Last adaptation to the version: 12.6.0
- Updated to Redesign of the webinterface
Functionality of the transparent proxy
The transparent proxy ensures that web page calls are routed through the HTTP proxy even without settings in the browser, so that the virus scanner and web filter can be used for these connections.
In order to be able to check SSL-encrypted connections for viruses and malware, the proxy must pretend to be a client to the web server on the Internet, so that the data can already be decrypted on the firewall.
These are to be passed on coded afterwards again to the actual Client in the internal network.
To achieve this, the feature SSL interception is used.
Configuration
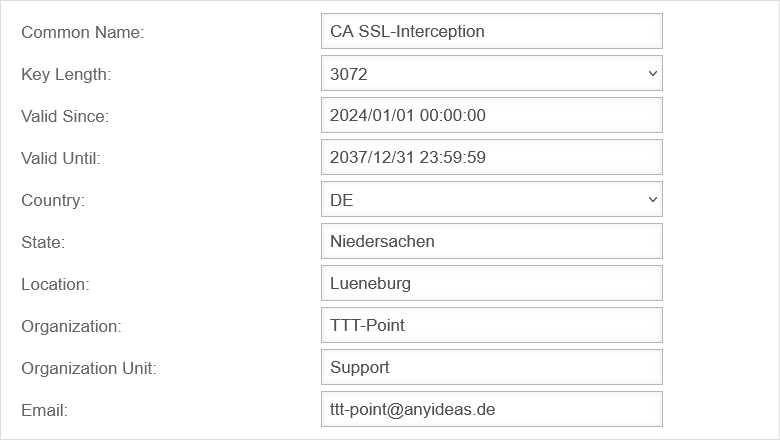
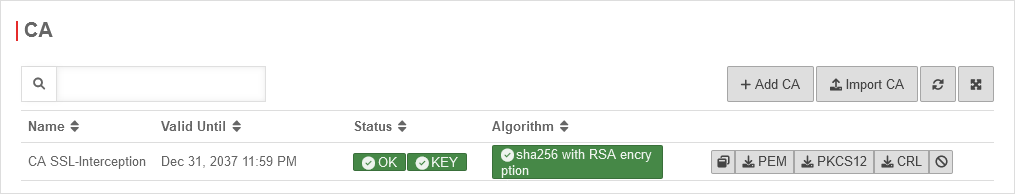
Certificate
SSL-Interception
Configuration under Area SSL Interception
| Caption | Value | Description | UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnApplicationsHTTP-Proxy 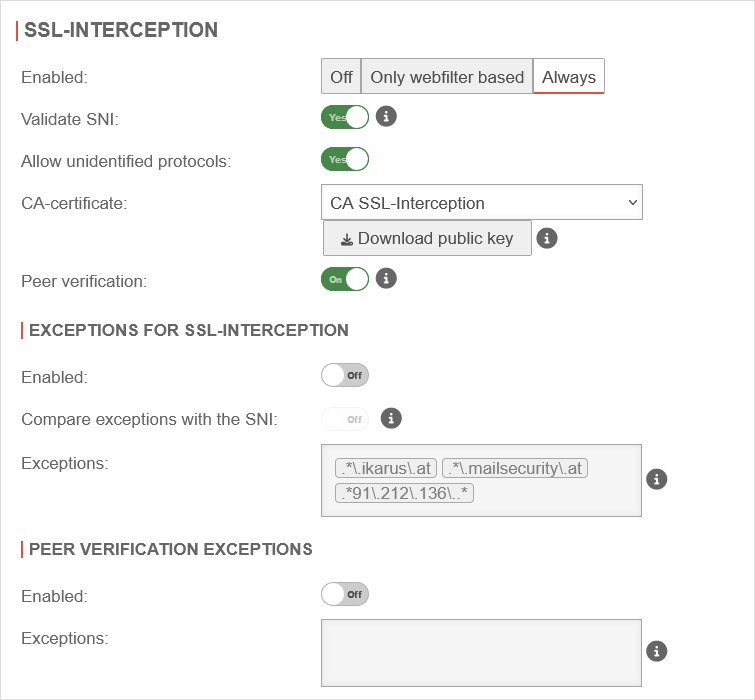 SSL Interception tab SSL Interception tab
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Enabled | The SSL-Interception is turned off | ||
| When enabled, only connections blocked by the web filter are intercepted. This avoids the problem that there are sites that do not tolerate an interruption of the encryption (e.g. banking software) without having to define an exception for it. | |||
| Activates the SSL interception | |||
| Validate SNI: Nur im globalen Konfigurationsprofil Wird an zusätzliche Konfigurationsprofile vererbt |
Yes | When activated, any SNI in the ClientHello of the TLS handshake is checked. The host name contained is resolved and the addresses in the result are compared with the target address of the intercepted request. If they do not match, the connection is closed. Without Server Name Indication validation, clients can manipulate SNI arbitrarily to bypass the web filter. This setting should only be considered as a last resort when it seems impossible to standardize the DNS settings between the HTTP proxy and the UTM clients. If the client and UTM use different DNS servers, this can lead to false positives.
| |
| Allow non identified protocols: | Yes | If this switch is deactivated, unrecognized protocols are blocked. | |
| CA-Certificate: | CA-SSL-Interception | Here, a CA must be selected that can re-encrypt the connection after decryption (and scanning). The public key of the CA must be installed on all client computers that are to use SSL Interception. Download can be done here directly with . | |
| The public key should be installed on the clients that are going to use SSL interception to avoid certificate errors. | |||
| Peer verification: not for Only webfilter based Nur im globalen Konfigurationsprofil Wird an zusätzliche Konfigurationsprofile vererbt |
On | This should definitely be enabled! With this, the HTTP proxy checks whether the certificate of the called page is trustworthy. Since the browser only sees the local certificate, a check by the browser is no longer possible. | |
Exceptions for SSL-Interception Exceptions for SSL-Interception not for Only webfilter based | |||
| Enabled | Off | It is possible to define exceptions in the format of Regular Expressions. However, since only https can arrive here, it is not filtered for protocols, unlike the virus scanner. New exceptions can be added directly in the input field. So an exception for www.securepoint.de would be:
.*\.securepoint\.de" | |
| Compare exceptions with the SNI: Only available if salidate SNI is active. |
Off | Applies Server Name Indication validation only to activated Exceptions of SSL-Interception . | |
| Ausnahmen: | .*\.ttt-point\.de Vordefiniert im Globalen Konfigurationsprofil: .*\.ikarus\.at.*\.mailsecurity\.at .*91\.212\.136\..* |
Ausnahmen bestimmen, hier für ttt-point.de | |
Peer verification exceptions Peer verification exceptions only if peer verification is active | |||
| Enabled | Off | Here exceptions for certificate verification in regex format can be added.
| |
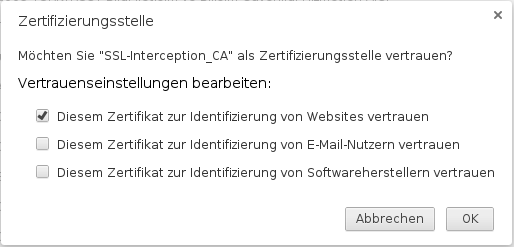
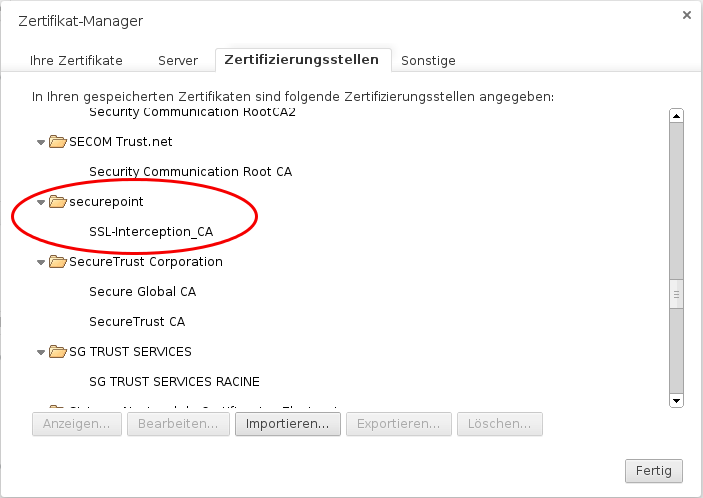
Add certificate to the browser
To do this, the public part of the CA is downloaded via the button ![]() .
.
Either by logging in from each individual client on the UTM to store the CA on them or it is downloaded once and stored on a USB stick or network storage. The certificate is then added to the browser via this route.
Transparent mode
UTMuser@firewall.name.fqdnApplications 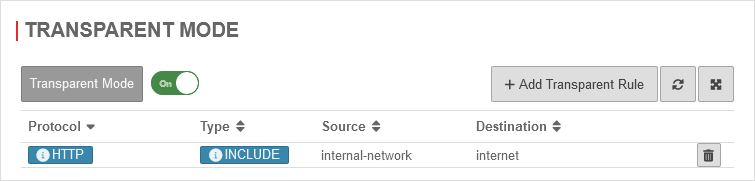 Transparent mode activated
Transparent mode activated
ACtivate under Area Transparent mode with Transparent mode On
Create HTTPS rule
In the default setting, transparent mode is already enabled for the HTTP protocol over port 80.
To set this up for the HTTPS protocol and port 443 as well, another rule is added by clicking the button.
Packet filter rules
Packet filter rule for access to DNS resolution
| # | Source | Destination | Service | NAT | Action | Active | |||
| 2 | Accept | On |
Examples of exceptions for Windows update server
For more examples on how to set up SSL interception, authentication exceptions, virus scanners, and web filters regarding Windows updates, see the knowledge base article Windows Updates with HTTP Proxy and Web Filter
Troubleshooting
Situation
- UTM with active transparent HTTP proxy for HTTP and HTTPS.
- SSL interception running in "Web Filter Based" mode.
Error message in the browser
ERROR_SSL_PROTOCOL_ERROR
or
ssl_error_rx_record_too_long
Log message in the UTM
Log message of Squid (menu ) in the UTM:
2021-09-15T16:50:20.003+02:00|squid|8933|1631717419.981 1 192.0.2.192 NONE/200 0 CONNECT 104.96.47.5:443 - HIER_NONE/- -
2021-09-15T16:50:20.007+02:00|squid|8933|1631717420.007 27 192.0.2.192 NONE_ABORTED/409 12387 CONNECT loadbalancing.ttt-point.de:443 - HIER_NONE/- text/html
2021-09-15T16:50:20.007+02:00|squid|8933|1631717420.007 27 192.0.2.192 NONE_ABORTED/409 12387 CONNECT loadbalancing.ttt-point.de:443 - HIER_NONE/- text/html
2021-09-15T16:50:22.652+02:00|squid|8933|SECURITY ALERT: Host header forgery detected on local=192.0.2.22:443 remote=192.168.175.10:28144 FD 9 flags=33 (local IP does not match any domain IP)
2021-09-15T16:50:22.654+02:00|squid|8933|SECURITY ALERT: on URL: loadbalancing.ttt-point.de:443
Meaning
- The client starts a TCP connection to an HTTPS server
- The connection is intercepted by the UTM → Transparent Proxy
- The HTTP proxy (Squid) checks the connection and analyzes the TLS handshake
- The information obtained, such as the SNI, is thereby resolved and compared with the original IP address
- In this case, the original IP and the resolved IP for the SNI (hostname) do not match and are therefore blocked by the HTTP proxy, resulting in the above mentioned error message
Cause
This behavior can be observed for hostnames with intensive load balancing.
If the provider gives different responses to DNS queries in a short period of time, the results in DNS resolution may differ between the client and the UTM.
This behavior can be caused by:
- Different DNS servers on client and UTM.
- Hostnames that are resolved differently by UTM and client with a very small TTL due to intensive load balancing.
- Use of DNS servers at different geographical locations.
In this case, a different IP address can be returned via the remote location for the called host names than at the local location of the UTM. (Geographic DNS Routing)
Solution
- Best Practice:
Auf dem Client wird die UTM als globaler Proxy-Server und ggf. für jede Anwendung als Proxy-Server eingetragen. - Workaround:
Auf Client und UTM werden die gleichen DNS-Server eingetragen.
In addition, it must be ensured that no DNS servers are used that are themselves already addressed via Geographic DNS Routing.
The Google servers, for example, differ despite identical IP address depending on the region from which they are called!