet filter rule The mapnet cannot be selected as a network object if it is still associated with an interface instead of an IP address.
| ||
| Source | |||
| Destination: | Map network of the head office | ||
| Service: | Exceptionally, an any rule makes sense here | ||
| Action: | |||
[ – ] NAT
| |||
| Type | |||
| Network object | Map network of the branch | ||
| Service: | Exceptionally, an any rule makes sense here | ||
| On the side of the Branch office for incoming mapping | |||
| Source | Map network of the head office | ||
| Destination: | |||
| Service: | Exceptionally, an any rule makes sense here | ||
| Action: | |||
[ + ] NAT |
notempty No NAT of the type NETMAP is needed for this anymore | ||
Packet filter rules
In addition to the netmap rules, other rules are needed to allow traffic between the respective local network and the respective remote network.
Two options are available:
Implied Rules
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewall 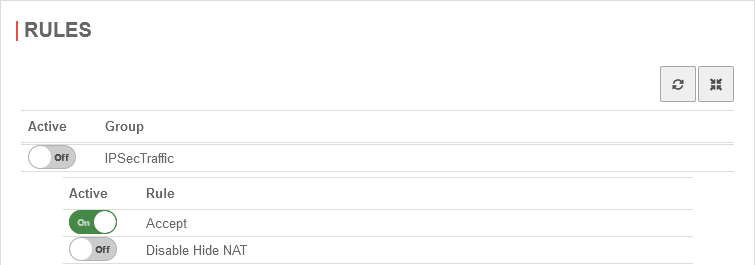 IPSec section in the implied rules
Head office & each branch
IPSec section in the implied rules
Head office & each branch
Menu → Group IpsecTraffic} → Rule Accept On
In this case rules are created in the background, which allow all services for all computers on both sides. (Default)
Dedicated packet filter rules
Custom packet filter rules that only allow services that are needed.
To do this, the IpsecTraffic Accept option in the -menu, section IpsecTraffic is to be disabled Off and packet filter rules are created manually.
The example assumes that server access from the branch to the head office is required.
Accessibility of hosts of the remote station
A host with the IP address 172.16.3.10 in the branch is addressed from the head office with the IP address 10.0.2.10.(Required rule is not shown in the example!)
A host with the IP address 172.16.3.120 in the head office is addressed from the branch office with the IP address 10.0.1.120.
Several branches have an identical subnetwork
| Local network | Public IP | Netmap | |
| 172.16.0.0/24 | 192.0.2.192 | not required | |
| Branch office 1: | 172.16.3.0/24 | 192.0.2.193 | not required |
| Branch office 2: | 172.16.3.0/24 | 192.0.2.194 | 10.0.1.0/24 |
Mapping is only set up on branches that use the same network as already has been set up on a VPN connection. No mapping is required in the head office if the internal network of the head office differs from that of the branches. One existing network can also be used without mapping in a branch.
Create VPN connection
| Create an IPSec site to site VPN connection, as described in the Wiki in the menu with the button. | |
Branch office 1 not depicted
In the example: |
|
| Branch office 2 (and other branches, if applicable)
In the example: »10.0.1.0/24 | |
| each branch
In the example: »172.16.0.0/24 | |
Head office
| |
Create network objects
| In Branch 2 (and in any other branch that uses a local network also used elsewhere) a network object is needed for the central office in the zone is needed, which can be used to perform the mapping.
|
|
| In addition, a second network object is created for the local network of the respective branch, which is mapped. The network object for the map network in the branch must be located in the zone of the internal network and gets the network IP 10.0.1.0/24 in this example. (Further branches receive another Mapnet in this place!) | |
Create a NETMAP rule
Packet filter rules
In addition to the netmap rules, other rules are needed to allow traffic between the respective local network and the respective remote network.
Two options are available:
Implied Rules
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnFirewall  IPSec section in the implied rules
Head office & each branch
IPSec section in the implied rules
Head office & each branch
Menu → Group IpsecTraffic} → Rule Accept On
In this case rules are created in the background, which allow all services for all computers on both sides. (Default)
Dedicated packet filter rules
notempty
Custom packet filter rules that only allow services that are needed.
To do this, the IpsecTraffic Accept option in the -menu, section IpsecTraffic is to be disabled Off and packet filter rules are created manually.
The example assumes that server access from the branch to the head office is required.
Accessibility of hosts of the remote station
A host with the IP address 172.16.3.10 in branch 1 is addressed from the head office with exactly this IP address (172.1.6.3.10).
A host with the IP address 172.16.3.10 in branch 2 is addressed from the head office with the mapped IP address 10.0.1.10.
A host with the IP address 172.16.0.120 in head office is addressed from the branch office with the IP address 172.16.0.120.